Slide ()
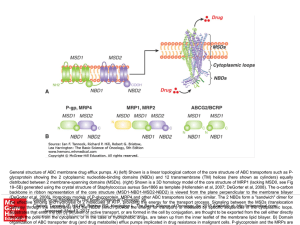
... General structure of ABC membrane drug efflux pumps. A) (left) Shown is a linear topological cartoon of the core structure of ABC transporters such as Pglycoprotein showing the 2 cytoplasmic nucleotide-binding domains (NBDs) and 12 transmembrane (TM) helices (here shown as cylinders) equally distrib ...
... General structure of ABC membrane drug efflux pumps. A) (left) Shown is a linear topological cartoon of the core structure of ABC transporters such as Pglycoprotein showing the 2 cytoplasmic nucleotide-binding domains (NBDs) and 12 transmembrane (TM) helices (here shown as cylinders) equally distrib ...
Guanide and biguanide compounds synthesized by the Teintze lab have... Amanda Kelley: Chemistry & Biochemistry
... receptor which is used by X4 strains of HIV to enter cells and is involved in cancer metastasis. Therefore, they may be able to inhibit both HIV infection and cancer metastasis. When the chemokine SDF-1 binds the CXCR4 receptor, it activates an intracellular signal transduction pathway triggering ch ...
... receptor which is used by X4 strains of HIV to enter cells and is involved in cancer metastasis. Therefore, they may be able to inhibit both HIV infection and cancer metastasis. When the chemokine SDF-1 binds the CXCR4 receptor, it activates an intracellular signal transduction pathway triggering ch ...
Where is DNA in prokaryotes
... 4. List 4 kinds of organic molecules and their building blocks. Examples of these molecules 5. Who was one of the first persons to observe live cells? 6. List all statements of the cell theory 7. Order of structures in living things, from the simplest to the most complex. Examples of organs 8. Funct ...
... 4. List 4 kinds of organic molecules and their building blocks. Examples of these molecules 5. Who was one of the first persons to observe live cells? 6. List all statements of the cell theory 7. Order of structures in living things, from the simplest to the most complex. Examples of organs 8. Funct ...
the-cell-factory Excellent
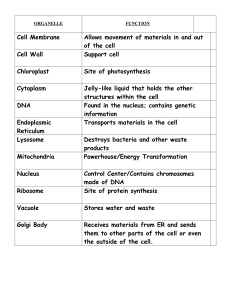
... and other materials from the ER for STORAGE or SECRETION outside the cell Proteins are “shipped” to final destination ...
... and other materials from the ER for STORAGE or SECRETION outside the cell Proteins are “shipped” to final destination ...
Cell Cycle
... Internal damage to cell causes Bcl-2 protein to release Apaf-1 Apoptotic stimulus - Bcl-x (a related protein Bax) penetrates mitochondrial membranes causing cytochrome c to be released Cytochrome C interacts with Apaf-1; both bind to iniator caspase, caspase 9 ...
... Internal damage to cell causes Bcl-2 protein to release Apaf-1 Apoptotic stimulus - Bcl-x (a related protein Bax) penetrates mitochondrial membranes causing cytochrome c to be released Cytochrome C interacts with Apaf-1; both bind to iniator caspase, caspase 9 ...
Notes0112
... Taste receptors synapse with dendritic elements of the primary afferent neurons of the gustratory pathway, causing the neurons to fire in response to appropriate stimuli above threshold levels These afferent fibres arise from cell bodies within three cranial nerve ganglia Afferent fibres within the ...
... Taste receptors synapse with dendritic elements of the primary afferent neurons of the gustratory pathway, causing the neurons to fire in response to appropriate stimuli above threshold levels These afferent fibres arise from cell bodies within three cranial nerve ganglia Afferent fibres within the ...
The Cell Theory
... 2. In the form of DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) 3. DNA is universal for all cells, an all living things - evidence of common ancestry 4. Chromatin is the complex of proteins and DNA, it condenses into chromosomes before cell division Cytoplasm (aka cytosol) 1. inside plasma membrane 2. contains water, ...
