CONCLUSIONS 133
... In addition to homodimerization, A2AR and dopamine D2 receptors (D2R) are able to form heterodimers. This heteromerization has been demonstrated in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells stably transfected with the D2R. Stimulation of A2AR and/or D2R induces co-agregation and co-internalization of both recepto ...
... In addition to homodimerization, A2AR and dopamine D2 receptors (D2R) are able to form heterodimers. This heteromerization has been demonstrated in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells stably transfected with the D2R. Stimulation of A2AR and/or D2R induces co-agregation and co-internalization of both recepto ...
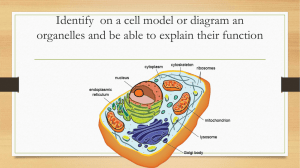
Identify on a cell model or diagram an organelles and be able to
... • Helps cell maintain shape and assisted with various movements for example in muscle movement ...
... • Helps cell maintain shape and assisted with various movements for example in muscle movement ...
Cell Structure and Function
... surface area. • Aerobic cellular respiration occurs in the cristae and the matrix • The liquid medium inside the cristae is called the matrix. ...
... surface area. • Aerobic cellular respiration occurs in the cristae and the matrix • The liquid medium inside the cristae is called the matrix. ...
Name
... Name………………………………………………………………………………………..Roll. No………………………….............. Signature……………………………………………………………………………………………… 4. The image below is that of an early embryo of the nematode worm C.elegans at the twocelled stage where the anterior cell is labelled “A” and the posterior cell is labelled “P”. D ...
... Name………………………………………………………………………………………..Roll. No………………………….............. Signature……………………………………………………………………………………………… 4. The image below is that of an early embryo of the nematode worm C.elegans at the twocelled stage where the anterior cell is labelled “A” and the posterior cell is labelled “P”. D ...
cell theory
... Cell theory The cell is the basic unit of structure All living things are composed of cells Unicellular and multi cellular all cells come from pre-existing cell Important organs in a cell Nuclease: contains the cells DNA brain of the cell Mitochondria: site of respiring provides the energy for the c ...
... Cell theory The cell is the basic unit of structure All living things are composed of cells Unicellular and multi cellular all cells come from pre-existing cell Important organs in a cell Nuclease: contains the cells DNA brain of the cell Mitochondria: site of respiring provides the energy for the c ...
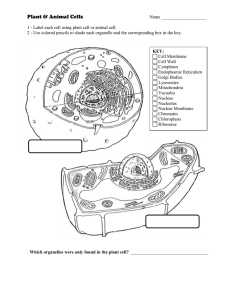
Cell and Cell Plasma Membrane Diagrams
... Transport through the cell membrane occurs in two basic ways. In passive transport, molecules pass through the cell membrane along a concentration gradient from high concentrations to low concentrations. Passive transport requires no energy and includes simple diffusion (movement of solutes) and osm ...
... Transport through the cell membrane occurs in two basic ways. In passive transport, molecules pass through the cell membrane along a concentration gradient from high concentrations to low concentrations. Passive transport requires no energy and includes simple diffusion (movement of solutes) and osm ...
Cell signalling ppt
... receptors on a second cell. The secreted molecule could be a hormone, neurotransmitter, histamine or other substance that either acts locally (paracrine), moves through the bloodstream to another organ (endocrine) or is released by a neuron (synaptic). The molecule binding with the receptor initiate ...
... receptors on a second cell. The secreted molecule could be a hormone, neurotransmitter, histamine or other substance that either acts locally (paracrine), moves through the bloodstream to another organ (endocrine) or is released by a neuron (synaptic). The molecule binding with the receptor initiate ...
www.cmu.edu.cn
... which transmit message from outside to inside of nucleous or from inside to outside of nucleous, also called DNA binding protein. ...
... which transmit message from outside to inside of nucleous or from inside to outside of nucleous, also called DNA binding protein. ...
(2) G Protein-Coupled Receptors
... which transmit message from outside to inside of nucleous or from inside to outside of nucleous, also called DNA binding protein. ...
... which transmit message from outside to inside of nucleous or from inside to outside of nucleous, also called DNA binding protein. ...
Bovine prolactin soluble receptor ECD ECD-11
... Prolactin is a pituitary hormone involved in the stimulation of milk production, salt and water regulation, growth, development and reproduction. The initial step in its action is the binding to a specific membrane receptor (prolactin receptor) which belongs to the superfamily of class 1 cytokine re ...
... Prolactin is a pituitary hormone involved in the stimulation of milk production, salt and water regulation, growth, development and reproduction. The initial step in its action is the binding to a specific membrane receptor (prolactin receptor) which belongs to the superfamily of class 1 cytokine re ...
