Chapter 6 - MrsAllisonMagee
... nutrients and water must be able to get to all parts of the cell (low surface area to volume ratio) ...
... nutrients and water must be able to get to all parts of the cell (low surface area to volume ratio) ...
cell jeopardy
... The disc under the stage that adjusts the amount of light is the What is the diaphragm? ...
... The disc under the stage that adjusts the amount of light is the What is the diaphragm? ...
Neural stem cells
... Functions of membrane proteins • Selective transport of certain substances (as channels or active transport molecules). • Receptors binding to information-providing ligands (such as hormones) to transmit signals. ...
... Functions of membrane proteins • Selective transport of certain substances (as channels or active transport molecules). • Receptors binding to information-providing ligands (such as hormones) to transmit signals. ...
File
... o Nucleus contains DNA and is the control center for the cell; BOTH Function means What is the purpose or special job performed Structure mean – What it looks like Why are plant cells’ vacuoles larger than animal cells’? Plants don’t know when they will receive water, so they must store more than an ...
... o Nucleus contains DNA and is the control center for the cell; BOTH Function means What is the purpose or special job performed Structure mean – What it looks like Why are plant cells’ vacuoles larger than animal cells’? Plants don’t know when they will receive water, so they must store more than an ...
Fulltext PDF - Indian Academy of Sciences
... preprolactin carried a sequence of amino acids that targeted them to the ER mediated ...
... preprolactin carried a sequence of amino acids that targeted them to the ER mediated ...
organelles - Fillingham
... Centrosomes – near nucleus, region where where microtubules grow Centrioles – located within centrosomes, used during mitosis and meiosis ...
... Centrosomes – near nucleus, region where where microtubules grow Centrioles – located within centrosomes, used during mitosis and meiosis ...
Cell Organelle Functions part 1
... to be used inside & outside of cell a. packages proteins into VESICLES [small bubbles] 7. Lysosomes –BREAK DOWN wastes, food & old cell parts using enzymes 8. Vacuoles – pouch that STORES water, food & some wastes a. very LARGE in PLANT; small in animal cells 9.. Mitochondria – makes ENERGY (ATP) fo ...
... to be used inside & outside of cell a. packages proteins into VESICLES [small bubbles] 7. Lysosomes –BREAK DOWN wastes, food & old cell parts using enzymes 8. Vacuoles – pouch that STORES water, food & some wastes a. very LARGE in PLANT; small in animal cells 9.. Mitochondria – makes ENERGY (ATP) fo ...
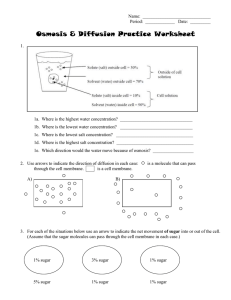
Diffusion, Osmosis, and Active Transport
... (Assume that the sugar molecules can pass through the cell membrane in each case.) ...
... (Assume that the sugar molecules can pass through the cell membrane in each case.) ...
Cell Structure Notes - Center Grove Schools
... Cytoplasm: Gelatin-like substance inside the cell. – Cytoskeleton: scaffolding-like structure in the cytoplasm which helps cell keep its shape. – In the cytoplasm, eukaryotic cells have organelles which help with cell life process. ...
... Cytoplasm: Gelatin-like substance inside the cell. – Cytoskeleton: scaffolding-like structure in the cytoplasm which helps cell keep its shape. – In the cytoplasm, eukaryotic cells have organelles which help with cell life process. ...
Cell Structure
... Scanning Tunneling Microscope – Uses needle-like probe to measure differences in voltage caused by electrons that leak from the surface – 3-D images – Living organisms can be viewed with this scope ...
... Scanning Tunneling Microscope – Uses needle-like probe to measure differences in voltage caused by electrons that leak from the surface – 3-D images – Living organisms can be viewed with this scope ...
CLASSIFYING LIVING THINGS
... Do you think each of the trillions of cells that are a part of you are either alive or once-living? Why? ...
... Do you think each of the trillions of cells that are a part of you are either alive or once-living? Why? ...
AP Midterm Review 09-10
... temperature. Such environments are thought to have been much more common on the primitive Earth. Thus, modern extremophiles survive only in places that their ancestors became adapted to long ago. Which of these is, consequently, a valid statement about modern extremophiles, assuming that their habit ...
... temperature. Such environments are thought to have been much more common on the primitive Earth. Thus, modern extremophiles survive only in places that their ancestors became adapted to long ago. Which of these is, consequently, a valid statement about modern extremophiles, assuming that their habit ...
cc-cf_saber_july-2016_1
... The messenger must bind to a receptor protein in or on its target cell to produce a response. CC3.1 Each messenger molecule can only bind to a specific receptor molecule. CC3.2 A cell can only respond to a messenger for which it has receptors. CC3.3 The solubility of the messenger determines the loc ...
