CELLULAR PHYSIOLOGY - Eastern Mediterranean University
... – Endothelial barrier function – Permit the passage of some ions and solutes in between adjacent cells ...
... – Endothelial barrier function – Permit the passage of some ions and solutes in between adjacent cells ...
CHAPTER 11 CELL COMMUNICATION
... In other cases, messenger molecules are secreted by the signaling cell. Some transmitting cells release local regulators that influence cells in the local vicinity. One class of local regulators in animals, growth factors, includes compounds that stimulate nearby target cells to grow and multipl ...
... In other cases, messenger molecules are secreted by the signaling cell. Some transmitting cells release local regulators that influence cells in the local vicinity. One class of local regulators in animals, growth factors, includes compounds that stimulate nearby target cells to grow and multipl ...
ap® biology 2013 scoring guidelines
... Question 8 asks students to use a model of a hormone-signaling pathway to explain how extracellular signals are converted to specific cellular responses. Students were presented with a visual representation of a generalized hormone-signaling pathway and asked to use the representation to explain the ...
... Question 8 asks students to use a model of a hormone-signaling pathway to explain how extracellular signals are converted to specific cellular responses. Students were presented with a visual representation of a generalized hormone-signaling pathway and asked to use the representation to explain the ...
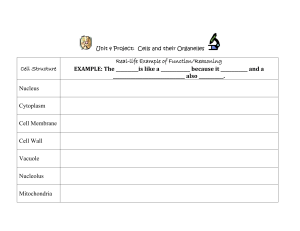
Vacuoles
... Keeps harmful materials away from cell Holds cell waste Stores protein for seeds Lets plants have leaves and flowers because of the high pressure in the cell • Vacuoles are found in plant and fungi cells ...
... Keeps harmful materials away from cell Holds cell waste Stores protein for seeds Lets plants have leaves and flowers because of the high pressure in the cell • Vacuoles are found in plant and fungi cells ...
Live Casino Roulette System
... Each cell in your body is as alive as you are. It “breathes,” takes in food, gets rid of wastes, reproduces, and in time, dies. Cells have different shapes, according to the work they do. Cells might look like cubes, rods, snowflakes, or even blobs of jelly. Every cell’s outer layer is a thin skin c ...
... Each cell in your body is as alive as you are. It “breathes,” takes in food, gets rid of wastes, reproduces, and in time, dies. Cells have different shapes, according to the work they do. Cells might look like cubes, rods, snowflakes, or even blobs of jelly. Every cell’s outer layer is a thin skin c ...
PARTS OF THE CELL CELL ORGANELLES
... NUCLEUS: controls most cell processes and contains DNA (code for all proteins and other molecules made by cells) ...
... NUCLEUS: controls most cell processes and contains DNA (code for all proteins and other molecules made by cells) ...
Can You Find it in Your Binder?
... In animal cells glucose molecules are stored in long chains called __________________. starch ...
... In animal cells glucose molecules are stored in long chains called __________________. starch ...
Ch 3 Check Your Progress Answers BC Biology 12 3.1 p 67 1
... peripheral proteins: structural; they help stabilize and shape the plasma membrane and play a role in signaling pathways integral proteins: determine a membrane’s specific functions 2. Distinguish between the roles of the various integral proteins in the plasma membrane identify pictures on page 82 ...
... peripheral proteins: structural; they help stabilize and shape the plasma membrane and play a role in signaling pathways integral proteins: determine a membrane’s specific functions 2. Distinguish between the roles of the various integral proteins in the plasma membrane identify pictures on page 82 ...
2nd Nine Weeks Exam Study Guide - Mr. Barger
... 21. The _______________________is the cell structure that contains the cell’s genetic material and controls the cell’s activities. 22. __________________________ are a type of cell that contains a nucleus, specialized organelles and genetic material. 23. ________________________ are organisms that a ...
... 21. The _______________________is the cell structure that contains the cell’s genetic material and controls the cell’s activities. 22. __________________________ are a type of cell that contains a nucleus, specialized organelles and genetic material. 23. ________________________ are organisms that a ...
WHAT LIMITS CELL SIZE
... DIFFUSION: Diffusion is a fast and efficient process over short distances, however becomes slow and inefficient as distance increases Ex: mitochondria at center of very large cell – can’t get necessary nutrients from diffusion ...
