Communication between Neurons
... the neurone. These are called Peptides and are made from chains of amino acids are basically short proteins. They are packaged up in vesicles by the Golgi bodies and sent along the axons down the microtubules at the hair raising speeds of between 1 -100mm per day. The majority of neurotransmitters a ...
... the neurone. These are called Peptides and are made from chains of amino acids are basically short proteins. They are packaged up in vesicles by the Golgi bodies and sent along the axons down the microtubules at the hair raising speeds of between 1 -100mm per day. The majority of neurotransmitters a ...
Unit 2: Cell and Cell Transport 3.1 Cell Theory • are the basic unit of
... 2) Hypertonic – fluid outside of cell has _______________ (____________) than cell; water moves __________________ 3) Hypotonic – fluid outside of cell has __________________ (_______________) than cell; water moves ____________________ ...
... 2) Hypertonic – fluid outside of cell has _______________ (____________) than cell; water moves __________________ 3) Hypotonic – fluid outside of cell has __________________ (_______________) than cell; water moves ____________________ ...
Megan Sechrist
... a region of higher concentration. This type of active transport requires energy. In this investigation you used a synthetic selectively permeable membrane that is incapable of producing energy. What type of molecular transport was shown in this investigation—diffusion or active transport? Explain h ...
... a region of higher concentration. This type of active transport requires energy. In this investigation you used a synthetic selectively permeable membrane that is incapable of producing energy. What type of molecular transport was shown in this investigation—diffusion or active transport? Explain h ...
Outline
... c. E from ATP change the shape of protein and moves the ion across the membrane d. The carrier release the ion and the remnants of the ATP )ADP and P) and back to original shape ...
... c. E from ATP change the shape of protein and moves the ion across the membrane d. The carrier release the ion and the remnants of the ATP )ADP and P) and back to original shape ...
Primary mediators
... cells, thereby producing vasodilation. It is also able to act as a chemoattractant to direct cells via chemotaxis to the site of inflammation. ...
... cells, thereby producing vasodilation. It is also able to act as a chemoattractant to direct cells via chemotaxis to the site of inflammation. ...
BSN/Briefing 24 - British Society for Neuroendocrinology
... factors to DNA and thus switch the availability of promoter sequences for activation or inhibition by the transcription factors that are critical for cellular activity. ...
... factors to DNA and thus switch the availability of promoter sequences for activation or inhibition by the transcription factors that are critical for cellular activity. ...
Introduction to Cells 1p1 2014
... How is DNA turned off (or on)? Methylation of DNA (turns off) Transcription factor proteins ...
... How is DNA turned off (or on)? Methylation of DNA (turns off) Transcription factor proteins ...
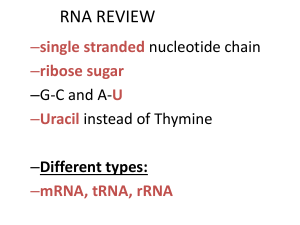
RNA and protein synthesis
... Proteins (polypeptides) are large polymers that are made from monomers called amino acids. Hundreds of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds and fold into a specific shape to make up a protein. There are 20 different types of amino acids. ...
... Proteins (polypeptides) are large polymers that are made from monomers called amino acids. Hundreds of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds and fold into a specific shape to make up a protein. There are 20 different types of amino acids. ...
Activins, mesoderm inducing factors, 123
... progress zone, limb development, 200 regulation of gene expression, 194-195 Retinoids, morphogenetic effects, 191-196 and steroids, regulation of transform ing grow th factor-beta, 139-147 Rhabdomeres, insect compound eye om m atidia, ...
... progress zone, limb development, 200 regulation of gene expression, 194-195 Retinoids, morphogenetic effects, 191-196 and steroids, regulation of transform ing grow th factor-beta, 139-147 Rhabdomeres, insect compound eye om m atidia, ...
Electrochemical Impulses
... 3. A reversal of charge occurs, called depolarization (this is the ‘firing’ of the neuron) 4. Once the inside of the neuron becomes positive, the Na+ gates close. 5. A Na+ - K+ pump in the cell membrane moves sodium out and potassium in, restoring the resting potential (called re-polarization) ...
... 3. A reversal of charge occurs, called depolarization (this is the ‘firing’ of the neuron) 4. Once the inside of the neuron becomes positive, the Na+ gates close. 5. A Na+ - K+ pump in the cell membrane moves sodium out and potassium in, restoring the resting potential (called re-polarization) ...
The Scientist : Lab Tools: Close Encounters
... The problem: Y2H measures only binary interactions, not multiprotein complexes. But coIP /MS requires high-quality, specific antibodies, few of which are available. Superti-Furga needed a generic way to isolate intact complexes from cells. The Solution: Superti-Furga and his team adapted a process c ...
... The problem: Y2H measures only binary interactions, not multiprotein complexes. But coIP /MS requires high-quality, specific antibodies, few of which are available. Superti-Furga needed a generic way to isolate intact complexes from cells. The Solution: Superti-Furga and his team adapted a process c ...
Cell Observations Lab
... Translucent means that you can see light through the specimen, but it is not transparent. 2. Place the piece of onion on a glass slide and add a drop or two of the Lugol's solution. ( iodine is a specific stain for plants.) Cover the slide with a cover slip using your best wet mount making technique ...
... Translucent means that you can see light through the specimen, but it is not transparent. 2. Place the piece of onion on a glass slide and add a drop or two of the Lugol's solution. ( iodine is a specific stain for plants.) Cover the slide with a cover slip using your best wet mount making technique ...
