Human Biology 303 Exam # 1 - Human Physiology and Diagnosis.
... 10) Cellular structures that function in movement and consist of numerous short hair-like extensions from the cell are called ________. 11) ________ is a metabolic process which creates ATP for the cell by the breakdown of glucose molecules in the cytoplasm. ...
... 10) Cellular structures that function in movement and consist of numerous short hair-like extensions from the cell are called ________. 11) ________ is a metabolic process which creates ATP for the cell by the breakdown of glucose molecules in the cytoplasm. ...
Cell Structure and Function Highlight Packet
... 1) _________________________________ 2) _________________________________ 3) _________________________________ 4) _________________________________ 5) _________________________________ 2. The main difference between the structure of the smooth ER versus the rough ER is that the rough ER has ________ ...
... 1) _________________________________ 2) _________________________________ 3) _________________________________ 4) _________________________________ 5) _________________________________ 2. The main difference between the structure of the smooth ER versus the rough ER is that the rough ER has ________ ...
Organelles: specialized subunits within a cell that have a specific
... • Form pockets around foreign materials and digest them • Engulf microscopic particles (Endocytosis) • Breakdown old organelles with enzymes • Garbage cleaners of the cell ...
... • Form pockets around foreign materials and digest them • Engulf microscopic particles (Endocytosis) • Breakdown old organelles with enzymes • Garbage cleaners of the cell ...
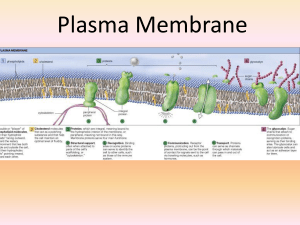
Plasma Membrane
... specific shapes exposed to the exterior that fit the shape of specific hormones 2. Enzymes – catalyze chemical reactions; may be on interior or exterior of the cell membrane; often grouped together for a chain reaction (called metabolic pathway) 3. Cell adhesion – proteins hook together to provide t ...
... specific shapes exposed to the exterior that fit the shape of specific hormones 2. Enzymes – catalyze chemical reactions; may be on interior or exterior of the cell membrane; often grouped together for a chain reaction (called metabolic pathway) 3. Cell adhesion – proteins hook together to provide t ...
Fates of Proteins in Cells
... rough ER before being attached to protein • Pro-oligosaccharides are assembled at the cytoplasmic surface of the rough ER – during this process they are anchored through bisphospate to a membrane lipid called dolichol. • The completed pro-oligosaccharide is then translocated to the luminal side of t ...
... rough ER before being attached to protein • Pro-oligosaccharides are assembled at the cytoplasmic surface of the rough ER – during this process they are anchored through bisphospate to a membrane lipid called dolichol. • The completed pro-oligosaccharide is then translocated to the luminal side of t ...
File
... share similar origin Prokaryotic cells engulfed by ancestors of eukaryotic cells Evidence: Double-membrane structure Have own ribosomes & DNA Reproduce independently within cell ...
... share similar origin Prokaryotic cells engulfed by ancestors of eukaryotic cells Evidence: Double-membrane structure Have own ribosomes & DNA Reproduce independently within cell ...
The G-Proteins - mustafaaltinisik.org.uk
... PLC also causes the influx of Ca++. Ca++ binds one of a family of Ca++ binding proteins (calmodulin). Ca++/calmodulin complex binds to yet other proteins and changes their functional activity. ...
... PLC also causes the influx of Ca++. Ca++ binds one of a family of Ca++ binding proteins (calmodulin). Ca++/calmodulin complex binds to yet other proteins and changes their functional activity. ...
medmicro4-weapons delivery – G+
... R = phosphodiester linked choline - chemically more stable than ester-linked D-Ala ...
... R = phosphodiester linked choline - chemically more stable than ester-linked D-Ala ...
Name Date ____ Period ___ #____ Parts of Prokaryotic
... RNA & protein FUNCTION: construction site for proteins CELL MEMBRANE or PLASMA MEMBRANE Made mainly of phosphate and lipids HYDROPHOBIC “tails” of phospholipids make molecules line up as a LIPID bilayer with POLAR heads facing out and NON-POLAR tails facing in Proteins attached to surface (inside or ...
... RNA & protein FUNCTION: construction site for proteins CELL MEMBRANE or PLASMA MEMBRANE Made mainly of phosphate and lipids HYDROPHOBIC “tails” of phospholipids make molecules line up as a LIPID bilayer with POLAR heads facing out and NON-POLAR tails facing in Proteins attached to surface (inside or ...