... DIFFUSION: Diffusion is a fast and efficient process over short distances, however becomes slow and inefficient as distance increases Ex: mitochondria at center of very large cell – can’t get necessary nutrients from diffusion ...
Slide 1
... 4. In the cell membrane model shown below, the molecules which move large molecules into and out of the cell are known as — A cholesterol B proteins C lipids D carbohydrates ...
... 4. In the cell membrane model shown below, the molecules which move large molecules into and out of the cell are known as — A cholesterol B proteins C lipids D carbohydrates ...
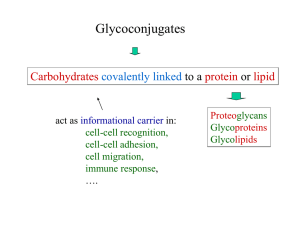
Bacterial Cell Walls Contain Peptidoglycans
... • Some are partially dependent • Others are not dependent on glycans • Some are glycan-dependent in one cell type but not in another • Some glycosylation sites are more important than others – Aid in certain sorting events • In later secretory pathway of glycoproteins in Golgi – Structural features ...
... • Some are partially dependent • Others are not dependent on glycans • Some are glycan-dependent in one cell type but not in another • Some glycosylation sites are more important than others – Aid in certain sorting events • In later secretory pathway of glycoproteins in Golgi – Structural features ...
Model Description Sheet
... with G proteins to activate a signaling cascade that leads to downstream effects including the modulation of various ion channels. The GABAB receptor is a dimer composed of two different subunits (GBR1 and GBR2), each with 7 helices within the membrane and an extracellular domain that binds GABA. On ...
... with G proteins to activate a signaling cascade that leads to downstream effects including the modulation of various ion channels. The GABAB receptor is a dimer composed of two different subunits (GBR1 and GBR2), each with 7 helices within the membrane and an extracellular domain that binds GABA. On ...
module 2 2.1.5 biological membranes student version
... Factors that affect membrane structure - Temperature ...
... Factors that affect membrane structure - Temperature ...
Answers for extension worksheet – Chapter 2
... round organelle, 25 nm in diameter, consisting of RNA and protein ...
... round organelle, 25 nm in diameter, consisting of RNA and protein ...
Part 1: True/False
... C. Waking up in the middle of the night and writing unintelligible notes to himself D. Showing that 'stuff' dripping from the vagus nerve slows down the heart <––– E. Showing that heartbeat is controlled by vagus nerve 15. Neuropeptide Y is a peptide neurotransmitter. What can you say about this pep ...
... C. Waking up in the middle of the night and writing unintelligible notes to himself D. Showing that 'stuff' dripping from the vagus nerve slows down the heart <––– E. Showing that heartbeat is controlled by vagus nerve 15. Neuropeptide Y is a peptide neurotransmitter. What can you say about this pep ...
Cellular compartmentalization
... Here is an illustration of how proteins targeted to the mitochondria are delivered. First the protein must carry the appropriate signal sequence. Then, it attaches to a receptor protein on the outer membrane. This complex diffuses until it reaches a contact site, where it is treaded through both ch ...
... Here is an illustration of how proteins targeted to the mitochondria are delivered. First the protein must carry the appropriate signal sequence. Then, it attaches to a receptor protein on the outer membrane. This complex diffuses until it reaches a contact site, where it is treaded through both ch ...
Types of Cells and Cell Size
... Within the plasma membrane, these nutrients and wastes move around by diffusion. Diffusion is fast and efficient over short distances Diffusion is slow and inefficient with larger distances. ...
... Within the plasma membrane, these nutrients and wastes move around by diffusion. Diffusion is fast and efficient over short distances Diffusion is slow and inefficient with larger distances. ...
LIFE CELLS
... • Have a cell membrane, cell wall • Three types of RNA polymerases (like eukarya) • May be extremophiles • Shape and size similar to bacteria (coccus/rod) • Single loop (plasmid) DNA, no nucleus EUKARYA: • Cytoplasm containing salts, minerals etc. • Nucleus= control centre, with nucleolus, nu ...
... • Have a cell membrane, cell wall • Three types of RNA polymerases (like eukarya) • May be extremophiles • Shape and size similar to bacteria (coccus/rod) • Single loop (plasmid) DNA, no nucleus EUKARYA: • Cytoplasm containing salts, minerals etc. • Nucleus= control centre, with nucleolus, nu ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.