1 - Website of Neelay Gandhi
... Due to Gram (-) bacteria Also b/o Gram (+) A. Ligand Any mol. that binds to receptor Some specialized Different adhesions expressed @ different times Bacteria can adhere to: Lipid Bilayer Cell Surface Receptors Indirectly (host molecules bound to surface) Types: ...
... Due to Gram (-) bacteria Also b/o Gram (+) A. Ligand Any mol. that binds to receptor Some specialized Different adhesions expressed @ different times Bacteria can adhere to: Lipid Bilayer Cell Surface Receptors Indirectly (host molecules bound to surface) Types: ...
So why do cells need to communicate?
... receptors / Heterotrimeric G proteins - many seven pass receptors with unknown number of ligands / hormones - all receptors act through G proteins ...
... receptors / Heterotrimeric G proteins - many seven pass receptors with unknown number of ligands / hormones - all receptors act through G proteins ...
6 per page - University of San Diego Home Pages
... receptors / Heterotrimeric G proteins - many seven pass receptors with unknown number of ligands / hormones - all receptors act through G proteins ...
... receptors / Heterotrimeric G proteins - many seven pass receptors with unknown number of ligands / hormones - all receptors act through G proteins ...
Fundamentals of Cell Biology
... networks – Cell-signaling molecules transmit information between cells – Intracellular signaling proteins propagate signals within a cell – A brief look at some common signaling ...
... networks – Cell-signaling molecules transmit information between cells – Intracellular signaling proteins propagate signals within a cell – A brief look at some common signaling ...
M001 Signalling to the translation initiation machinery Nahum
... activity is also controlled by phosphorylation of 4E-BPs (eIF4Ebinding proteins). 4E-BPs repress cap-dependent translation by binding to eIF4E. Upon their phosphorylation, 4E-BPs dissociate from eIF4E. The signalling pathway that leads to phosphorylation of 4E-BPs is the PI3K pathway. The mammalian ...
... activity is also controlled by phosphorylation of 4E-BPs (eIF4Ebinding proteins). 4E-BPs repress cap-dependent translation by binding to eIF4E. Upon their phosphorylation, 4E-BPs dissociate from eIF4E. The signalling pathway that leads to phosphorylation of 4E-BPs is the PI3K pathway. The mammalian ...
File
... 18. What does the Golgi apparatus look like? Stacks of flattened balloons 19. What is this organelles main function? Stores proteins and puts them into packages 20. Define vesicle. Packages / bags that carry protein molecules 21. Fg 4. What is occurring? Vesicles containing packages of protein are b ...
... 18. What does the Golgi apparatus look like? Stacks of flattened balloons 19. What is this organelles main function? Stores proteins and puts them into packages 20. Define vesicle. Packages / bags that carry protein molecules 21. Fg 4. What is occurring? Vesicles containing packages of protein are b ...
Carbohydrate: an organic molecule that provides energy for the cell
... Hypertonic: this occurs when the solute concentration is more outside than inside of the cell. Diffusion: the movement of “anything” from high to low concentrations. Osmosis: the movement of water molecules from high to low concentrations. Concentration Gradient: the difference between concentration ...
... Hypertonic: this occurs when the solute concentration is more outside than inside of the cell. Diffusion: the movement of “anything” from high to low concentrations. Osmosis: the movement of water molecules from high to low concentrations. Concentration Gradient: the difference between concentration ...
Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
... It produces tRNA molecules with their CCA 3' ends covalently linked to an amino acid Each tRNA is aminoacylated(or charged) with a specific amino acid by an aminoacyl tRNA synthase. There is normally a single aminoacyl tRNA synthetase for each amino acid, despite the fact that there can be more than ...
... It produces tRNA molecules with their CCA 3' ends covalently linked to an amino acid Each tRNA is aminoacylated(or charged) with a specific amino acid by an aminoacyl tRNA synthase. There is normally a single aminoacyl tRNA synthetase for each amino acid, despite the fact that there can be more than ...
Access Slides - Science Signaling
... (2000). Crystal structure of rhodopsin: A G protein-coupled receptor. Science 289 (5480):739-745. ...
... (2000). Crystal structure of rhodopsin: A G protein-coupled receptor. Science 289 (5480):739-745. ...
TAKS Obj 2 -BIOLOGY
... that have experienced years of sufficient rainfall, the annual rings of trees that have experienced a dry period will — These would F be softer indicate G grow at a faster rate more water, not less H be thinner J photosynthesize at a faster rate ...
... that have experienced years of sufficient rainfall, the annual rings of trees that have experienced a dry period will — These would F be softer indicate G grow at a faster rate more water, not less H be thinner J photosynthesize at a faster rate ...
Antibodies - Cloudfront.net
... • Two common classes are the IgM (immunoglobulins in mammals) and Gamma Globulins or IgG . • Provide most of the specific immunity against bacteria and viruses in extracellular fluid. • IgE are antibodies involved with allergic responses. • Mast Cells and Histamine ...
... • Two common classes are the IgM (immunoglobulins in mammals) and Gamma Globulins or IgG . • Provide most of the specific immunity against bacteria and viruses in extracellular fluid. • IgE are antibodies involved with allergic responses. • Mast Cells and Histamine ...
Chapter 4: A Tour of the Cell
... electron microscopes (TEM) are another type of very powerful microscopes. What are they used for, and how many times is the TEM in the book magnified? (Figure 4.2) 60,000X 5. Did prokaryotic or eukaryotic cells appear on Earth first? Prokaryotic cells 6. How does DNA control the cell (if it remains ...