... The messenger must bind to a receptor protein in or on its target cell to produce a response. CC3.1 Each messenger molecule can only bind to a specific receptor molecule. CC3.2 A cell can only respond to a messenger for which it has receptors. CC3.3 The solubility of the messenger determines the loc ...
Cell Wall
... a slimy, sticky substance that traps dust s and some microbes in the air pathways. Nucleus: the part of the cell that contains genetic information in the form of chromosomes. The nucleus controls the activities of the cell. Nitrate: Used to make proteins. Chemical fertilisers often supply nitrate io ...
... a slimy, sticky substance that traps dust s and some microbes in the air pathways. Nucleus: the part of the cell that contains genetic information in the form of chromosomes. The nucleus controls the activities of the cell. Nitrate: Used to make proteins. Chemical fertilisers often supply nitrate io ...
Cell junctions
... Above: gap junctions connecting the cytoplasm of two neighbouring animal cells Gap junctions are extremely important for coordinating cells in a tissue and tissues requiring precise coordination have lots of gap junctions, for example, cardiac muscle, which must beat in synchrony, or the smooth musc ...
... Above: gap junctions connecting the cytoplasm of two neighbouring animal cells Gap junctions are extremely important for coordinating cells in a tissue and tissues requiring precise coordination have lots of gap junctions, for example, cardiac muscle, which must beat in synchrony, or the smooth musc ...
LS1a Problem Set #2
... 1. (16 points) The Her2 receptor is a receptor tyrosine kinase, similar to the EGF receptor, whose activation leads to cell growth and proliferation. In many breast cancers, Her2 receptor mutations have been isolated. a. (4 points) Ligand binding causes the Her2 receptor to dimerize. How does dimeri ...
... 1. (16 points) The Her2 receptor is a receptor tyrosine kinase, similar to the EGF receptor, whose activation leads to cell growth and proliferation. In many breast cancers, Her2 receptor mutations have been isolated. a. (4 points) Ligand binding causes the Her2 receptor to dimerize. How does dimeri ...
Central Dogma
... • Clathrin-mediated endocytosis is the specific uptake of large extracellular molecules such as proteins, membrane localized receptors and ion-channels. These receptors are associated with the cytosolic protein clathrin which initiates the formation of a vesicle by forming a crystalline coat on the ...
... • Clathrin-mediated endocytosis is the specific uptake of large extracellular molecules such as proteins, membrane localized receptors and ion-channels. These receptors are associated with the cytosolic protein clathrin which initiates the formation of a vesicle by forming a crystalline coat on the ...
Membrane Transport
... • ● Osmosis is the diffusion of water through a selectively permeable barrier. Water will tend to move across the membrane until equilibrium is reached, when this occurs the two solutions will be isotonic, the same. • ● When a solution is more concentrated with solute it is said to be hypertonic, wh ...
... • ● Osmosis is the diffusion of water through a selectively permeable barrier. Water will tend to move across the membrane until equilibrium is reached, when this occurs the two solutions will be isotonic, the same. • ● When a solution is more concentrated with solute it is said to be hypertonic, wh ...
Cell Structure and Function
... direction. They appeared to have a great deal of energy, some of them moved very quickly. When one of these life forms stopped or slowed down, the others behind it responded. They slowed down and gave off a reddish light from the back, and sometimes they would make honking noises. They would stop to ...
... direction. They appeared to have a great deal of energy, some of them moved very quickly. When one of these life forms stopped or slowed down, the others behind it responded. They slowed down and gave off a reddish light from the back, and sometimes they would make honking noises. They would stop to ...
Chem331 Lect 14 Membranes
... Single Channel Pores: Made up of dimer, trimer, etc. multimeric protein subunits : Multimeric subunit assemblies where each subunit has its own pore: Facilitated Diffusion Membrane Channel Proteins Channels are often selective for a particular type of ion or molecule. ...
... Single Channel Pores: Made up of dimer, trimer, etc. multimeric protein subunits : Multimeric subunit assemblies where each subunit has its own pore: Facilitated Diffusion Membrane Channel Proteins Channels are often selective for a particular type of ion or molecule. ...
amphipathic
... The composition of a membrane regulates the degree of its fluidity • Membrane lipids with fatty acyl side chains that are saturated ...
... The composition of a membrane regulates the degree of its fluidity • Membrane lipids with fatty acyl side chains that are saturated ...
Cell Death Process
... • Cell death can occur by either of two distinct mechanisms – apoptosis or necrosis. • Apoptosis: originally defined according to a set of characteristic ultrastructural features that include nuclear and cytoplasmic condensation, cell fragmentation and phagocytosis. • Necrosis: cell death as the res ...
... • Cell death can occur by either of two distinct mechanisms – apoptosis or necrosis. • Apoptosis: originally defined according to a set of characteristic ultrastructural features that include nuclear and cytoplasmic condensation, cell fragmentation and phagocytosis. • Necrosis: cell death as the res ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.