Slide 1
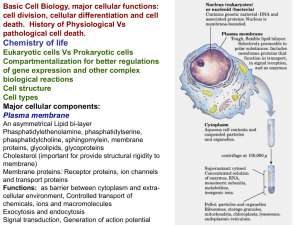
... Membrane proteins: Receptor proteins, ion channels and transport proteins Functions: as barrier between cytoplasm and extracellular environment, Controlled transport of chemicals, ions and macromolecules Exocytosis and endocytosis Signal transduction, Generation of action potential ...
... Membrane proteins: Receptor proteins, ion channels and transport proteins Functions: as barrier between cytoplasm and extracellular environment, Controlled transport of chemicals, ions and macromolecules Exocytosis and endocytosis Signal transduction, Generation of action potential ...
Worksheet on Cell Communication
... How do hormones travel to their targets in animal cells and in plant cells? ...
... How do hormones travel to their targets in animal cells and in plant cells? ...
Cell Communication Webquest 2014
... ** Click on the receptor tyrosine kinase in the animation. Then click on the correct signal molecule to activate the receptor tyrosine kinase shown. 21. How does the bonding of the signal molecule to the receptor tyrosine kinase lead to the activation tyrosine-kinase enzymes? 22. How does the activa ...
... ** Click on the receptor tyrosine kinase in the animation. Then click on the correct signal molecule to activate the receptor tyrosine kinase shown. 21. How does the bonding of the signal molecule to the receptor tyrosine kinase lead to the activation tyrosine-kinase enzymes? 22. How does the activa ...
Characteristics Of Life - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
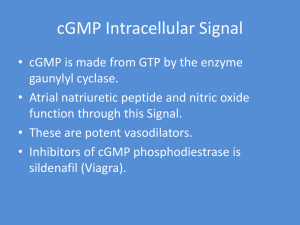
... exert their effects through G-protein linked receptors. ...
... exert their effects through G-protein linked receptors. ...
File
... If a chemical acts on cells in the immediate vicinity of the cell that secreted it, its is called ____ signal. ...
... If a chemical acts on cells in the immediate vicinity of the cell that secreted it, its is called ____ signal. ...
AP Biology - AdamsAPBiostars
... outside the cell. • IP3 (inositol triphosphate) is the ligand for a gated calcium channel in the membrane of the ER, which stores Ca2+ at high concentrations. • When IP3 binds, Ca2+ flows into the cytosol, where it activates proteins of many signaling pathways. • Increasing cytosolic concentration o ...
... outside the cell. • IP3 (inositol triphosphate) is the ligand for a gated calcium channel in the membrane of the ER, which stores Ca2+ at high concentrations. • When IP3 binds, Ca2+ flows into the cytosol, where it activates proteins of many signaling pathways. • Increasing cytosolic concentration o ...
Outline Section 4
... b. Convergent, or redundant, cross-talk for essential responses occurs when two or more ligands can produce the same target mechanism 3. Multiple target mechanism pathways and divergent crosstalk a. Divergent cross-talk for complex, integrated responses where a single ligand can activate two or mor ...
... b. Convergent, or redundant, cross-talk for essential responses occurs when two or more ligands can produce the same target mechanism 3. Multiple target mechanism pathways and divergent crosstalk a. Divergent cross-talk for complex, integrated responses where a single ligand can activate two or mor ...
038-Signal Transduction Pathways Activity-V Morris
... Step 2: "The binding of the ligand causes a conformation change to the subunits on G-protein. The alpha subunit will move to a protein called adenlyl cyclase." Move the alpha subunit to the adenylyl cyclase. Step 3: Adenylyl cyclase is now ready to convert ATP into cAMP. Take off 2 phosphates from A ...
... Step 2: "The binding of the ligand causes a conformation change to the subunits on G-protein. The alpha subunit will move to a protein called adenlyl cyclase." Move the alpha subunit to the adenylyl cyclase. Step 3: Adenylyl cyclase is now ready to convert ATP into cAMP. Take off 2 phosphates from A ...
PowerPoint 簡報
... Common features of signaling systems that detects hormones, light, smells, and tetastes ...
... Common features of signaling systems that detects hormones, light, smells, and tetastes ...
Molecular Interactions in Cell events
... Any change in signal type is called signal transduction A signal transduction pathway is a series of responses to the bonding of a signal molecule All receptor proteins have an active site. They are specific to signal molecules. Therefore, signals will only act on target cells that have these recept ...
... Any change in signal type is called signal transduction A signal transduction pathway is a series of responses to the bonding of a signal molecule All receptor proteins have an active site. They are specific to signal molecules. Therefore, signals will only act on target cells that have these recept ...
Problem 5: Bacterial Cell Signaling
... kinase inside the cell. Is the receptor a peripheral or integral membrane protein? ...
... kinase inside the cell. Is the receptor a peripheral or integral membrane protein? ...
