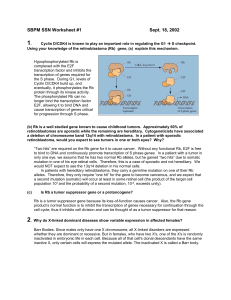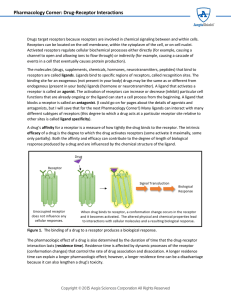
Pharmacology Corner: Drug-Receptor Interactions
... Drugs target receptors because receptors are involved in chemical signaling between and within cells. Receptors can be located on the cell membrane, within the cytoplasm of the cell, or on cell nuclei. Activated receptors regulate cellular biochemical processes either directly (for example, causing ...
... Drugs target receptors because receptors are involved in chemical signaling between and within cells. Receptors can be located on the cell membrane, within the cytoplasm of the cell, or on cell nuclei. Activated receptors regulate cellular biochemical processes either directly (for example, causing ...
Slide ()
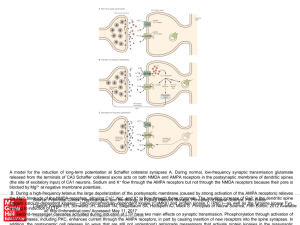
... the Biology of Explicit Memory Storage, Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon triggers calcium-dependent kinases—calcium/calmodulin–dependent kinase (CaMKII) and protein kinase C (PKC)—as well as the tyrosine kinase Fyn, Citation: Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, ...
... the Biology of Explicit Memory Storage, Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon triggers calcium-dependent kinases—calcium/calmodulin–dependent kinase (CaMKII) and protein kinase C (PKC)—as well as the tyrosine kinase Fyn, Citation: Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, ...
Modification of Cell Surface/ Cell Communication
... To foster student understanding of this concept, instructors can choose an illustrative example such as: • Ligand-gated ion channels • Second messengers, such as cyclic GMP, cyclic AMP calcium ions (Ca2+), and inositol triphosphate (IP3) 3. Many signal transduction pathways include: i. Protein modif ...
... To foster student understanding of this concept, instructors can choose an illustrative example such as: • Ligand-gated ion channels • Second messengers, such as cyclic GMP, cyclic AMP calcium ions (Ca2+), and inositol triphosphate (IP3) 3. Many signal transduction pathways include: i. Protein modif ...
Chapter 9 How Cells Reproduce
... Figure 2: p53 re-enforces G1 and G2 cell cycle arrest after DNA damage through the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21WAF1/CIPI Mdm2 and Bax are other p53 transcriptional targets, with Mdm2 regulating p53 levels and Bax mediating apoptosis ...
... Figure 2: p53 re-enforces G1 and G2 cell cycle arrest after DNA damage through the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21WAF1/CIPI Mdm2 and Bax are other p53 transcriptional targets, with Mdm2 regulating p53 levels and Bax mediating apoptosis ...
Mechanisms of cell communication
... Signaling molecules could be proteins, small peptides, amino acids, nucleotides, steroids, retinoids, fatty acid derivatives, nitric oxide, carbon monoxide The signaling molecule could either be secreted from the signaling cell or it could stay tightly bound to the cell surface of the signaling cel ...
... Signaling molecules could be proteins, small peptides, amino acids, nucleotides, steroids, retinoids, fatty acid derivatives, nitric oxide, carbon monoxide The signaling molecule could either be secreted from the signaling cell or it could stay tightly bound to the cell surface of the signaling cel ...
Chapter 34
... vasoconstriction, mitogenesis, tissue changes Vasoactive intestinal peptide stimulates AC (to make cAMP) via G proteins, and its effects are synergistic with those of other neurotransmitters ...
... vasoconstriction, mitogenesis, tissue changes Vasoactive intestinal peptide stimulates AC (to make cAMP) via G proteins, and its effects are synergistic with those of other neurotransmitters ...
INTRODUCTION TO EMBRYOLOGY
... Ligand binds its receptor….. Conformational change occurs in the receptor…. Cytoplasmic region gains an enzymatic activity (mostly kinase)…. Phosphorylation of some cytoplasmic proteins…. Activation of a transcription factor…. Activation or inhibition of genes. ...
... Ligand binds its receptor….. Conformational change occurs in the receptor…. Cytoplasmic region gains an enzymatic activity (mostly kinase)…. Phosphorylation of some cytoplasmic proteins…. Activation of a transcription factor…. Activation or inhibition of genes. ...
Classroom Cell Communication
... cytoplasm or within the nucleus. The signals can be sent over short distances (direct contact) or over long distances (via the blood stream). Some signals that are nonpolar may enter the cell without reception and act directly in the nucleus. There are three major signal transduction pathways: G-Pro ...
... cytoplasm or within the nucleus. The signals can be sent over short distances (direct contact) or over long distances (via the blood stream). Some signals that are nonpolar may enter the cell without reception and act directly in the nucleus. There are three major signal transduction pathways: G-Pro ...
Cell Communication (Plan)
... Types of cell signaling as a function of distance travelled by chemical signal Important features of cell signaling. The three stages of cell signaling in general and map of details: a. external ligands or hormones (1st messengers): chemistry b. protein receptors (membrane-bound & soluble) Signal tr ...
