3-1 part 2
... *rough is abundant in WBC. It contains ribosomes and works in protein synthesis *smooth is abundant in liver cells. It does not have ribosomes and it is used in lipid synthesis. ...
... *rough is abundant in WBC. It contains ribosomes and works in protein synthesis *smooth is abundant in liver cells. It does not have ribosomes and it is used in lipid synthesis. ...
1 Table S1. Pathway/Function Gene Symbol Fold Change Function
... apoptosis characterized by a rapid and robust release of cytochrome C from the mitochondria and activation of BAX and caspases 2, 3, 6, 8 and 9 ...
... apoptosis characterized by a rapid and robust release of cytochrome C from the mitochondria and activation of BAX and caspases 2, 3, 6, 8 and 9 ...
Chapter 1 Eukaryotic Cells Section 1
... Cell Wall – rigid (stiff) structure that gives support to plant cells Cell membrane – protective barrier that encloses a cell Cytoskeleton – web of proteins in the cytoplasm that keep the membrane from collapsing Nucleus – largest organelle in a eukaryotic cell, contains DNA that directs all cell ac ...
... Cell Wall – rigid (stiff) structure that gives support to plant cells Cell membrane – protective barrier that encloses a cell Cytoskeleton – web of proteins in the cytoplasm that keep the membrane from collapsing Nucleus – largest organelle in a eukaryotic cell, contains DNA that directs all cell ac ...
Slide 1 - AccessPharmacy
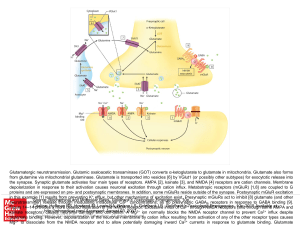
... Glutamatergic neurotransmission. Glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase (GOT) converts α-ketoglutarate to glutamate in mitochondria. Glutamate also forms from glutamine via mitochondrial glutaminase. Glutamate is transported into vesicles [6] by VGlut1 (or possibly other subtypes) for exocytotic release ...
... Glutamatergic neurotransmission. Glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase (GOT) converts α-ketoglutarate to glutamate in mitochondria. Glutamate also forms from glutamine via mitochondrial glutaminase. Glutamate is transported into vesicles [6] by VGlut1 (or possibly other subtypes) for exocytotic release ...
Moving Molecules and Cellular Energy Crossword
... 10. movement from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration 11. process during which a cell takes in a substance by surrounding it with the cell membrane 12. diffusion of water molecules only through a membrane Down 1. series of reactions that convert light energy, water, and ...
... 10. movement from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration 11. process during which a cell takes in a substance by surrounding it with the cell membrane 12. diffusion of water molecules only through a membrane Down 1. series of reactions that convert light energy, water, and ...
lec 010v2 cell communication
... c. The cytoplasm is NEGATIVE in charge in RELATION to the extracellular fluid because of an unequal distribution of anions and cations on opposite sides of the membrane. d. The difference in electrical charge (voltage) across a cell's plasma membrane, due to the differential distribution of ions. Me ...
... c. The cytoplasm is NEGATIVE in charge in RELATION to the extracellular fluid because of an unequal distribution of anions and cations on opposite sides of the membrane. d. The difference in electrical charge (voltage) across a cell's plasma membrane, due to the differential distribution of ions. Me ...
BMB-Symposium 2015
... 14:30–14:45 Andreas Dotzauer: Molecular interactions of hepatitis A virus proteins with cellular membranes and their meaning for virus replication and release 14:45–15:00 Ralf Dringen: Modulation of the Metabolism of Brain Cells by Drugs and Environmental Toxins ...
... 14:30–14:45 Andreas Dotzauer: Molecular interactions of hepatitis A virus proteins with cellular membranes and their meaning for virus replication and release 14:45–15:00 Ralf Dringen: Modulation of the Metabolism of Brain Cells by Drugs and Environmental Toxins ...
G protein-coupled receptor - Bryn Mawr School Faculty Web Pages
... Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
... Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
Ass4 - The University of Sydney
... Protein kinase C becomes activated after dissociation of its regulatory subunits Phospholipase C hydrolyses phospholipids in the ER membrane, leading to Ca2+ release Diacyl glycerol is phosphorylated and becomes incorporated into the cell membrane ...
... Protein kinase C becomes activated after dissociation of its regulatory subunits Phospholipase C hydrolyses phospholipids in the ER membrane, leading to Ca2+ release Diacyl glycerol is phosphorylated and becomes incorporated into the cell membrane ...