... 2. In the form of DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) 3. DNA is universal for all cells, an all living things - evidence of common ancestry 4. Chromatin is the complex of proteins and DNA, it condenses into chromosomes before cell division Cytoplasm (aka cytosol) 1. inside plasma membrane 2. contains water, ...
Name: Date: 1. The is the source of most of the cellular energy. A
... 15. The _____________ functions to package molecules into vesicles that can be transported out of a cell. A) ...
... 15. The _____________ functions to package molecules into vesicles that can be transported out of a cell. A) ...
Neuron Structure and Function
... • Both these signaling cascades are used in multiple biological systems • In the nervous system neurotransmitter binding to specific metabotropic receptors can trigger these cascades • Photoreceptor and olfactory neurons also use parts of these cascades for their sensory transduction ...
... • Both these signaling cascades are used in multiple biological systems • In the nervous system neurotransmitter binding to specific metabotropic receptors can trigger these cascades • Photoreceptor and olfactory neurons also use parts of these cascades for their sensory transduction ...
1. The drawing shows part of a root hair cell. (a) Use words from the
... Name the process by which these gases move into and out of the cell. ...
... Name the process by which these gases move into and out of the cell. ...
Cell Description #1 A cell is enclosed by a plasma membrane, which
... synthesizing selected molecules and then processing, sorting, and directing them to their proper locations. In addition, plant cells contain chloroplasts, which are responsible for photosynthesis, whereby the energy of sunlight is used to convert molecules of carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O) int ...
... synthesizing selected molecules and then processing, sorting, and directing them to their proper locations. In addition, plant cells contain chloroplasts, which are responsible for photosynthesis, whereby the energy of sunlight is used to convert molecules of carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O) int ...
Name - St. Rose of Lima School
... Which organelles are common to both plant and animal cells? Why is the vacuole larger in the plant cell? _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ ...
... Which organelles are common to both plant and animal cells? Why is the vacuole larger in the plant cell? _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ ...
Chapter 5 Section 2
... These are used in chemical reactions in the cytoplasm Found in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes Most common organelle ...
... These are used in chemical reactions in the cytoplasm Found in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes Most common organelle ...
Virtual Cell Worksheet
... 5. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) is a series of double membranes that loop back and forth between the cell membrane and the nucleus. These membranes fill the cytoplasm but you cannot see them because they are very transparent. The rough E.R. has ribosomes attached to it. This gives it its texture. Thes ...
... 5. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) is a series of double membranes that loop back and forth between the cell membrane and the nucleus. These membranes fill the cytoplasm but you cannot see them because they are very transparent. The rough E.R. has ribosomes attached to it. This gives it its texture. Thes ...
The Cell Membrane
... Controls what enters and leaves the cell Allows some things in and keeps others out ...
... Controls what enters and leaves the cell Allows some things in and keeps others out ...
Unit 2 Vocabulary:
... The movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration The diffusion of water across a cell membrane A cell membrane that only permits certain molecules to enter or leave the cell ...
... The movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration The diffusion of water across a cell membrane A cell membrane that only permits certain molecules to enter or leave the cell ...
Cell Processes Study Guide
... Carbon Dioxide + Water + Sunlight -------- Glucose + Oxygen Cellular Respiration – this process takes place in the mitochondrion of the cell Glucose + Oxygen ---------Carbon Dioxide + Water + ATP (useable cell energy) Know the “chemical” representations for each of the chemicals in BOTH equations Fe ...
... Carbon Dioxide + Water + Sunlight -------- Glucose + Oxygen Cellular Respiration – this process takes place in the mitochondrion of the cell Glucose + Oxygen ---------Carbon Dioxide + Water + ATP (useable cell energy) Know the “chemical” representations for each of the chemicals in BOTH equations Fe ...
Ch. 7 part 2 (PM and Osmosis)
... specific channels allow specific material in & out H2O channel, salt channel, sugar channel, etc. ...
... specific channels allow specific material in & out H2O channel, salt channel, sugar channel, etc. ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.