Alphabodies – working inside the cell
... proteins; similarly, biologics, including antibodies, lack the ability to penetrate through cell membranes, and therefore can only address another 10%, that exist as extracellular proteins. It is therefore estimated that the vast majority of all potential protein targets, more than 80%, are currentl ...
... proteins; similarly, biologics, including antibodies, lack the ability to penetrate through cell membranes, and therefore can only address another 10%, that exist as extracellular proteins. It is therefore estimated that the vast majority of all potential protein targets, more than 80%, are currentl ...
" Exploring the Unique Dual Function and the Evolutionary
... Endocytosis and lysosomal protein trafficking is essential in pathogenic parasites since it is directly linked to vital parasite-specific processes, e.g. host cell invasion, nutrition, and cell differentiation into resistant stages, as in the case of Giardia. Recently, we have identified a protein c ...
... Endocytosis and lysosomal protein trafficking is essential in pathogenic parasites since it is directly linked to vital parasite-specific processes, e.g. host cell invasion, nutrition, and cell differentiation into resistant stages, as in the case of Giardia. Recently, we have identified a protein c ...
Biology Chapter 5, Lesson 1 Notes
... The membrane allows some proteins and molecules to pass through its walls and others not to pass (selectively permeable). There are transport proteins in the plasma membrane that help molecules cross through the membrane. The fluid mosaic model of a cell membrane has phospholipids and proteins ...
... The membrane allows some proteins and molecules to pass through its walls and others not to pass (selectively permeable). There are transport proteins in the plasma membrane that help molecules cross through the membrane. The fluid mosaic model of a cell membrane has phospholipids and proteins ...
Signaling Mechanisms, Cellular Adhesion, and Stem Cells
... Cells n a multicellular organism need to communicate with other cells In signal transduction molecules on the cell membane, assist, transmit,and amplify messages. Transduction means to change the signal from the environment into a common message understood by the cell. ...
... Cells n a multicellular organism need to communicate with other cells In signal transduction molecules on the cell membane, assist, transmit,and amplify messages. Transduction means to change the signal from the environment into a common message understood by the cell. ...
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
... Measure system-wide parameters •Numbers of molecules and species •Reaction rates •Interactions among protein species (what binds and with what affinity) • Changes in protein modification (e.g. phosphorylation due to activity of kinases and phosphatases) ...
... Measure system-wide parameters •Numbers of molecules and species •Reaction rates •Interactions among protein species (what binds and with what affinity) • Changes in protein modification (e.g. phosphorylation due to activity of kinases and phosphatases) ...
Slide ()
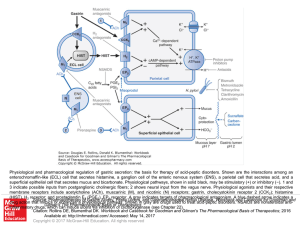
... Physiological and pharmacological regulation of gastric secretion: the basis for therapy of acid-peptic disorders. Shown are the interactions among an enterochromaffin-like (ECL) cell that secretes histamine, a ganglion cell of the enteric nervous system (ENS), a parietal cell that secretes acid, an ...
... Physiological and pharmacological regulation of gastric secretion: the basis for therapy of acid-peptic disorders. Shown are the interactions among an enterochromaffin-like (ECL) cell that secretes histamine, a ganglion cell of the enteric nervous system (ENS), a parietal cell that secretes acid, an ...
Study Guide
... how phylogenetic trees group genetic sequences according to relatedness. Note that, according to Figure 1, T1R3, T1R2, and T1R1 are all derived from an ancestral T1R gene. Receptor activity assays (Figures 2 and 3). These assays were not described fully in the paper or its online supplement, so he ...
... how phylogenetic trees group genetic sequences according to relatedness. Note that, according to Figure 1, T1R3, T1R2, and T1R1 are all derived from an ancestral T1R gene. Receptor activity assays (Figures 2 and 3). These assays were not described fully in the paper or its online supplement, so he ...
4-2-pt.1
... attached loosely to the inner or outer membrane. Integral Proteins – extend into, or through the membrane. Transmembrane Proteins – appear at both the inner and outer surface. ...
... attached loosely to the inner or outer membrane. Integral Proteins – extend into, or through the membrane. Transmembrane Proteins – appear at both the inner and outer surface. ...
Section 2 cont.
... The inside of a cell (like a nerve cell) is slightly more negative than the outside This electrical gradient (difference in charges) enables impulses to be sent ...
... The inside of a cell (like a nerve cell) is slightly more negative than the outside This electrical gradient (difference in charges) enables impulses to be sent ...
Cells
... The CELL THEORY: – All living things are made of cells. – Cells come from pre-existing cells. – Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in all living organisms. ...
... The CELL THEORY: – All living things are made of cells. – Cells come from pre-existing cells. – Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in all living organisms. ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.