The Cell Part 1 Chapter 2 Lesson 2
... Cell Boundaries The cell membrane is a flexible covering that protects the inside of a cell from the environment outside a cell. Found in all cells. A cell wall is a stiff structure outside the cell membrane that protects a cell from attack by viruses and other harmful organisms. Found in plant cel ...
... Cell Boundaries The cell membrane is a flexible covering that protects the inside of a cell from the environment outside a cell. Found in all cells. A cell wall is a stiff structure outside the cell membrane that protects a cell from attack by viruses and other harmful organisms. Found in plant cel ...
Pinar Tulay cell molecules_17
... • Lipids are a loosely defined group of molecules with one main characteristic: they are insoluble in water (owing to their very high proportion of nonpolar C—H bonds). • The main groups of compounds classified as lipids are triglycerides, phospholipids, steroids, prostaglandins, and ...
... • Lipids are a loosely defined group of molecules with one main characteristic: they are insoluble in water (owing to their very high proportion of nonpolar C—H bonds). • The main groups of compounds classified as lipids are triglycerides, phospholipids, steroids, prostaglandins, and ...
Mitochondrion File
... functions. These compartments or regions include the outer membrane, the intermembrane space, the inner membrane, and the cristae and matrix. Mitochondrial proteins vary depending on the tissue and the species. In humans, 615 distinct types of protein have been identified from cardiac mitochondria,[ ...
... functions. These compartments or regions include the outer membrane, the intermembrane space, the inner membrane, and the cristae and matrix. Mitochondrial proteins vary depending on the tissue and the species. In humans, 615 distinct types of protein have been identified from cardiac mitochondria,[ ...
A17 - Viktor`s Notes for the Neurosurgery Resident
... potentials in neurons. sensory receptors may be: a) neurons (distal tip of peripheral axon of sensory neuron) – e.g. in skin receptors. b) specialized cells (that release neurotransmitter and generate action potentials in neurons) – e.g. in complex sense organs (vision, hearing, equilibrium, taste ...
... potentials in neurons. sensory receptors may be: a) neurons (distal tip of peripheral axon of sensory neuron) – e.g. in skin receptors. b) specialized cells (that release neurotransmitter and generate action potentials in neurons) – e.g. in complex sense organs (vision, hearing, equilibrium, taste ...
Biochemistry Course #: - College of Pharmacy at Howard University
... 1. Typically fibrous proteins consist largely of a single type of secondary structure. Globular proteins often contain several types of secondary structure. 2. The two groups differ functionally in that the structures that provide support, shape, and external protection to vertebrates are made of fi ...
... 1. Typically fibrous proteins consist largely of a single type of secondary structure. Globular proteins often contain several types of secondary structure. 2. The two groups differ functionally in that the structures that provide support, shape, and external protection to vertebrates are made of fi ...
CELL STRUCTURE_2012_crossing the
... sucrose against its concentration gradient. Extracellular fluid ...
... sucrose against its concentration gradient. Extracellular fluid ...
Chapter 12 - Membrane Transport . PPT - A
... • Carrier proteins – move the solute across the membrane by binding it on one side and transporting it to the other side – Requires a conformation change • Channel protein – small hydrophilic pores that allow for solutes to pass through – Use diffusion to move across – Also called ion channels when ...
... • Carrier proteins – move the solute across the membrane by binding it on one side and transporting it to the other side – Requires a conformation change • Channel protein – small hydrophilic pores that allow for solutes to pass through – Use diffusion to move across – Also called ion channels when ...
semicircular canals
... 1. Specialized sensory cell (receptor) detects a physical or chemical change. 2. The physical or chemical change causes action potentials in sensory neurons. 3. Sensory neurons carry action potentials through cranial nerves or spinal nerves to the CNS. 4. Typically the sensory information is carried ...
... 1. Specialized sensory cell (receptor) detects a physical or chemical change. 2. The physical or chemical change causes action potentials in sensory neurons. 3. Sensory neurons carry action potentials through cranial nerves or spinal nerves to the CNS. 4. Typically the sensory information is carried ...
1 - Biology D118
... the movement of molecules from and area of greater concentration to an area of lesser concentration. Concentration is the amount of a substance in a given area. Carbon dioxide is constantly made by the cells as they use energy (break down ATP into ADP and then recharge ADP into ATP). Therefore the ...
... the movement of molecules from and area of greater concentration to an area of lesser concentration. Concentration is the amount of a substance in a given area. Carbon dioxide is constantly made by the cells as they use energy (break down ATP into ADP and then recharge ADP into ATP). Therefore the ...
Press release No 1: Curing parkinson`s with stem cell
... the pattern of the daughter cells which emerge from the stem cells. Therefore, it is critical that the cells communicate with their environment. ...
... the pattern of the daughter cells which emerge from the stem cells. Therefore, it is critical that the cells communicate with their environment. ...
Cell Structures – Part 3 - Glasgow Independent Schools
... E. Evolutionary Significance? (They were believed to have been purple bacteria. Remember bacteria are prokaryotes. They entered into a symbiotic relationship with a larger prokaryote that could provide protection in return for extra energy. Together they would have an evolutionary advantage over oth ...
... E. Evolutionary Significance? (They were believed to have been purple bacteria. Remember bacteria are prokaryotes. They entered into a symbiotic relationship with a larger prokaryote that could provide protection in return for extra energy. Together they would have an evolutionary advantage over oth ...