Stellingen behorende bij het proefschrift Liprin
... Liprin-alpha proteins regulate neuronal development and synapse function 1. All liprin proteins are not created equal. 2. Connecting cell adhesion molecules to the neuronal cytoskeleton is critical for axon growth and branching. 3. Some proteins function by disappearing rather than arriving. 4. Alth ...
... Liprin-alpha proteins regulate neuronal development and synapse function 1. All liprin proteins are not created equal. 2. Connecting cell adhesion molecules to the neuronal cytoskeleton is critical for axon growth and branching. 3. Some proteins function by disappearing rather than arriving. 4. Alth ...
Chapter 3 (part 2) – Protein Function
... • Enzymes and bound ligand go through a number of intermediate forms of different geometry. They are all called transition states. • The energy that it takes to get to the most unstable transition state is called the activation energy. • Enzymes speed reactions by selectively stabilizing the transi ...
... • Enzymes and bound ligand go through a number of intermediate forms of different geometry. They are all called transition states. • The energy that it takes to get to the most unstable transition state is called the activation energy. • Enzymes speed reactions by selectively stabilizing the transi ...
The Cell Membrane
... • Floating around in the cell membrane are different kinds of proteins. • Generally, these proteins structurally fall into three categories. ...
... • Floating around in the cell membrane are different kinds of proteins. • Generally, these proteins structurally fall into three categories. ...
Molecular Identification and the Immunolocalization of Purinergic Signaling Receptors in... Mammalian Vomeronasal Organ
... Information about the external world is conveyed through the nervous system via specialized sensory organs such as the vomeronasal organ (VNO). The VNO is crucial for pheromone detection and the regulation of social behavior in many mammals. Recent research has shown that purinergic signaling pathwa ...
... Information about the external world is conveyed through the nervous system via specialized sensory organs such as the vomeronasal organ (VNO). The VNO is crucial for pheromone detection and the regulation of social behavior in many mammals. Recent research has shown that purinergic signaling pathwa ...
Parts of a Eukaryotic Cell - Downey Unified School District
... Are located on cell membrane: on the outside of the cell and ...
... Are located on cell membrane: on the outside of the cell and ...
Chapter 16
... Activating mutations in growth factor receptors or their signaling pathways commonly are associated with cancers. Transforming growth factor ß (TGFß) plays widespread roles in regulating development in both vertebrates and invertebrates. Despite their names, all three types of human TGFßs exert anti ...
... Activating mutations in growth factor receptors or their signaling pathways commonly are associated with cancers. Transforming growth factor ß (TGFß) plays widespread roles in regulating development in both vertebrates and invertebrates. Despite their names, all three types of human TGFßs exert anti ...
Robertson-1
... analytical techniques, scientists can conclude whether or not a certain gene is being expressed. ...
... analytical techniques, scientists can conclude whether or not a certain gene is being expressed. ...
cell structure
... • Theme: Molecular Organization ----> Structure ----> Function • Significant molecules in cells, their general structure and function • Major cell structural features • How structure determines function • Biochemistry-only identification of major molecules and forces which drive reactions and determ ...
... • Theme: Molecular Organization ----> Structure ----> Function • Significant molecules in cells, their general structure and function • Major cell structural features • How structure determines function • Biochemistry-only identification of major molecules and forces which drive reactions and determ ...
Characteristic for receptor cells
... directly influencing ion channels in membrane of receptor • Weak acid vinegar ionize in water to produce protons (H+) and anions (- ions), in mud puppy, H+ ions block specific type of K+ channel in receptor • For salty substances like table salt Na+ and other cations act as stimuli, Na+ ions of salt ...
... directly influencing ion channels in membrane of receptor • Weak acid vinegar ionize in water to produce protons (H+) and anions (- ions), in mud puppy, H+ ions block specific type of K+ channel in receptor • For salty substances like table salt Na+ and other cations act as stimuli, Na+ ions of salt ...
Cellular Biology Script Slide 1. For this first unit we start by reviewing
... must be available for the brain, does not move across the cell membrane of most other cells. It needs a door to be opened by insulin and then carried into the cell. The membrane protein is also involved in cellular communication with its numerous receptors to receive “the text messages” sent via mol ...
... must be available for the brain, does not move across the cell membrane of most other cells. It needs a door to be opened by insulin and then carried into the cell. The membrane protein is also involved in cellular communication with its numerous receptors to receive “the text messages” sent via mol ...
cell surface receptors
... Examples of these: Ligands in ECM – collagen, fibronectin, and laminin Important for cellular processes including: cell adhesion, cell migration, signal transduction, and cell growth/death ...
... Examples of these: Ligands in ECM – collagen, fibronectin, and laminin Important for cellular processes including: cell adhesion, cell migration, signal transduction, and cell growth/death ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.