4.6 Isosceles and Equilateral Triangles
... Warm Up • Explain what information you would need to prove two triangles congruent. Draw an example to help guide your response. ...
... Warm Up • Explain what information you would need to prove two triangles congruent. Draw an example to help guide your response. ...
answers
... Intro: a polygon is defined as a shape on a plane (a 2D shape) that is bounded by a certain number of straight line segments that form a loop. Examples at right: We often think of polygons like rectangles, triangles, pentagons, where the internal angles at each vertex are less than 180o… These are e ...
... Intro: a polygon is defined as a shape on a plane (a 2D shape) that is bounded by a certain number of straight line segments that form a loop. Examples at right: We often think of polygons like rectangles, triangles, pentagons, where the internal angles at each vertex are less than 180o… These are e ...
Investigate Angle Sums in Polygons
... 1. Look for a pattern in the last column of the table. What is the sum of the ...
... 1. Look for a pattern in the last column of the table. What is the sum of the ...
regular polygon
... Geometry - branch of mathematics that deals with points, lines, planes and solids and examines their properties. • Types of the line of the triangle • Polygon ...
... Geometry - branch of mathematics that deals with points, lines, planes and solids and examines their properties. • Types of the line of the triangle • Polygon ...
Teacher Technology Companion for Grade 7 Geometry
... Teacher Technology Companion for Grade 7 Geometry Overall Expectations: (Ontario Mathematics Curriculum, rev. 2005) ► 7m43: construct related lines, and classify triangles, quadrilaterals, and prisms;; ► 7m44: develop an understanding of similarity, and distinguish similarity and congruence; ► 7m45: ...
... Teacher Technology Companion for Grade 7 Geometry Overall Expectations: (Ontario Mathematics Curriculum, rev. 2005) ► 7m43: construct related lines, and classify triangles, quadrilaterals, and prisms;; ► 7m44: develop an understanding of similarity, and distinguish similarity and congruence; ► 7m45: ...
5A Interior Angles in Polygons
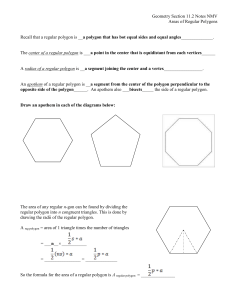
... When congruent isosceles triangles are drawn from the center of a regular polygon, why is the base angle sum of any one of the isosceles triangles equivalent to the measure of an interior angle of the polygon? ...
... When congruent isosceles triangles are drawn from the center of a regular polygon, why is the base angle sum of any one of the isosceles triangles equivalent to the measure of an interior angle of the polygon? ...
8-7
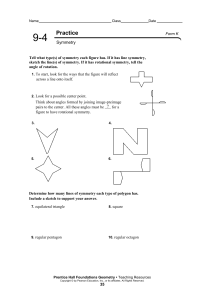
... Tell whether each shape is a polygon. If so, give its name and tell whether it appears to be regular or not regular. The shape is a closed plane figure formed by 3 or more line segments. polygon There are 8 sides and 8 angles. ...
... Tell whether each shape is a polygon. If so, give its name and tell whether it appears to be regular or not regular. The shape is a closed plane figure formed by 3 or more line segments. polygon There are 8 sides and 8 angles. ...
Connections Geometry Semester One Review Guide page 3
... __________________________ 4-sided shape with two sets of parallel sides __________________________ 8-sided with all equal sides & all equal angles __________________________ 4-sided shape with all equal angles __________________________ angle between 90 and 180 degrees ...
... __________________________ 4-sided shape with two sets of parallel sides __________________________ 8-sided with all equal sides & all equal angles __________________________ 4-sided shape with all equal angles __________________________ angle between 90 and 180 degrees ...
Tessellation

A tessellation of a flat surface is the tiling of a plane using one or more geometric shapes, called tiles, with no overlaps and no gaps. In mathematics, tessellations can be generalized to higher dimensions and a variety of geometries.A periodic tiling has a repeating pattern. Some special kinds include regular tilings with regular polygonal tiles all of the same shape, and semi-regular tilings with regular tiles of more than one shape and with every corner identically arranged. The patterns formed by periodic tilings can be categorized into 17 wallpaper groups. A tiling that lacks a repeating pattern is called ""non-periodic"". An aperiodic tiling uses a small set of tile shapes that cannot form a repeating pattern. In the geometry of higher dimensions, a space-filling or honeycomb is also called a tessellation of space.A real physical tessellation is a tiling made of materials such as cemented ceramic squares or hexagons. Such tilings may be decorative patterns, or may have functions such as providing durable and water-resistant pavement, floor or wall coverings. Historically, tessellations were used in Ancient Rome and in Islamic art such as in the decorative tiling of the Alhambra palace. In the twentieth century, the work of M. C. Escher often made use of tessellations, both in ordinary Euclidean geometry and in hyperbolic geometry, for artistic effect. Tessellations are sometimes employed for decorative effect in quilting. Tessellations form a class of patterns in nature, for example in the arrays of hexagonal cells found in honeycombs.