Cellular Chemical Reactions
... atoms and molecules interacting. In this process, called a chemical reaction, bonds between atoms are broken and new bonds to make different molecules. ...
... atoms and molecules interacting. In this process, called a chemical reaction, bonds between atoms are broken and new bonds to make different molecules. ...
Chapter 4 (Part A) : Eukaryotic Cells
... 6. Lysosomes: special vesicles that contain digestive enzymes and acid fuse with other vesicles functions: recycle old molecules and organelles lyse infecting bacteria, etc.; Mycobacterium tuberculosis prevents fusion of lysosome with vesicle in cell containing the bacteria; the bacteria then ride ...
... 6. Lysosomes: special vesicles that contain digestive enzymes and acid fuse with other vesicles functions: recycle old molecules and organelles lyse infecting bacteria, etc.; Mycobacterium tuberculosis prevents fusion of lysosome with vesicle in cell containing the bacteria; the bacteria then ride ...
Ch 3 - Fort Bend ISD
... • Do NOT have a membrane surrounding genetic material, therefore, can make proteins simultaneously when reading genetic code. • Lack some structures found in Eukaryotic cells ...
... • Do NOT have a membrane surrounding genetic material, therefore, can make proteins simultaneously when reading genetic code. • Lack some structures found in Eukaryotic cells ...
Active Transport Across the Cell Membrane
... The plasma membranes of adjacent cells are usually separated by extracellular fluids that allow transport of nutrients and wastes to and from the bloodstream. In certain tissues, however, the membranes of adjacent cells mayjoin and form a junction. Three kinds of cell junctions are recognized: •Desm ...
... The plasma membranes of adjacent cells are usually separated by extracellular fluids that allow transport of nutrients and wastes to and from the bloodstream. In certain tissues, however, the membranes of adjacent cells mayjoin and form a junction. Three kinds of cell junctions are recognized: •Desm ...
CHEM523 Exam2
... E) There exist >100 orphan GPCRs in the human genome with no known ligand. 22. Which of the following is not involved in signal transduction by the -adrenergic receptor pathway? ...
... E) There exist >100 orphan GPCRs in the human genome with no known ligand. 22. Which of the following is not involved in signal transduction by the -adrenergic receptor pathway? ...
Regulation of the Cell Cycle
... Cells in the intestine for example live only three days and must be constantly replaced, whereas cells of the liver live for more than a year. Brain cells on the other hand may never ...
... Cells in the intestine for example live only three days and must be constantly replaced, whereas cells of the liver live for more than a year. Brain cells on the other hand may never ...
Extracellular components
... – Special ECM – Under epithelial cells – Separates them from connective tissue ...
... – Special ECM – Under epithelial cells – Separates them from connective tissue ...
Structure and function of cell components
... Made of actin protein Present throughout the cell, but most common just inside the plasma membrane Readily assembled and disassembled Function ...
... Made of actin protein Present throughout the cell, but most common just inside the plasma membrane Readily assembled and disassembled Function ...
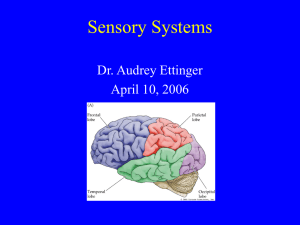
Sensory Systems - Cedar Crest College
... • Chemoreceptors are similar to neurotransmitter receptors • 10,000 odorants recognized by humans • 1,000 kinds of odorant receptors • Each odorant activates a subset of receptors • Pattern of receptors bound indicates odorant ...
... • Chemoreceptors are similar to neurotransmitter receptors • 10,000 odorants recognized by humans • 1,000 kinds of odorant receptors • Each odorant activates a subset of receptors • Pattern of receptors bound indicates odorant ...
Organelles Cheat Sheet
... - Digestive 'plant' for proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates - Transports undigested material to cell membrane for removal - Vary in shape depending on process being carried out - Cell breaks down if lysosome explodes ...
... - Digestive 'plant' for proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates - Transports undigested material to cell membrane for removal - Vary in shape depending on process being carried out - Cell breaks down if lysosome explodes ...
Cells: Chapter 2
... – protein synthesis occurs here for those proteins that will be routed out of cell ...
... – protein synthesis occurs here for those proteins that will be routed out of cell ...
