Operating Manual
... The raiser respectively positioner is exclusively responsible for the safety of the system and equipment where the unit will be integrated. During installation or maintenance all general and also all country- and application-specific safety rules and standards must be observed. If the device is used ...
... The raiser respectively positioner is exclusively responsible for the safety of the system and equipment where the unit will be integrated. During installation or maintenance all general and also all country- and application-specific safety rules and standards must be observed. If the device is used ...
Simulation and Performance Analysis of Parallel Resonant Inverter
... density. The resonant tank can be of various topologies including the commonly used ones such as parallel resonant tank, series resonant tank, LCC, LLC and LC-LC resonant tanks. Class D is one of the power stage prototypes of electronic ballast. Also half bridge topology has extensively applications ...
... density. The resonant tank can be of various topologies including the commonly used ones such as parallel resonant tank, series resonant tank, LCC, LLC and LC-LC resonant tanks. Class D is one of the power stage prototypes of electronic ballast. Also half bridge topology has extensively applications ...
Low-voltage coherent electron imaging based on a single
... ptychographic CDI is that the entire imaged area is no longer limited by the oversampling condition. The oversampling condition must still be met by focusing the beam to a sufficiently small size on the sample for recording each diffraction pattern. Although current electron-beam based coherent imag ...
... ptychographic CDI is that the entire imaged area is no longer limited by the oversampling condition. The oversampling condition must still be met by focusing the beam to a sufficiently small size on the sample for recording each diffraction pattern. Although current electron-beam based coherent imag ...
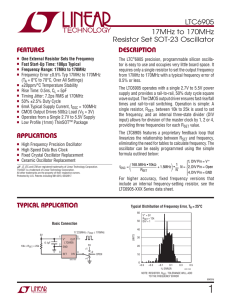
Oscillator
... Wien-Bridge Oscillator The lead-lag circuit permits only a signal with a frequency equal to fr to appear in phase on the noninverting input. The feedback signal is amplified and continually reinforced, resulting in a buildup of the output voltage. When the output signal reaches the zener breakd ...
... Wien-Bridge Oscillator The lead-lag circuit permits only a signal with a frequency equal to fr to appear in phase on the noninverting input. The feedback signal is amplified and continually reinforced, resulting in a buildup of the output voltage. When the output signal reaches the zener breakd ...
LTC1051/LTC1053 - Dual/Quad Precision Zero
... The LTC1051/LTC1053 have an offset voltage of 0.5µV, drift of 0.01µV/°C, DC to 10Hz, input noise voltage typically 1.5µVP-P and typical voltage gain of 140dB. The slew rate of 4V/µs and gain bandwidth product of 2.5MHz are achieved with only 1mA of supply current per op amp. Overload recover times f ...
... The LTC1051/LTC1053 have an offset voltage of 0.5µV, drift of 0.01µV/°C, DC to 10Hz, input noise voltage typically 1.5µVP-P and typical voltage gain of 140dB. The slew rate of 4V/µs and gain bandwidth product of 2.5MHz are achieved with only 1mA of supply current per op amp. Overload recover times f ...
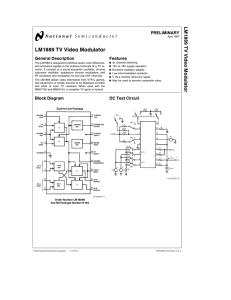
LM1889 TV Video Modulator
... Larger resistor values can be used to increase the gain, but capacitance at pin 13 will reduce the bandwidth. Notice that equi-bandwidth encoding of the color difference signals is implied as both modulator outputs are internally connected and summed into the same load resistor. ...
... Larger resistor values can be used to increase the gain, but capacitance at pin 13 will reduce the bandwidth. Notice that equi-bandwidth encoding of the color difference signals is implied as both modulator outputs are internally connected and summed into the same load resistor. ...
DeSantis_LBNL - CLASSE Wiki
... Since the kicker is substantially shorter than half the bunch separation, it is possible to prefire the pulser, at the price of a slightly higher power dissipation, to ensure deflecting field uniformity along the bunch path. ...
... Since the kicker is substantially shorter than half the bunch separation, it is possible to prefire the pulser, at the price of a slightly higher power dissipation, to ensure deflecting field uniformity along the bunch path. ...
26.5-40 and 76.5-90 GHz the Multichannel Radiometer - ELVA-1
... Just at the entrance of the Module the signal is amplified with a bandpass amplifier (1, Fig. 17). Then the second frequency conversion is occurred that transforms the input signals with the frequency band 1.5÷15 GHz into output signals with frequencies within a range from 0 … 425 MHz. Balanced mixe ...
... Just at the entrance of the Module the signal is amplified with a bandpass amplifier (1, Fig. 17). Then the second frequency conversion is occurred that transforms the input signals with the frequency band 1.5÷15 GHz into output signals with frequencies within a range from 0 … 425 MHz. Balanced mixe ...
MAX660 CMOS Monolithic Voltage Converter _______________General Description ___________________________ Features
... Note: In all modes, the frequency of the signal appearing at CAP+ and CAP- is one-half that of the oscillator. Also, an undesirable effect of lowering the oscillator frequency is that the effective output resistance of the charge pump increases. This can be compensated by increasing the value of the ...
... Note: In all modes, the frequency of the signal appearing at CAP+ and CAP- is one-half that of the oscillator. Also, an undesirable effect of lowering the oscillator frequency is that the effective output resistance of the charge pump increases. This can be compensated by increasing the value of the ...
Klystron

A klystron is a specialized linear-beam vacuum tube, invented in 1937 by American electrical engineers Russell and Sigurd Varian, which is used as an amplifier for high radio frequencies, from UHF up into the microwave range. Low-power klystrons are used as oscillators in terrestrial microwave relay communications links, while high-power klystrons are used as output tubes in UHF television transmitters, satellite communication, and radar transmitters, and to generate the drive power for modern particle accelerators.In the klystron, an electron beam interacts with the radio waves as it passes through resonant cavities, metal boxes along the length of the tube. The electron beam first passes through a cavity to which the input signal is applied. The energy of the electron beam amplifies the signal, and the amplified signal is taken from a cavity at the other end of the tube. The output signal can be coupled back into the input cavity to make an electronic oscillator to generate radio waves. The gain of klystrons can be high, 60 dB (one million) or more, with output power up to tens of megawatts, but the bandwidth is narrow, usually a few percent although it can be up to 10% in some devices.A reflex klystron is an obsolete type in which the electron beam was reflected back along its path by a high potential electrode, used as an oscillator.The name klystron comes from the stem form κλυσ- (klys) of a Greek verb referring to the action of waves breaking against a shore, and the suffix -τρον (""tron"") meaning the place where the action happens. The name ""klystron"" was suggested by Hermann Fränkel, a professor in the classics department at Stanford University when the klystron was under development.