Chapter 2 - UT Mathematics
... five Common Notions and first four Postulates of Euclid. In other words, there is a geometry in which neither the Fifth Postulate nor any of its alternatives is taken as an axiom. This geometry is called Absolute Geometry, and an account of it can be found in several textbooks - in Coxeter’s book “I ...
... five Common Notions and first four Postulates of Euclid. In other words, there is a geometry in which neither the Fifth Postulate nor any of its alternatives is taken as an axiom. This geometry is called Absolute Geometry, and an account of it can be found in several textbooks - in Coxeter’s book “I ...
Scope Geo Reg FINAL - The School District of Palm Beach County
... • Use the Side-Splitter Theorem and the Triangle-Anglecongruence, similarity, and symmetry. Know that images Bisector Theorem formed by translations, reflections, and rotations are Ratios and • Use the Pythagorean Theorem Proportions congruent to the original shape. Create and verify tessellations • ...
... • Use the Side-Splitter Theorem and the Triangle-Anglecongruence, similarity, and symmetry. Know that images Bisector Theorem formed by translations, reflections, and rotations are Ratios and • Use the Pythagorean Theorem Proportions congruent to the original shape. Create and verify tessellations • ...
Lesson Plan Format
... www.westex.org HS, Teacher Website Name _________________________ Geometry H 7.2 Ratio & Proportion Today’s Goal I will be able to: 1. identify similar polygons. 2. apply properties of similar polygons to solve problems. ...
... www.westex.org HS, Teacher Website Name _________________________ Geometry H 7.2 Ratio & Proportion Today’s Goal I will be able to: 1. identify similar polygons. 2. apply properties of similar polygons to solve problems. ...
Chapter 2 - UT Mathematics
... the five Common Notions and first four Postulates of Euclid. In other words, there is a geometry in which neither the Fifth Postulate nor any of its alternatives is taken as an axiom. This geometry is called Absolute Geometry, and an account of it can be found in several textbooks - in Coxeter’s boo ...
... the five Common Notions and first four Postulates of Euclid. In other words, there is a geometry in which neither the Fifth Postulate nor any of its alternatives is taken as an axiom. This geometry is called Absolute Geometry, and an account of it can be found in several textbooks - in Coxeter’s boo ...
nSpire activity
... b. When the number of sides in a regular polygon increases by 1, why does the interior angle sum increase by 180°? ...
... b. When the number of sides in a regular polygon increases by 1, why does the interior angle sum increase by 180°? ...
shapes
... • A special quadrilateral with 2 pairs of equal sides, opposite sides are parallel, and opposite angles are equal. ...
... • A special quadrilateral with 2 pairs of equal sides, opposite sides are parallel, and opposite angles are equal. ...
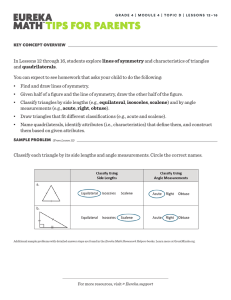
Classify each triangle by its side lengths and angle measurements
... where the line of symmetry would be and what makes it a line of symmetry. Be careful of objects such as doors and windows. They could have a line of symmetry, but if there’s a knob or crank on just one side, then they are not symmetrical. ▪▪ Ask your child to name and draw all the quadrilaterals she ...
... where the line of symmetry would be and what makes it a line of symmetry. Be careful of objects such as doors and windows. They could have a line of symmetry, but if there’s a knob or crank on just one side, then they are not symmetrical. ▪▪ Ask your child to name and draw all the quadrilaterals she ...
Geometry and Trigonometry Syllabus
... those in a coordinate plane using slope -Equations of parallel and perpendicular lines -Algebra: equations of lines, graphing, solving linear ...
... those in a coordinate plane using slope -Equations of parallel and perpendicular lines -Algebra: equations of lines, graphing, solving linear ...
Similar Polygons
... Two polygons with the same shape are called similar polygons. The symbol for “is similar to” is ∼. (Example: ABC EFG) (Notice that is a portion of the “is congruent to” symbol, ≅.) When two polygons are similar, these two facts both must be true: – Corresponding angles are equal. – The ratios ...
... Two polygons with the same shape are called similar polygons. The symbol for “is similar to” is ∼. (Example: ABC EFG) (Notice that is a portion of the “is congruent to” symbol, ≅.) When two polygons are similar, these two facts both must be true: – Corresponding angles are equal. – The ratios ...
Tessellation

A tessellation of a flat surface is the tiling of a plane using one or more geometric shapes, called tiles, with no overlaps and no gaps. In mathematics, tessellations can be generalized to higher dimensions and a variety of geometries.A periodic tiling has a repeating pattern. Some special kinds include regular tilings with regular polygonal tiles all of the same shape, and semi-regular tilings with regular tiles of more than one shape and with every corner identically arranged. The patterns formed by periodic tilings can be categorized into 17 wallpaper groups. A tiling that lacks a repeating pattern is called ""non-periodic"". An aperiodic tiling uses a small set of tile shapes that cannot form a repeating pattern. In the geometry of higher dimensions, a space-filling or honeycomb is also called a tessellation of space.A real physical tessellation is a tiling made of materials such as cemented ceramic squares or hexagons. Such tilings may be decorative patterns, or may have functions such as providing durable and water-resistant pavement, floor or wall coverings. Historically, tessellations were used in Ancient Rome and in Islamic art such as in the decorative tiling of the Alhambra palace. In the twentieth century, the work of M. C. Escher often made use of tessellations, both in ordinary Euclidean geometry and in hyperbolic geometry, for artistic effect. Tessellations are sometimes employed for decorative effect in quilting. Tessellations form a class of patterns in nature, for example in the arrays of hexagonal cells found in honeycombs.