... Types of cell signaling as a function of distance travelled by chemical signal Important features of cell signaling. The three stages of cell signaling in general and map of details: a. external ligands or hormones (1st messengers): chemistry b. protein receptors (membrane-bound & soluble) Signal tr ...
Endocrine System 1 - Napa Valley College
... paracrine substances (e.g., prostaglandins) - exert local effects on neighboring cells B. Chemical Classification of Hormones 1. Lipophilic (lipid-soluble) e.g., steroid hormones, thyroid hormones, eicosanoids - cross the plasma membrane - bind to intracellular (cytoplasmic) receptors 2. Lipophobic ...
... paracrine substances (e.g., prostaglandins) - exert local effects on neighboring cells B. Chemical Classification of Hormones 1. Lipophilic (lipid-soluble) e.g., steroid hormones, thyroid hormones, eicosanoids - cross the plasma membrane - bind to intracellular (cytoplasmic) receptors 2. Lipophobic ...
Old exams 1. Which one of these answers best describes a
... 84.Sulfonylurea drugs increase insulin secretion. The mechanism of this action can be best described as ...
... 84.Sulfonylurea drugs increase insulin secretion. The mechanism of this action can be best described as ...
Gene Section CBLb (Cas-Br-M (murine) ecotropic retroviral transforming sequence b)
... Regulation of signal transduction; CBLb has been shown to inhibit c-Jun terminal kinase (JNK) activation mediated by the (VAV oncoprotein and EGF receptor (EGFR) signaling; in contrast, a direct interaction between CBLb and the kinase ZAP-70 induces a positive signal in T cells. ...
... Regulation of signal transduction; CBLb has been shown to inhibit c-Jun terminal kinase (JNK) activation mediated by the (VAV oncoprotein and EGF receptor (EGFR) signaling; in contrast, a direct interaction between CBLb and the kinase ZAP-70 induces a positive signal in T cells. ...
Questions with Answers
... close enough proximity to cause autophosphorylation. Thus, signaling would be rampant, and the cell would be able to replicate without the presence of extracellular growth factors. Thus, the cell would become cancerous. ...
... close enough proximity to cause autophosphorylation. Thus, signaling would be rampant, and the cell would be able to replicate without the presence of extracellular growth factors. Thus, the cell would become cancerous. ...
powerpoint
... Normal cellular ras protein activates cellular processes when GTP is bound and is inactive when GTP has been hydrolyzed to GDP Mutant (oncogenic) forms of ras have severely impaired GTPase activity, so remain active for long periods, stimulating excessive growth and metabolic activity - causing tumo ...
... Normal cellular ras protein activates cellular processes when GTP is bound and is inactive when GTP has been hydrolyzed to GDP Mutant (oncogenic) forms of ras have severely impaired GTPase activity, so remain active for long periods, stimulating excessive growth and metabolic activity - causing tumo ...
Unit 1 PPT 6 (2cii Signal transduction)
... In this form of signal transduction the binding of a ligand stimulates a transmembrane enzyme directly. These molecules span the bilayer, existing singly or as two proteins stimulated by dimers. Ligand binding stimulates an enzyme directly rather than via a G-protein. The cytoplasmic portion contain ...
... In this form of signal transduction the binding of a ligand stimulates a transmembrane enzyme directly. These molecules span the bilayer, existing singly or as two proteins stimulated by dimers. Ligand binding stimulates an enzyme directly rather than via a G-protein. The cytoplasmic portion contain ...
I`m a real “powerhouse” That`s plain to see. I break down food To
... That’s plain to see. I break down food To release energy. MITOCHONDRIA ...
... That’s plain to see. I break down food To release energy. MITOCHONDRIA ...
DR 4-2 Active Transport
... a. a large protein in the cell membrane that transports a specific ion b. acts as a signal molecule in the cytoplasm ...
... a. a large protein in the cell membrane that transports a specific ion b. acts as a signal molecule in the cytoplasm ...
Welcome to Biochemistry/Endocrinology
... • Deliberately unstable – levels rise rapidly upon secretion, but fall fast when it stops • Biochemical response may be very rapid, by altering existing enzyme activities, or slower, where gene expression levels change • Act through two receptor types: cell surface and nuclear • Display remarkable s ...
... • Deliberately unstable – levels rise rapidly upon secretion, but fall fast when it stops • Biochemical response may be very rapid, by altering existing enzyme activities, or slower, where gene expression levels change • Act through two receptor types: cell surface and nuclear • Display remarkable s ...
Concept 11.2 Reception: A signaling molecule binds to a receptor
... - The part of the receptor protein going inside the cytoplasm functions as a tyrosine kinase, an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group from ATP to the amino acid tyrosine. ...
... - The part of the receptor protein going inside the cytoplasm functions as a tyrosine kinase, an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group from ATP to the amino acid tyrosine. ...
Cell to Cell Communication
... that is almost touching the sender. – Plants and animals use hormones to signal at ...
... that is almost touching the sender. – Plants and animals use hormones to signal at ...
ch_11 cell communication
... that is almost touching the sender. – Plants and animals use hormones to signal at ...
... that is almost touching the sender. – Plants and animals use hormones to signal at ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.