Cell Transport Systems
... water into the cell. This is called a hypertonic solution. The cell can lose water and "shrivel" this is called crenation. • Cells in larger organisms are surrounded by solution with roughly equal concentrations of H2O and solvents. This is called an isotonic solution. ...
... water into the cell. This is called a hypertonic solution. The cell can lose water and "shrivel" this is called crenation. • Cells in larger organisms are surrounded by solution with roughly equal concentrations of H2O and solvents. This is called an isotonic solution. ...
Cell Transport Systems
... water into the cell. This is called a hypertonic solution. The cell can lose water and "shrivel" this is called crenation. • Cells in larger organisms are surrounded by solution with roughly equal concentrations of H2O and solvents. This is called an isotonic solution. ...
... water into the cell. This is called a hypertonic solution. The cell can lose water and "shrivel" this is called crenation. • Cells in larger organisms are surrounded by solution with roughly equal concentrations of H2O and solvents. This is called an isotonic solution. ...
W3310-4310_study_que..
... 2. Describe how icosahedral and enveloped virions attach to cell receptors. ...
... 2. Describe how icosahedral and enveloped virions attach to cell receptors. ...
The Cytoplasm The Cytosol a Viscous watery fluid which all the
... • Inner membrane has folds called cristae • It is in the inner membrane that the enzymes responsible for the production of ATP is concentrated ! Space between cristae called the matrix ! Contains enzymes ...
... • Inner membrane has folds called cristae • It is in the inner membrane that the enzymes responsible for the production of ATP is concentrated ! Space between cristae called the matrix ! Contains enzymes ...
Eukaryotic Cell Organelles
... Cell Wall – firm, rigid structure located outside the plasma membrane of plant cells, fungi cells, most bacteria, and some protists. ***Provides support and protection. ...
... Cell Wall – firm, rigid structure located outside the plasma membrane of plant cells, fungi cells, most bacteria, and some protists. ***Provides support and protection. ...
Lecture 6
... a. most are transmembrane b. selective transport c. some are enzymes d. some are receptors for signal transduction i.e., for neurotransmitters and hormones ...
... a. most are transmembrane b. selective transport c. some are enzymes d. some are receptors for signal transduction i.e., for neurotransmitters and hormones ...
Lecture 6
... a. most are transmembrane b. selective transport c. some are enzymes d. some are receptors for signal transduction i.e., for neurotransmitters and hormones ...
... a. most are transmembrane b. selective transport c. some are enzymes d. some are receptors for signal transduction i.e., for neurotransmitters and hormones ...
Learning Objectives
... Explain the mechanism of action of acetylcholine in modulating muscle contraction. Give the receptors through which these neurotransmitters carry out these functions. ...
... Explain the mechanism of action of acetylcholine in modulating muscle contraction. Give the receptors through which these neurotransmitters carry out these functions. ...
Structures found in Eukaryotes Continued 4. • Formed by • Vesicles
... Cell respiration takes place ...
... Cell respiration takes place ...
Unit 4 Notes
... • Intracellular Receptors—chemical messengers (small & hydrophobic) enter cell and bind to a receptor in the cytoplasm or nucleus o Testosterone—small steroid hormone • Activates receptor protein in cytoplasm of target cell by binding to it • Activated receptor protein (with attached testosterone) e ...
... • Intracellular Receptors—chemical messengers (small & hydrophobic) enter cell and bind to a receptor in the cytoplasm or nucleus o Testosterone—small steroid hormone • Activates receptor protein in cytoplasm of target cell by binding to it • Activated receptor protein (with attached testosterone) e ...
Using light as a superglue for proteins and their binding partners
... precise target proteins. This has strongly limited research into specific interactions between molecules. In the current study, the scientists take this basic principle to a new level. The aim was to develop a novel type of molecular switch that specific proteins recognize and can be activated by li ...
... precise target proteins. This has strongly limited research into specific interactions between molecules. In the current study, the scientists take this basic principle to a new level. The aim was to develop a novel type of molecular switch that specific proteins recognize and can be activated by li ...
Meili, R and R.A. Firtel (2002). Leading the way. Nature Cell Biol. 4
... of chemical signals, is a feature of a wide variety of eukaryotic cells. Chemotaxis is important for many biological responses, from the movement of leukocytes towards sites of infection or inflammation to the aggregation of Dictyostelium discoideum amoebae to form a multicellular organism. Recent w ...
... of chemical signals, is a feature of a wide variety of eukaryotic cells. Chemotaxis is important for many biological responses, from the movement of leukocytes towards sites of infection or inflammation to the aggregation of Dictyostelium discoideum amoebae to form a multicellular organism. Recent w ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.