Membrane-bound organelles and a nucleus that contains DNA
... Diffusion is the process that moves molecules from HIGH concentration to LOW concentration Receptor Protein ...
... Diffusion is the process that moves molecules from HIGH concentration to LOW concentration Receptor Protein ...
Cell Size and Shape
... Each cell has a plasma membrane, a boundary between its interior and the outside environment The interior consists of cytoplasm and an innermost region of DNA ...
... Each cell has a plasma membrane, a boundary between its interior and the outside environment The interior consists of cytoplasm and an innermost region of DNA ...
Life Science Notes – Diffusion/Osmosis/Active Transport
... Molecules are always moving. They bump into each other and spread apart. ...
... Molecules are always moving. They bump into each other and spread apart. ...
Free sample of
... C) transforms cellular energy D) initiates aerobic metabolism 2. Although energy is not made in mitochondria, they are known as the “power plants” of the cell because they: A) contain RNA for protein synthesis. B) utilize glycolysis for oxidative energy. C) extract energy from organic compounds. D) ...
... C) transforms cellular energy D) initiates aerobic metabolism 2. Although energy is not made in mitochondria, they are known as the “power plants” of the cell because they: A) contain RNA for protein synthesis. B) utilize glycolysis for oxidative energy. C) extract energy from organic compounds. D) ...
Chloroplasts
... In the beginning, there were Cells… • Bacteria are thought to be the earliest forms of life on the planet. • Simple life flourished in tidal pools near the sea. • Water was warm and full of nutrients. ...
... In the beginning, there were Cells… • Bacteria are thought to be the earliest forms of life on the planet. • Simple life flourished in tidal pools near the sea. • Water was warm and full of nutrients. ...
- cK-12
... a) Molecules flow down the concentration gradient. b) Molecules flow against the concentration gradient. c) From an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. d) none of the above 7. Which best describes an hypertonic solution? a) The solution outside of the cell has a lower concent ...
... a) Molecules flow down the concentration gradient. b) Molecules flow against the concentration gradient. c) From an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. d) none of the above 7. Which best describes an hypertonic solution? a) The solution outside of the cell has a lower concent ...
Eukaryotic Cells
... • Lipids are fat and cholesterol that do not dissolve in water • Phospholipids contains lipids and phosphorous • Cell membrane has two layers of phospholipids • Hydrophophic “water fearing” • Hydrophillic “water loving ...
... • Lipids are fat and cholesterol that do not dissolve in water • Phospholipids contains lipids and phosphorous • Cell membrane has two layers of phospholipids • Hydrophophic “water fearing” • Hydrophillic “water loving ...
Slide 1
... accumulating in the cell thereby preventing excess osmosis into the cell, which could potentially cause the cell to burst. • b. The pump maintains the concentration gradients of Na+ and K+ across the cell membrane, which many cells use to help in the transport of other substances, such as glucose ac ...
... accumulating in the cell thereby preventing excess osmosis into the cell, which could potentially cause the cell to burst. • b. The pump maintains the concentration gradients of Na+ and K+ across the cell membrane, which many cells use to help in the transport of other substances, such as glucose ac ...
Name Bozeman – Evolutionary Significance of Cell Communication
... 2. How does cell communication exist between single celled organisms like bacteria? 3. How does cell communication exist within a multicellular organism? 4. Why is it significant that signal transduction pathways are almost identical in both single-celled and multicellular organisms? How does this r ...
... 2. How does cell communication exist between single celled organisms like bacteria? 3. How does cell communication exist within a multicellular organism? 4. Why is it significant that signal transduction pathways are almost identical in both single-celled and multicellular organisms? How does this r ...
Cell Division and Mitosis
... All organisms are composed of cells The cell is the basic unit of life All cells have a double-layered plasma membrane Membranes consist largely of phospholipid and protein molecules ...
... All organisms are composed of cells The cell is the basic unit of life All cells have a double-layered plasma membrane Membranes consist largely of phospholipid and protein molecules ...
Cells overview - Appoquinimink High School
... • Packages and delivers proteins synthesized by ribosomes • Proteins arrive at this spot in vesicles, where glycoproteins are to be received ...
... • Packages and delivers proteins synthesized by ribosomes • Proteins arrive at this spot in vesicles, where glycoproteins are to be received ...
Study Guide – Body Systems - Fifth Grade: Ocean Knoll Read!
... 1. Osmosis is the diffusion of water across a membrane. 2. Organelles are structures that perform specific functions in a cell. 3. Diffusion is a process that spreads substances through a gas or liquid. 4. The cytoplasm is a thick fluid between the nucleus and cell membrane. 5. The nucleus is the ce ...
... 1. Osmosis is the diffusion of water across a membrane. 2. Organelles are structures that perform specific functions in a cell. 3. Diffusion is a process that spreads substances through a gas or liquid. 4. The cytoplasm is a thick fluid between the nucleus and cell membrane. 5. The nucleus is the ce ...
1.3 study guide - Peoria Public Schools
... Cell membranes include phospholipids and proteins. These proteins may be classified as integral or peripheral proteins. It is the hydrophobic and hydrophilic properties of phospholipids that maintain the structure of cell membranes. Functions of membrane proteins include hormone binding sites, ...