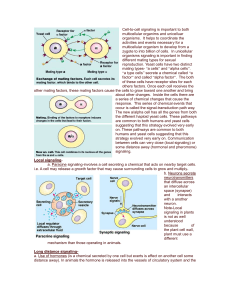
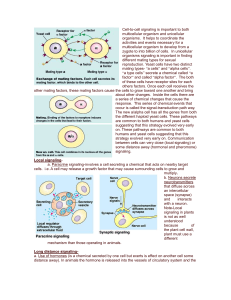
Cell-to-cell signaling is important to both multicellular organims and
... enzyme (adenlate cylase) in the plasma membrane causes this reaction to occur. In this example, epinephrine activates a receptor site, which in turns activates the Gprotein. The G protein now activates adenlyate cyclase, which then makes cAMP from ATP. cAMP activates the epinephrine pathway which ul ...
... enzyme (adenlate cylase) in the plasma membrane causes this reaction to occur. In this example, epinephrine activates a receptor site, which in turns activates the Gprotein. The G protein now activates adenlyate cyclase, which then makes cAMP from ATP. cAMP activates the epinephrine pathway which ul ...
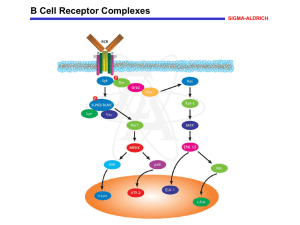
B Cell Receptor Complexes - Sigma
... family are activated initially and phosphorylate CD79 and CD79ß, thereby creating phosphotyrosine motifs that recruit downstream signaling molecules. In particular, phosphorylation of the BCR complex leads to the recruitment and activation of the protein tyrosine kinase Syk, which, in turn, promote ...
... family are activated initially and phosphorylate CD79 and CD79ß, thereby creating phosphotyrosine motifs that recruit downstream signaling molecules. In particular, phosphorylation of the BCR complex leads to the recruitment and activation of the protein tyrosine kinase Syk, which, in turn, promote ...
Cell Structure and Function
... Process: Synthesis of New Molecules Proteins play a role in nearly all biological processes. Examples of protein functions: structure (cell membrane proteins, cytoskeleton proteins, proteins of the connective tissue), enzymes for cell reactions (enzymes are proteins), ...
... Process: Synthesis of New Molecules Proteins play a role in nearly all biological processes. Examples of protein functions: structure (cell membrane proteins, cytoskeleton proteins, proteins of the connective tissue), enzymes for cell reactions (enzymes are proteins), ...
Chapter 11 LT
... I can distinguish between hydrophilic and hydrophobic ligands and identify where the receptors for each type are located. I can describe how the following receive cell signals and start transduction: G-protein coupled receptors tyrosine kinase receptors ion channels I can identify and describe the r ...
... I can distinguish between hydrophilic and hydrophobic ligands and identify where the receptors for each type are located. I can describe how the following receive cell signals and start transduction: G-protein coupled receptors tyrosine kinase receptors ion channels I can identify and describe the r ...
ppt
... Researchers found that the cytoplasmic enzyme could be activated by the membrane-bound epinephrine in broken cells, as long as all parts were present. They discovered that another molecule delivered the message from the “first messenger,” epinephrine, to the enzyme. The second messenger was later d ...
... Researchers found that the cytoplasmic enzyme could be activated by the membrane-bound epinephrine in broken cells, as long as all parts were present. They discovered that another molecule delivered the message from the “first messenger,” epinephrine, to the enzyme. The second messenger was later d ...
Long distance signaling
... enzyme (adenylate cyclase) in the plasma membrane causes this reaction to occur. In this example, epinephrine activates a receptor site, which in turns activates the Gprotein. The G protein now activates adenlyate cyclase, which then makes cAMP from ATP. cAMP activates the epinephrine pathway which ...
... enzyme (adenylate cyclase) in the plasma membrane causes this reaction to occur. In this example, epinephrine activates a receptor site, which in turns activates the Gprotein. The G protein now activates adenlyate cyclase, which then makes cAMP from ATP. cAMP activates the epinephrine pathway which ...
Cell signalling - Bilkent University
... elaborate intercellular communication network that coordinates the growth, differentiation, and metabolism of the multitude of cells in diverse tissues and organs. • Errors in cellular information processing are responsible for diseases such as cancer, autoimmunity, and diabetes. By understanding ce ...
... elaborate intercellular communication network that coordinates the growth, differentiation, and metabolism of the multitude of cells in diverse tissues and organs. • Errors in cellular information processing are responsible for diseases such as cancer, autoimmunity, and diabetes. By understanding ce ...
File
... The receptor proteins for steroid hormones are transcription factors. Only once the hormone signal has bound to the receptor can the transcription factor bind to gene regulatory sequences of DNA for transcription to occur. ...
... The receptor proteins for steroid hormones are transcription factors. Only once the hormone signal has bound to the receptor can the transcription factor bind to gene regulatory sequences of DNA for transcription to occur. ...
11 Cell Communication
... Up to 60% of all medicines exert their effects through G-protein linked receptors. ...
... Up to 60% of all medicines exert their effects through G-protein linked receptors. ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.