SAS Science: Cells- The Basic Unit of Life (Ch. 4)
... 30. Proteins are made from amino acids in the smallest organelle, which is called a(n) a. Mitochondria c. ribosome b. Lysosome d. chloroplast 31. A network of protein in the cytoplasm of some cells, which defines the shape of animal cells, is called the a. Cell wall c. Golgi complex b. Cytoskeleton ...
... 30. Proteins are made from amino acids in the smallest organelle, which is called a(n) a. Mitochondria c. ribosome b. Lysosome d. chloroplast 31. A network of protein in the cytoplasm of some cells, which defines the shape of animal cells, is called the a. Cell wall c. Golgi complex b. Cytoskeleton ...
49) Plants respond to their environment in many different ways
... Correct Answer: - Acid rain will cause a decrease in the number of seeds that germinate. Note: Do not allow credit for a hypothesis written in the form of a question. - The control group would be watered with water at pH 7, while the experimental groups would be watered with water at pH less than 7 ...
... Correct Answer: - Acid rain will cause a decrease in the number of seeds that germinate. Note: Do not allow credit for a hypothesis written in the form of a question. - The control group would be watered with water at pH 7, while the experimental groups would be watered with water at pH less than 7 ...
MULTIPLE CHOICE. There are 60 questions on this exam. All
... C) Both A & B are correct D) None of the choices are correct. 34) The cholesterol associated with cell membranes A) is attached to membrane proteins and extends into the watery environment surrounding the cell. B) helps to stabilize the cell membrane at higher or lower temperature. C) is an abnormal ...
... C) Both A & B are correct D) None of the choices are correct. 34) The cholesterol associated with cell membranes A) is attached to membrane proteins and extends into the watery environment surrounding the cell. B) helps to stabilize the cell membrane at higher or lower temperature. C) is an abnormal ...
Major molecule of food
... monomers that are linked together to create large macromolecules, which are known as polymers. When monomers are linked together to synthesize a biological polymer, they undergo a process called synthesis. ...
... monomers that are linked together to create large macromolecules, which are known as polymers. When monomers are linked together to synthesize a biological polymer, they undergo a process called synthesis. ...
Final Answer Game Biology Review
... The movement of materials against the concentration gradient that requires ATP energy to accomplish is a. b. c. d. ...
... The movement of materials against the concentration gradient that requires ATP energy to accomplish is a. b. c. d. ...
P-glycoprotein Activation Monitored via ATP Hydrolysis and ATP
... We investigated the relationship between the rate of ATP hydrolysis and ATP synthesis upon P-glycoprotein activation for several structurally different drugs, including local anaesthetics, cyclic peptides, and cytotoxic drugs. ATP hydrolysis was assessed by spectroscopically monitoring the release o ...
... We investigated the relationship between the rate of ATP hydrolysis and ATP synthesis upon P-glycoprotein activation for several structurally different drugs, including local anaesthetics, cyclic peptides, and cytotoxic drugs. ATP hydrolysis was assessed by spectroscopically monitoring the release o ...
Cell Structure and Function - Mount Mansfield Union High
... • Proposes that today’s eukaryotic cells evolved by a symbiosis in which one species of prokaryote was engulfed by and lived inside another species of prokaryote • Mitochondria and chloroplasts are thought to be two prime examples of this theory – Double membranes – Both contain circular DNA similar ...
... • Proposes that today’s eukaryotic cells evolved by a symbiosis in which one species of prokaryote was engulfed by and lived inside another species of prokaryote • Mitochondria and chloroplasts are thought to be two prime examples of this theory – Double membranes – Both contain circular DNA similar ...
Osmosis Scenarios - Garnet Valley School District
... 4. If there is more solute inside a membrane than outside, solute particles will move across the membrane to the __________________________ of the cell to achieve equilibrium. 5. Describe the process of osmosis. ...
... 4. If there is more solute inside a membrane than outside, solute particles will move across the membrane to the __________________________ of the cell to achieve equilibrium. 5. Describe the process of osmosis. ...
Organic Molecules Quiz
... 19. Which of the following best describes the composition of a nucleotide? A. a pair of six-carbon rings attached to each other B. a carbon atom joined to hydrogen and three functional groups C. a chain of carbon atoms with a carboxyl group bonded to one end D. a five-carbon sugar attached to a pho ...
... 19. Which of the following best describes the composition of a nucleotide? A. a pair of six-carbon rings attached to each other B. a carbon atom joined to hydrogen and three functional groups C. a chain of carbon atoms with a carboxyl group bonded to one end D. a five-carbon sugar attached to a pho ...
The Chemistry of Living Things
... • It could be the constant process of photosynthesis in plants or the building of complex proteins in the cells of your body. ...
... • It could be the constant process of photosynthesis in plants or the building of complex proteins in the cells of your body. ...
2054, Chap. 5, page 1 I. Microbial Nutrition (Chapter 5) A. Common
... 2. specific organisms have different capabilities for assimilation and may favor particular molecules 3. N primarily in amino acids and nucleotides 4. P primarily in nucleotides and phospholipids 5. S primarily in amino acids E. growth factors 1. organic compounds that are essential cell components ...
... 2. specific organisms have different capabilities for assimilation and may favor particular molecules 3. N primarily in amino acids and nucleotides 4. P primarily in nucleotides and phospholipids 5. S primarily in amino acids E. growth factors 1. organic compounds that are essential cell components ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.