SBI 4U biochem 3
... (longer chain = more intermolecular interactions) can contribute to fluidity. • Presence of cholesterol decreases fluidity at room temperature by increasing intermolecular forces. Cholesterol can increase fluidity at lower temperatures by breaking up the tight packing of the phospholipids. ...
... (longer chain = more intermolecular interactions) can contribute to fluidity. • Presence of cholesterol decreases fluidity at room temperature by increasing intermolecular forces. Cholesterol can increase fluidity at lower temperatures by breaking up the tight packing of the phospholipids. ...
Centrioles are self-replicating organelles made up
... nine bundles of microtubules and are found only in animal cells. They appear to help in organizing cell division, but aren't essential to the process. Cilia and Flagella - For single-celled eukaryotes, cilia and flagella are essential for the locomotion of individual organisms. In multicellular orga ...
... nine bundles of microtubules and are found only in animal cells. They appear to help in organizing cell division, but aren't essential to the process. Cilia and Flagella - For single-celled eukaryotes, cilia and flagella are essential for the locomotion of individual organisms. In multicellular orga ...
รายงานการลาศึกษาต่อป.โท-ป.เอก พญ. ศรัณยภิญ โพธิกานนท์ ภาควิชา
... into haemophilia for the development of a more efficient and safer gene therapy ...
... into haemophilia for the development of a more efficient and safer gene therapy ...
Cell Structure and Function Study Guide
... What are the contributions of Robert Hooke, Anton van Leuwenhoek, Matthias Schleiden, Theodor Schwann, and Rudolph Virchow to our understanding of cells? What are the three parts of the cell theory? How are molecules, organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms related? Be ...
... What are the contributions of Robert Hooke, Anton van Leuwenhoek, Matthias Schleiden, Theodor Schwann, and Rudolph Virchow to our understanding of cells? What are the three parts of the cell theory? How are molecules, organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms related? Be ...
b-cells - APBiology2015-2016
... • The fragments will later appear on the cell surface inside a molecule because it is now a plasma cell. • T-cells help b-cells function properly by releasing chemicals that signal the b-cells to divide in multiples and attack invaders inside the cell that may interfere with the signal pathway. ...
... • The fragments will later appear on the cell surface inside a molecule because it is now a plasma cell. • T-cells help b-cells function properly by releasing chemicals that signal the b-cells to divide in multiples and attack invaders inside the cell that may interfere with the signal pathway. ...
Chemistry of Neurotransmitters
... few milliseconds, the ACh released has been eliminated again. The cleavage products choline and acetate are taken up again by the presynaptic neuron and reused for acetylcholine synthesis. ...
... few milliseconds, the ACh released has been eliminated again. The cleavage products choline and acetate are taken up again by the presynaptic neuron and reused for acetylcholine synthesis. ...
Cell A.
... The ability of a single ligand-binding event to trigger so many pathways is a key difference between these receptors and G-protein-linked receptors. Ligand independent activation of tyrosin-kinase receptor Mutation (突變) ...
... The ability of a single ligand-binding event to trigger so many pathways is a key difference between these receptors and G-protein-linked receptors. Ligand independent activation of tyrosin-kinase receptor Mutation (突變) ...
Signal transmission at synapses
... 2. Hydrolysis: in the synaptict cleft (restores the resting potential in the postsynaptic membrane) ...
... 2. Hydrolysis: in the synaptict cleft (restores the resting potential in the postsynaptic membrane) ...
Golgi apparatus
... Ribosomes attached to rough ER synthesize proteins that leave cells via the Golgi complex; smooth ER synthesizes lipids incorporated in cell membranes, steroid hormones, and certain carbohydrates used to form glycoproteins. ...
... Ribosomes attached to rough ER synthesize proteins that leave cells via the Golgi complex; smooth ER synthesizes lipids incorporated in cell membranes, steroid hormones, and certain carbohydrates used to form glycoproteins. ...
Lab 8: Atomic force microscopy imaging of cells PI: Lab Instructor: Summary
... In this laboratory, you will use the atomic force microscope to image the structure and stiffness of living and chemically fixed human microvascular endothelial cells. The pN- to nN-scale mechanical force used to create these images allows you to observe both the micrometer-scale height of these cel ...
... In this laboratory, you will use the atomic force microscope to image the structure and stiffness of living and chemically fixed human microvascular endothelial cells. The pN- to nN-scale mechanical force used to create these images allows you to observe both the micrometer-scale height of these cel ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.