Outline 4.2 (M)
... Membrane Receptor Proteins • Cells must also respond to important information and filter out unimportant information. • Cells can receive the messages carried by certain signal molecules because the cell membrane contains specialized proteins, called receptor proteins, that bind these signal molecul ...
... Membrane Receptor Proteins • Cells must also respond to important information and filter out unimportant information. • Cells can receive the messages carried by certain signal molecules because the cell membrane contains specialized proteins, called receptor proteins, that bind these signal molecul ...
Connect!
... Cells not meant to receive a specific message simply do not have the corresponding receptor in their cell membranes ...
... Cells not meant to receive a specific message simply do not have the corresponding receptor in their cell membranes ...
Document
... Induction of EGFP expression by 1 nM IL-1 in HeLa cells transiently transfected with a pIL8 reporter ...
... Induction of EGFP expression by 1 nM IL-1 in HeLa cells transiently transfected with a pIL8 reporter ...
Ch 10
... • DNA binding domain is zinc finger • Zn finger dimer binds at the hormone response element • Transcription factor—activate or inhibit • Steroidal anti‐inflammatory ...
... • DNA binding domain is zinc finger • Zn finger dimer binds at the hormone response element • Transcription factor—activate or inhibit • Steroidal anti‐inflammatory ...
與細胞核內受器蛋白結合的激素Hormones That Bind to Nuclear
... Actions are mediated by 2nd messengers (signal-transduction mechanisms). ...
... Actions are mediated by 2nd messengers (signal-transduction mechanisms). ...
Cell signalling
... • very potent neurotoxins • bind to receptor and prevent opening of Na+ channel – e.g. cobratoxin from Indian cobra ...
... • very potent neurotoxins • bind to receptor and prevent opening of Na+ channel – e.g. cobratoxin from Indian cobra ...
Chapter 8 Questions
... diffusion 1. Relate the functions of the cell membrane to homeostasis. 2. Describe the types of substanes that can pass through the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane. 3. Outline four functions of proteins within the cell membrane. 4. What would happen if the cell membrane were fully permeable to al ...
... diffusion 1. Relate the functions of the cell membrane to homeostasis. 2. Describe the types of substanes that can pass through the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane. 3. Outline four functions of proteins within the cell membrane. 4. What would happen if the cell membrane were fully permeable to al ...
C 2.3 Applications of Cellular Transport in Industry and Medicine
... *** Liposomes are fluid filled sacs surrounded by a phospholipid bilayer identical to that found in the cell (Mr. S says you might want to know this!!)*** Water soluble drugs are transported within the Liposomes so when they reach your cells the membranes of the cell and liposome can fuse thus deliv ...
... *** Liposomes are fluid filled sacs surrounded by a phospholipid bilayer identical to that found in the cell (Mr. S says you might want to know this!!)*** Water soluble drugs are transported within the Liposomes so when they reach your cells the membranes of the cell and liposome can fuse thus deliv ...
Cells B
... Roles of Membrane Receptors • Contact signaling • touching and recognition of cells • receptors on one or both cells recognize proteins/glycoproteins on other cell’s surface • regulates development, growth, immunity, etc. ...
... Roles of Membrane Receptors • Contact signaling • touching and recognition of cells • receptors on one or both cells recognize proteins/glycoproteins on other cell’s surface • regulates development, growth, immunity, etc. ...
Unit 1 Lesson 3 - Belle Vernon Area School District
... Eukaryotic cells can differ from each other depending on their jobs Structure is the arrangement of parts Function is the activity the parts carry out Ex: plant and animal cells differ, cells in a single organism can be different depending on function Most cells in multicellular organisms have a spe ...
... Eukaryotic cells can differ from each other depending on their jobs Structure is the arrangement of parts Function is the activity the parts carry out Ex: plant and animal cells differ, cells in a single organism can be different depending on function Most cells in multicellular organisms have a spe ...
G-Protein Coupled Signal Transduction
... such as STH (human growth hormone) and insulin or neurotransmitters such as acetylcholine, they are unable to pass directly through the lipid bilayer. ...
... such as STH (human growth hormone) and insulin or neurotransmitters such as acetylcholine, they are unable to pass directly through the lipid bilayer. ...
Key concepts: Apoptosis Animal cells can activate an intracellular
... before there is any leakage of cytoplasmic contents. Apoptosis is mediated by proteolytic enzymes called caspases, which cleave specific intracellular proteins to help kill the cell. Caspases are present in all nucleated animal cells as inactive precursors. Initiator caspases are activated when brou ...
... before there is any leakage of cytoplasmic contents. Apoptosis is mediated by proteolytic enzymes called caspases, which cleave specific intracellular proteins to help kill the cell. Caspases are present in all nucleated animal cells as inactive precursors. Initiator caspases are activated when brou ...
Cell Communication
... One signal-activated receptor activates another protein, which activates another molecule, etc., etc. These act as relay molecules Often the message is transferred using protein kinases, which transfer phosphate groups from ATP molecules to proteins ...
... One signal-activated receptor activates another protein, which activates another molecule, etc., etc. These act as relay molecules Often the message is transferred using protein kinases, which transfer phosphate groups from ATP molecules to proteins ...
Marine Turtle Expeditions
... • d. cAMP or cGMP formed and act as 2nd messenger and changes cell function in cytoplasm ...
