TAP 103- 2: Current and charge in electron beams
... a vacuum tube and show some properties of the beam. These are charge and energy transfer and electric deflection by charge distributions within the tube. These notes assume an electron deflection tube is used. If this is not available then a Maltese cross tube does just as well. Start by explaining ...
... a vacuum tube and show some properties of the beam. These are charge and energy transfer and electric deflection by charge distributions within the tube. These notes assume an electron deflection tube is used. If this is not available then a Maltese cross tube does just as well. Start by explaining ...
MURI Book 4
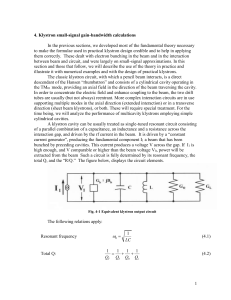
... The two definitions are equivalent. Basically, klystrons are resonant, narrowband devices. Nevertheless, they are usually required to have some limited bandwidth. This bandwidth is primarily set by the R/Q of the output circuit, although the front end of the tube is required to produce sufficient fu ...
... The two definitions are equivalent. Basically, klystrons are resonant, narrowband devices. Nevertheless, they are usually required to have some limited bandwidth. This bandwidth is primarily set by the R/Q of the output circuit, although the front end of the tube is required to produce sufficient fu ...
Carrier Mobility
... • Nearly free electrons can easily move in a semiconductor since they are not part of a chemical bond between atoms. • Valence electrons are shared between atoms. It turns out that a valence electron can also exchange places with another valence electron that is being shared with a ...
... • Nearly free electrons can easily move in a semiconductor since they are not part of a chemical bond between atoms. • Valence electrons are shared between atoms. It turns out that a valence electron can also exchange places with another valence electron that is being shared with a ...
electricity : answer key
... ELECTRICITY : ANSWER KEY SECTION REVIEW 4-1 1. ELECTRONICS STUDIES THE RELEASE, BEHAVIOR, AND EFFECTS OF ELECTRONS USED TO CARRY INFORMATION. ELECTRICITY USES ELECTRIC CURRENTS TO POWER DEVICES BY CONVERTING THE ENERGY OF MOVING ELECTRONS INTO HEAT AND LIGHT ENERGY. 2. ELECTRONS IN A VACUUM TUBE FOR ...
... ELECTRICITY : ANSWER KEY SECTION REVIEW 4-1 1. ELECTRONICS STUDIES THE RELEASE, BEHAVIOR, AND EFFECTS OF ELECTRONS USED TO CARRY INFORMATION. ELECTRICITY USES ELECTRIC CURRENTS TO POWER DEVICES BY CONVERTING THE ENERGY OF MOVING ELECTRONS INTO HEAT AND LIGHT ENERGY. 2. ELECTRONS IN A VACUUM TUBE FOR ...
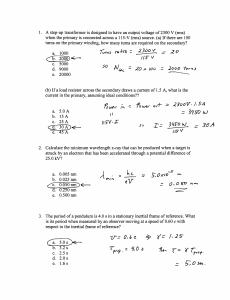
A step-up transformer is designed to have an output voltage of 2300
... A step-up transformer is designed to have an output voltage of 2300 V (rms) when the primary is connected across a 115-V (rnis) source. (a) If there are 100 turns on the primary winding, how many turns are required on the secondary? a. 1000 ...
... A step-up transformer is designed to have an output voltage of 2300 V (rms) when the primary is connected across a 115-V (rnis) source. (a) If there are 100 turns on the primary winding, how many turns are required on the secondary? a. 1000 ...
6 ELECTRON BEAMS
... • The CRO uses a narrow beam of electrons to trace out waveforms and other signals on a fluorescent screen • A bright spot is formed on the screen where the beam strikes it • If the beam is deflected, the spot moves • If the spot moves fast enough, it appears as a line • To deflect the beam, there a ...
... • The CRO uses a narrow beam of electrons to trace out waveforms and other signals on a fluorescent screen • A bright spot is formed on the screen where the beam strikes it • If the beam is deflected, the spot moves • If the spot moves fast enough, it appears as a line • To deflect the beam, there a ...
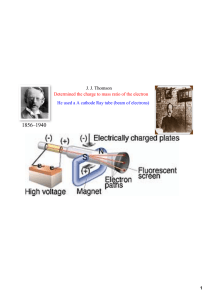
J. J. Thomson Determined the charge to mass ratio
... and other chemists, but their experiments did not provide any direct evidence that atoms actually exist. At the end of the 19th century, there was still some doubt about whether all matter was made up of atoms. By 1900, experiments were providing more direct evidence. ...
... and other chemists, but their experiments did not provide any direct evidence that atoms actually exist. At the end of the 19th century, there was still some doubt about whether all matter was made up of atoms. By 1900, experiments were providing more direct evidence. ...
Klystron

A klystron is a specialized linear-beam vacuum tube, invented in 1937 by American electrical engineers Russell and Sigurd Varian, which is used as an amplifier for high radio frequencies, from UHF up into the microwave range. Low-power klystrons are used as oscillators in terrestrial microwave relay communications links, while high-power klystrons are used as output tubes in UHF television transmitters, satellite communication, and radar transmitters, and to generate the drive power for modern particle accelerators.In the klystron, an electron beam interacts with the radio waves as it passes through resonant cavities, metal boxes along the length of the tube. The electron beam first passes through a cavity to which the input signal is applied. The energy of the electron beam amplifies the signal, and the amplified signal is taken from a cavity at the other end of the tube. The output signal can be coupled back into the input cavity to make an electronic oscillator to generate radio waves. The gain of klystrons can be high, 60 dB (one million) or more, with output power up to tens of megawatts, but the bandwidth is narrow, usually a few percent although it can be up to 10% in some devices.A reflex klystron is an obsolete type in which the electron beam was reflected back along its path by a high potential electrode, used as an oscillator.The name klystron comes from the stem form κλυσ- (klys) of a Greek verb referring to the action of waves breaking against a shore, and the suffix -τρον (""tron"") meaning the place where the action happens. The name ""klystron"" was suggested by Hermann Fränkel, a professor in the classics department at Stanford University when the klystron was under development.