Ribosomes translate the genetic message from mRNA that
... They attach firmly to the phospholipids only drastic measure as using of detergent can release them. (2) Peripheral protein = are external to lipid bilayer. They are attached to the head by week bonds which easily break by changing PH Function: Participate in enzymatic activities. Maintain ionic ...
... They attach firmly to the phospholipids only drastic measure as using of detergent can release them. (2) Peripheral protein = are external to lipid bilayer. They are attached to the head by week bonds which easily break by changing PH Function: Participate in enzymatic activities. Maintain ionic ...
Chapter 5: Homeostasis and Transport Lesson 1: Cell Structures
... cell transport processes. Integral proteins are transmembrane proteins, which means that they are proteins with hydrophobic regions that extend into and often completely span the hydrophobic interior of the plasma membrane. The outer regions of integral proteins are hydrophilic and can easily make c ...
... cell transport processes. Integral proteins are transmembrane proteins, which means that they are proteins with hydrophobic regions that extend into and often completely span the hydrophobic interior of the plasma membrane. The outer regions of integral proteins are hydrophilic and can easily make c ...
Ch 45 Notes
... • The response to a lipid-soluble hormone is usually a change in gene expression. • Steroids, thyroid hormones, and the hormonal form of vitamin D enter target cells and bind to protein receptors in the cytoplasm or nucleus. • Protein-receptor complexes then act as transcription factors in the nucle ...
... • The response to a lipid-soluble hormone is usually a change in gene expression. • Steroids, thyroid hormones, and the hormonal form of vitamin D enter target cells and bind to protein receptors in the cytoplasm or nucleus. • Protein-receptor complexes then act as transcription factors in the nucle ...
Moonlighting organelles—signals and cellular architecture
... morphogenesis with the requirements of their environment, the interaction between microtubules and cell wall must be target of signalling. Phospholipase D as linker between microtubules and plasma membrane seems to be a central player in this context. In the “New Ideas in Cell Biology” of the curren ...
... morphogenesis with the requirements of their environment, the interaction between microtubules and cell wall must be target of signalling. Phospholipase D as linker between microtubules and plasma membrane seems to be a central player in this context. In the “New Ideas in Cell Biology” of the curren ...
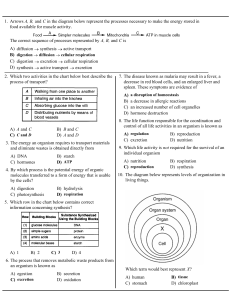
1. Arrows A, B, and C in the diagram below represent the processes
... 24. The diagram below represents the synthesis of a portion of a complex molecule in an organism. ...
... 24. The diagram below represents the synthesis of a portion of a complex molecule in an organism. ...
_____ Name Date ______ Mrs. G-M (Biology) Period ______ List of
... o …in plant cells? o …in freshwater protists (ex. Paramecium)? Why do some protists need “contractile vacuoles”? ...
... o …in plant cells? o …in freshwater protists (ex. Paramecium)? Why do some protists need “contractile vacuoles”? ...
Pull out the stops for plasticity
... similar role — they open only when the neuron is already depolarized, forming a positivefeedback loop that increases Ca2+ influx and depolarization3. The activation of NMDA receptors is essential for many forms of longlasting synaptic plasticity. However, positive-feedback loops are inherently dange ...
... similar role — they open only when the neuron is already depolarized, forming a positivefeedback loop that increases Ca2+ influx and depolarization3. The activation of NMDA receptors is essential for many forms of longlasting synaptic plasticity. However, positive-feedback loops are inherently dange ...
Sensation
... • Transduction: the transforming of stimulus energies (like sights, sounds, smells) into neural impulses our brains can interpret • Retina sends message to your brain via the optic nerve • Rods/cones-> bipolar cells-> ganglion cells-> axons form… optic nerve-> thalamus-> occipital lobe (visual corte ...
... • Transduction: the transforming of stimulus energies (like sights, sounds, smells) into neural impulses our brains can interpret • Retina sends message to your brain via the optic nerve • Rods/cones-> bipolar cells-> ganglion cells-> axons form… optic nerve-> thalamus-> occipital lobe (visual corte ...
Figure S1: Confirmation of IRGM1 palmitoylation. HEK293T cells
... Figure S7: Expression levels of HA-tagged DHHC constructs. HA-DHHCs 1-23 or GST were cotransfected into HEK293T cells with FLAG-TLR2. A portion of the cell lysate was subjected to antiHA immunoporecipitation followed by SDS-PAGE and anti-HA Western blotting. DHHCs are glycosylated proteins appearin ...
... Figure S7: Expression levels of HA-tagged DHHC constructs. HA-DHHCs 1-23 or GST were cotransfected into HEK293T cells with FLAG-TLR2. A portion of the cell lysate was subjected to antiHA immunoporecipitation followed by SDS-PAGE and anti-HA Western blotting. DHHCs are glycosylated proteins appearin ...
Osmosis in Red Blood Cells
... it is diffusion (across a membrane) from a high concentration to a lower concentration. • However, this time the rate of diffusion is greatly accelerated by the action of membrane proteins that act as carrier molecules and aid in diffusion. http://www.northland.cc.mn.us/biology/Biology1111/animation ...
... it is diffusion (across a membrane) from a high concentration to a lower concentration. • However, this time the rate of diffusion is greatly accelerated by the action of membrane proteins that act as carrier molecules and aid in diffusion. http://www.northland.cc.mn.us/biology/Biology1111/animation ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.