... electron microscopes (TEM) are another type of very powerful microscopes. What are they used for, and how many times is the TEM in the book magnified? (Figure 4.2) 60,000X 5. Did prokaryotic or eukaryotic cells appear on Earth first? Prokaryotic cells 6. How does DNA control the cell (if it remains ...
Monkemeier - Madison Public Schools
... a. This is the outer boundary of a bacteria (prokaryote). It provides structure and support. b. This is the area in the cytoplasm that contains the chromosome (DNA) c. This is the only membrane that the bacteria (prokaryote) is allowed to have. It lies just inside the cell wall. d. This is the fluid ...
... a. This is the outer boundary of a bacteria (prokaryote). It provides structure and support. b. This is the area in the cytoplasm that contains the chromosome (DNA) c. This is the only membrane that the bacteria (prokaryote) is allowed to have. It lies just inside the cell wall. d. This is the fluid ...
Relationship between mutation and resistance to fluoroquinolones
... The development of single cells to a functional organ and finally a complete organism is an amazing interplay of numerous factors. Since their identification, a class of proteins called basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) proteins has been found to be involved in various developmental processes. Generally ...
... The development of single cells to a functional organ and finally a complete organism is an amazing interplay of numerous factors. Since their identification, a class of proteins called basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) proteins has been found to be involved in various developmental processes. Generally ...
Chapter 10 Section 3 Notes Answer Key
... 1. contains instructions for making specific proteins 2. RNA carries the codes for making proteins to the nucleus for the ribosomes in the cytoplasm a. Messenger RNA carries the code that directs the order in which the amino acid bond. b. Ribosomal RNA makes up ribosomes where proteins are built c. ...
... 1. contains instructions for making specific proteins 2. RNA carries the codes for making proteins to the nucleus for the ribosomes in the cytoplasm a. Messenger RNA carries the code that directs the order in which the amino acid bond. b. Ribosomal RNA makes up ribosomes where proteins are built c. ...
pruitt_ppt_ch04b
... Effect of osmosis on cells in various solutions • Hypotonic solutions – High concentration of water in extracellular fluid compared to inside the cells causes net movement of water into the cell. – Results in increased cell size. – Can cause cell to ...
... Effect of osmosis on cells in various solutions • Hypotonic solutions – High concentration of water in extracellular fluid compared to inside the cells causes net movement of water into the cell. – Results in increased cell size. – Can cause cell to ...
Omnis cellula e cellula, that each cell derives from a pre
... 3.5 billion years ago. Since that time, cells have continuously divided. At first they existed as single cells. Over time they got together and formed ever more complex organisms, culminating in man. Each of us starts life by the joining of one cell from our father and one cell from our mother. Like ...
... 3.5 billion years ago. Since that time, cells have continuously divided. At first they existed as single cells. Over time they got together and formed ever more complex organisms, culminating in man. Each of us starts life by the joining of one cell from our father and one cell from our mother. Like ...
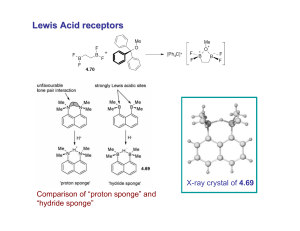
Lewis Acid receptors
... In real-world applications, non-competitive counter-ions are not generally encountered and hence inter-ion competition can be significant. Also, salts rarely, if ever, exist as separate ions unless the medium is highly solvating. Therefore, the most effective ionic recognition strategy is to design ...
... In real-world applications, non-competitive counter-ions are not generally encountered and hence inter-ion competition can be significant. Also, salts rarely, if ever, exist as separate ions unless the medium is highly solvating. Therefore, the most effective ionic recognition strategy is to design ...
CARBOHYDRATES, lipids and proteins handout
... Composed of C, H, O but ratio is less predictable than in carbohydrates – neutral fats, phospholipids and steroids Primary use = fuel for production of ATP and fuel storage Secondary use = structural components of the cell membrane and hormones Some examples: triglycerides = #1 most common l ...
... Composed of C, H, O but ratio is less predictable than in carbohydrates – neutral fats, phospholipids and steroids Primary use = fuel for production of ATP and fuel storage Secondary use = structural components of the cell membrane and hormones Some examples: triglycerides = #1 most common l ...
10 E all qs
... Q2: What is facilitated diffusion? A2: The movement of molecules from an area of high to low concentration with the help of channel protein. Q3: What is simple diffusion? A3: The movement of molecules from an area of high to low concentration through the selectively permeable membrane. Q4: What is a ...
... Q2: What is facilitated diffusion? A2: The movement of molecules from an area of high to low concentration with the help of channel protein. Q3: What is simple diffusion? A3: The movement of molecules from an area of high to low concentration through the selectively permeable membrane. Q4: What is a ...
The “brains” of the cell, that directs cell activities and contains
... The “brains” of the cell, that directs cell activities and contains genetic material called chromosomes made of DNA ...
... The “brains” of the cell, that directs cell activities and contains genetic material called chromosomes made of DNA ...
Name - DiBiasioScience
... a. cytoplasm and ribosomes c. microtubules and microfilaments b. nucleolus and nucleus d. chromosomes _____ 8. Which structure makes proteins using coded instructions that come from the nucleus? a. Golgi apparatus c. vacuole b. mitochondrion d. ribosome _____ 9. Which organelle would you expect to f ...
... a. cytoplasm and ribosomes c. microtubules and microfilaments b. nucleolus and nucleus d. chromosomes _____ 8. Which structure makes proteins using coded instructions that come from the nucleus? a. Golgi apparatus c. vacuole b. mitochondrion d. ribosome _____ 9. Which organelle would you expect to f ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.