... Cell membranes include phospholipids and proteins. These proteins may be classified as integral or peripheral proteins. It is the hydrophobic and hydrophilic properties of phospholipids that maintain the structure of cell membranes. Functions of membrane proteins include hormone binding sites, ...
Lecture #3 Date
... No organelles with membranes Ribosomes: protein synthesis Plasma membrane (all cells); semi-permeable Cytoplasm/cytosol (all cells) ...
... No organelles with membranes Ribosomes: protein synthesis Plasma membrane (all cells); semi-permeable Cytoplasm/cytosol (all cells) ...
Name: Cell Biology Test #1: 50 points
... of a cell. Other hormones are produced in such small amounts that they would be unable to create changes in cellular function. Fro these hormones amplification of the extracellular message is made possible by causing intracellular enzymes to change their function. For example insulin stimulates a ty ...
... of a cell. Other hormones are produced in such small amounts that they would be unable to create changes in cellular function. Fro these hormones amplification of the extracellular message is made possible by causing intracellular enzymes to change their function. For example insulin stimulates a ty ...
Domain - Cells preassessment quesitons
... portion of the molecules that make up a cell membrane. The phospholipid molecules serve to • A help cells recognize each other • B allow glucose molecules into the cell • C prevent the passage of certain molecules into the cell • D line up amino acids for protein ...
... portion of the molecules that make up a cell membrane. The phospholipid molecules serve to • A help cells recognize each other • B allow glucose molecules into the cell • C prevent the passage of certain molecules into the cell • D line up amino acids for protein ...
Interphase: Chromosomes are doubled
... Spindle fibers appear Centrioles pulled to opposite ends of cell Crossing over ...
... Spindle fibers appear Centrioles pulled to opposite ends of cell Crossing over ...
Name
... 11. ________________________ has polar and non-polar parts and makes up the majority of the cell membrane. 12. The material that gets dissolved in a solution is called the ________________. 13. _________________ is the material that does the dissolving in a solution. 14. Identification (ID) tags tha ...
... 11. ________________________ has polar and non-polar parts and makes up the majority of the cell membrane. 12. The material that gets dissolved in a solution is called the ________________. 13. _________________ is the material that does the dissolving in a solution. 14. Identification (ID) tags tha ...
Chapter 3 Anatomy Notes
... Some cells have a free surface that is extensively folded to form many tiny, slender projections called microvilli Each microvillus is covered by the cell membrane and has a small amount of cytoplasm inside of it Microvilli are common in cells that absorb materials, such as cells of the small in ...
... Some cells have a free surface that is extensively folded to form many tiny, slender projections called microvilli Each microvillus is covered by the cell membrane and has a small amount of cytoplasm inside of it Microvilli are common in cells that absorb materials, such as cells of the small in ...
No Slide Title
... • 5. Some animal cells have _______ that store food, water, wastes, and other materials. • 6. Small structures that function as factories to produce proteins are ________ . • 7. Endoplasmic Reticulum are passageways that _____ proteins and other materials. ...
... • 5. Some animal cells have _______ that store food, water, wastes, and other materials. • 6. Small structures that function as factories to produce proteins are ________ . • 7. Endoplasmic Reticulum are passageways that _____ proteins and other materials. ...
Solution - Glencoe
... 5. contains the cell’s DNA and manages cell functions ______________________ chlorophyll 6. green pigment that traps light energy from the sun ______________________ organ 7. group of two or more tissues that perform an activity together ______________________ mitochondria 8. organelles in which foo ...
... 5. contains the cell’s DNA and manages cell functions ______________________ chlorophyll 6. green pigment that traps light energy from the sun ______________________ organ 7. group of two or more tissues that perform an activity together ______________________ mitochondria 8. organelles in which foo ...
What is the Chapter 4 Test Like
... o How do you calculate surface area to volume ratios? o What is the significance of surface area to volume ratios? o Is a small cell or a large cell more efficient? 2. Activity: The Cell Theory o What were the contributions of each of the timeline people? o Can you list the three parts of the cell t ...
... o How do you calculate surface area to volume ratios? o What is the significance of surface area to volume ratios? o Is a small cell or a large cell more efficient? 2. Activity: The Cell Theory o What were the contributions of each of the timeline people? o Can you list the three parts of the cell t ...
Slide ()
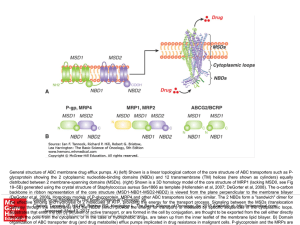
... General structure of ABC membrane drug efflux pumps. A) (left) Shown is a linear topological cartoon of the core structure of ABC transporters such as Pglycoprotein showing the 2 cytoplasmic nucleotide-binding domains (NBDs) and 12 transmembrane (TM) helices (here shown as cylinders) equally distrib ...
... General structure of ABC membrane drug efflux pumps. A) (left) Shown is a linear topological cartoon of the core structure of ABC transporters such as Pglycoprotein showing the 2 cytoplasmic nucleotide-binding domains (NBDs) and 12 transmembrane (TM) helices (here shown as cylinders) equally distrib ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.