10R - donnellymath
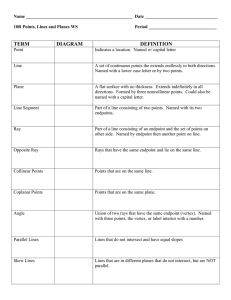
... _____3. Two lines perpendicular to the same plane are coplanar. _____4. Two planes are perpendicular to each other if and only if one plane contains a line perpendicular to the second plane. ...
... _____3. Two lines perpendicular to the same plane are coplanar. _____4. Two planes are perpendicular to each other if and only if one plane contains a line perpendicular to the second plane. ...
Geometry Unit 2 - Polygon Sample Tasks
... What is the measure of each central angle in the regular dodecagon? Find the measure of each angle of the regular dodecagon. Extend one of the sides of the regular dodecagon. What is the measure of the exterior angle that is formed when one of the sides is extended? ...
... What is the measure of each central angle in the regular dodecagon? Find the measure of each angle of the regular dodecagon. Extend one of the sides of the regular dodecagon. What is the measure of the exterior angle that is formed when one of the sides is extended? ...
Unwrapped Standards: G.CO.3 - Given a rectangle
... Common Core Standards - Resource Page The resources below have been created to assist teachers' understanding and to aid instruction of this standard. Standard: G.CO.3 - Given a rectangle, parallelogram, trapezoid, or regular polygon, describe the rotations and Domain reflections that carry it onto ...
... Common Core Standards - Resource Page The resources below have been created to assist teachers' understanding and to aid instruction of this standard. Standard: G.CO.3 - Given a rectangle, parallelogram, trapezoid, or regular polygon, describe the rotations and Domain reflections that carry it onto ...
Geometry Syllabus
... Angle Relationships in Circles Segment Relationships in Circles Circles in the Coordinate Plane ...
... Angle Relationships in Circles Segment Relationships in Circles Circles in the Coordinate Plane ...
UNIT PLAN TEMPLATE
... Slide – a transformation that slides each point of a figure the same distance in the same direction Sphere- a curved surface in which each point is equidistant from a single point called the center Square- a rectangle with four equal sides and four equal angles Square pyramid – pyramid whose base is ...
... Slide – a transformation that slides each point of a figure the same distance in the same direction Sphere- a curved surface in which each point is equidistant from a single point called the center Square- a rectangle with four equal sides and four equal angles Square pyramid – pyramid whose base is ...
Voc
... two shapes are Similar when the only difference is size (and possibly the need to move, turn or flip one ...
... two shapes are Similar when the only difference is size (and possibly the need to move, turn or flip one ...
euclidean parallel postulate
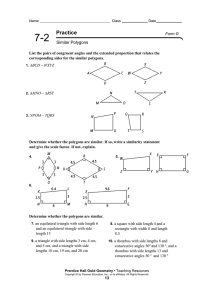
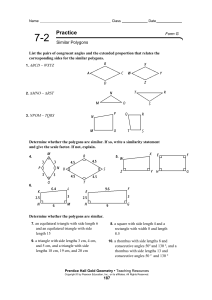
... written ∆ABC ~ ∆DEF , when all three pairs of corresponding angles are congruent and the lengths of all three pairs of corresponding sides are proportional. To establish similarity of triangles, however, it is not necessary to establish congruence of all pairs of angles and proportionality of all p ...
... written ∆ABC ~ ∆DEF , when all three pairs of corresponding angles are congruent and the lengths of all three pairs of corresponding sides are proportional. To establish similarity of triangles, however, it is not necessary to establish congruence of all pairs of angles and proportionality of all p ...
Geometry Unit 1 Review (sections 6.1 – 6.7)
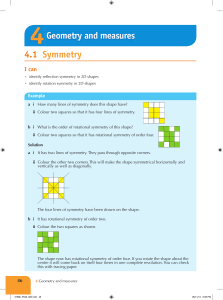
... 18. List all of the degrees of rotational symmetry for the shape to the left. ...
... 18. List all of the degrees of rotational symmetry for the shape to the left. ...
6.7 Regular Polygons
... 14. Find the magnitude of rotation/each interior angle of a polygon! Since regular polygons have lines of symmetry, we can use those lines of symmetry, and the center point to find out the magnitude of rotation and the interior angle. Using the figure at the right, draw the lines of symmetry and plo ...
... 14. Find the magnitude of rotation/each interior angle of a polygon! Since regular polygons have lines of symmetry, we can use those lines of symmetry, and the center point to find out the magnitude of rotation and the interior angle. Using the figure at the right, draw the lines of symmetry and plo ...
Tessellation

A tessellation of a flat surface is the tiling of a plane using one or more geometric shapes, called tiles, with no overlaps and no gaps. In mathematics, tessellations can be generalized to higher dimensions and a variety of geometries.A periodic tiling has a repeating pattern. Some special kinds include regular tilings with regular polygonal tiles all of the same shape, and semi-regular tilings with regular tiles of more than one shape and with every corner identically arranged. The patterns formed by periodic tilings can be categorized into 17 wallpaper groups. A tiling that lacks a repeating pattern is called ""non-periodic"". An aperiodic tiling uses a small set of tile shapes that cannot form a repeating pattern. In the geometry of higher dimensions, a space-filling or honeycomb is also called a tessellation of space.A real physical tessellation is a tiling made of materials such as cemented ceramic squares or hexagons. Such tilings may be decorative patterns, or may have functions such as providing durable and water-resistant pavement, floor or wall coverings. Historically, tessellations were used in Ancient Rome and in Islamic art such as in the decorative tiling of the Alhambra palace. In the twentieth century, the work of M. C. Escher often made use of tessellations, both in ordinary Euclidean geometry and in hyperbolic geometry, for artistic effect. Tessellations are sometimes employed for decorative effect in quilting. Tessellations form a class of patterns in nature, for example in the arrays of hexagonal cells found in honeycombs.