... • d. cAMP or cGMP formed and act as 2nd messenger and changes cell function in cytoplasm ...
Supplementary Figure Legends (doc 60K)
... CRC and NSCLC cell lines. A) Cancer cells were analyzed by immunoblotting for EGFR, pEGFR, MEK 1/2, p-MEK1/2, AKT, p-AKT, RAS Total (RAS-T) levels and RAS activity (RASACT). B) Signal intensity was quantified using the Image J freeware. Cells were grouped as either sensitive (IC50 at 96 hrs ≤ 1μM) o ...
... CRC and NSCLC cell lines. A) Cancer cells were analyzed by immunoblotting for EGFR, pEGFR, MEK 1/2, p-MEK1/2, AKT, p-AKT, RAS Total (RAS-T) levels and RAS activity (RASACT). B) Signal intensity was quantified using the Image J freeware. Cells were grouped as either sensitive (IC50 at 96 hrs ≤ 1μM) o ...
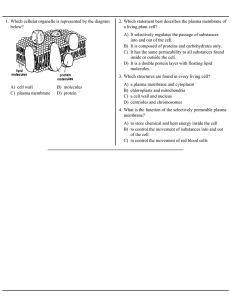
A) cell wall B) molecules C) plasma membrane D) protein 1. Which
... 2. Which statement best describes the plasma membrane of a living plant cell? A) It selectively regulates the passage of substances into and out of the cell. B) It is composed of proteins and carbohydrates only. C) It has the same permeability to all substances found inside or outside the cell. D) I ...
... 2. Which statement best describes the plasma membrane of a living plant cell? A) It selectively regulates the passage of substances into and out of the cell. B) It is composed of proteins and carbohydrates only. C) It has the same permeability to all substances found inside or outside the cell. D) I ...
Prokaryotic Cell Structure
... refractile bodies in the cytoplasm when viewed in a phase contrast microscope. These so-called inclusion bodies. …….. Glycogen, volutin granules or metachromatic granules . Bacteria contain proteins resembling both the actin and nonactin cytoskeletal proteins of eukaryotic cells as additional prote ...
... refractile bodies in the cytoplasm when viewed in a phase contrast microscope. These so-called inclusion bodies. …….. Glycogen, volutin granules or metachromatic granules . Bacteria contain proteins resembling both the actin and nonactin cytoskeletal proteins of eukaryotic cells as additional prote ...
1. The gel like substance that provides support for the cell. 2. the
... 1. The gel like substance that provides support for the cell. 2. the outer layer of a cell that gives support to the plant cell. 3. organelle in green plant cells-site of photosynthesis (makes food). 4. organelles that release energy by breaking down food 5. Storage of water and nutrients in cells 6 ...
... 1. The gel like substance that provides support for the cell. 2. the outer layer of a cell that gives support to the plant cell. 3. organelle in green plant cells-site of photosynthesis (makes food). 4. organelles that release energy by breaking down food 5. Storage of water and nutrients in cells 6 ...
(null): Can You Identify These Cell Structures.doc, filename=Can
... You can find me in the cytoplasm Or attached to the E.R.’s wall What am I?__________________ I’ve been called a “storage tank” ...
... You can find me in the cytoplasm Or attached to the E.R.’s wall What am I?__________________ I’ve been called a “storage tank” ...
1. dia
... minutes (for protein- and lipid-mediated kinase cascades), hours, or days (for gene expression). • There is usually an amplification of the signal - one hormone can elicit the response of over 108 molecules • Many disease processes, such as diabetes, heart disease, autoimmunity, and cancer arise fro ...
... minutes (for protein- and lipid-mediated kinase cascades), hours, or days (for gene expression). • There is usually an amplification of the signal - one hormone can elicit the response of over 108 molecules • Many disease processes, such as diabetes, heart disease, autoimmunity, and cancer arise fro ...
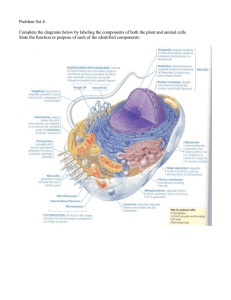
Problem Set 4:
... surface area would the eukaryotic cell have? 100X b. Proportionally how much more volume would it have? 1000X ...
... surface area would the eukaryotic cell have? 100X b. Proportionally how much more volume would it have? 1000X ...
Active Transport Notes
... Occurs when the cell membranes forms a vesicle (like an envelope) around an item that needs to ENTER the cell. ...
... Occurs when the cell membranes forms a vesicle (like an envelope) around an item that needs to ENTER the cell. ...
Mid Term Review 2008
... glucose are included in a group of organic molecules called Carbohydrates ...
... glucose are included in a group of organic molecules called Carbohydrates ...
BIOL 201: Cell Biology and Metabolism
... They don’t require receptors on the surface of the cell, but because they can go through the cell membrane, can interact with intracellular receptors (can be in the cytoplasm or in the nucleus) When these molecules interact with the receptors, there ultimate change will be at the level of the geneti ...
... They don’t require receptors on the surface of the cell, but because they can go through the cell membrane, can interact with intracellular receptors (can be in the cytoplasm or in the nucleus) When these molecules interact with the receptors, there ultimate change will be at the level of the geneti ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.