Cell Membrane
... Co-transport and counter transport: is transport of one or more solutes against an electrochemical gradient, coupled to the transport of another solute down an ...
... Co-transport and counter transport: is transport of one or more solutes against an electrochemical gradient, coupled to the transport of another solute down an ...
C1. The common points of control are as follows: 1. DNA
... occurs on cytosine at a CG sequence. After de novo methylation has occurred, it is passed from mother to daughter cell via a maintenance methylase. Since DNA replication is semiconservative, the newly made DNA contains one strand that is methylated and one that is not. The maintenance methylase reco ...
... occurs on cytosine at a CG sequence. After de novo methylation has occurred, it is passed from mother to daughter cell via a maintenance methylase. Since DNA replication is semiconservative, the newly made DNA contains one strand that is methylated and one that is not. The maintenance methylase reco ...
KEY | Cell Review Worksheet | Chapter 3
... 19. What might cause a molecule to move from the outside of the cell to the inside (with no energy)? Molecules would move from outside of the cell to the inside, if there was a higher concentration of ...
... 19. What might cause a molecule to move from the outside of the cell to the inside (with no energy)? Molecules would move from outside of the cell to the inside, if there was a higher concentration of ...
Notes on Mitosis
... No partner is required - think of vast oceans, or of organisms that are not mobile. How would they be able to reproduce? Exact copies of parent. ...
... No partner is required - think of vast oceans, or of organisms that are not mobile. How would they be able to reproduce? Exact copies of parent. ...
Intro to Cells
... surface area to volume ratio Cells with greater surface – to – volume ratio can ...
... surface area to volume ratio Cells with greater surface – to – volume ratio can ...
Cell Parts - Garnet Valley
... Eukaryotic Cells- contain organelles - Genetic Material is located in nucleus - some Unicellular and Multicellular organisms ...
... Eukaryotic Cells- contain organelles - Genetic Material is located in nucleus - some Unicellular and Multicellular organisms ...
1-Lec1- 2014
... chemicals and provide with the surprising ability to create copies of themselves by growing and dividing in two. ...
... chemicals and provide with the surprising ability to create copies of themselves by growing and dividing in two. ...
Basic Biochemistry
... Nucleotides joined by phosphodiester bonds Examples of nucleic acids include DNA, RNA, ...
... Nucleotides joined by phosphodiester bonds Examples of nucleic acids include DNA, RNA, ...
Possible Ligand-binding Proteins in the Olfactory Epithelium of the
... these chemicals caused harmful effect to living organisms including humans. The mechanism causing such toxic effects on the organisms are still not well-understood and possibly different from the each chemical. However, the first step of the toxic effects should be an interaction between such enviro ...
... these chemicals caused harmful effect to living organisms including humans. The mechanism causing such toxic effects on the organisms are still not well-understood and possibly different from the each chemical. However, the first step of the toxic effects should be an interaction between such enviro ...
Cells - Mad River Local Schools
... Contains chemicals that breaks down unneeded cell parts/molecules; only found in SOME plants ...
... Contains chemicals that breaks down unneeded cell parts/molecules; only found in SOME plants ...
Chapter 4
... Prokaryotic Cells • Simplest organisms • Lack a membrane-bound nucleus – DNA is present in the nucleoid ...
... Prokaryotic Cells • Simplest organisms • Lack a membrane-bound nucleus – DNA is present in the nucleoid ...
Cell Unit Review
... 1) Tissues in which similar cells function together 2) Organelles that carry out different functions 3) Organs that help to carry out a specific life activity 4) Systems that are responsible for a specific life activity ...
... 1) Tissues in which similar cells function together 2) Organelles that carry out different functions 3) Organs that help to carry out a specific life activity 4) Systems that are responsible for a specific life activity ...
Document
... ____ 9.What is the genetic material contained inside a cell’s nucleus? a. protein c. DNA b. lipids d. nucleolus _____ 10. The function of proteins in a cell is to a. control chemical reactions. c. cover the nucleus. b. store genetic information. d. copy messages from DNA. _____ 11. What is the nucle ...
... ____ 9.What is the genetic material contained inside a cell’s nucleus? a. protein c. DNA b. lipids d. nucleolus _____ 10. The function of proteins in a cell is to a. control chemical reactions. c. cover the nucleus. b. store genetic information. d. copy messages from DNA. _____ 11. What is the nucle ...
Biology Play Dough Mitosis Use your notes to answer the following
... Biology Play Dough Mitosis Use your notes to answer the following questions about cell division. Use complete sentences. ...
... Biology Play Dough Mitosis Use your notes to answer the following questions about cell division. Use complete sentences. ...
Slide ()
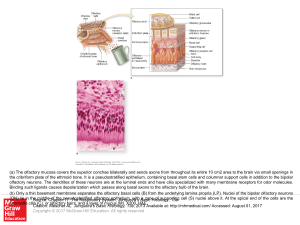
... (a) The olfactory mucosa covers the superior conchae bilaterally and sends axons from throughout its entire 10 cm2 area to the brain via small openings in the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone. It is a pseudostratified epithelium, containing basal stem cells and columnar support cells in addition ...
... (a) The olfactory mucosa covers the superior conchae bilaterally and sends axons from throughout its entire 10 cm2 area to the brain via small openings in the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone. It is a pseudostratified epithelium, containing basal stem cells and columnar support cells in addition ...
The Cell Structure - Sonoma Valley High School
... Basic Cell Structures Micrometer (1,000 times smaller than a millimeter) The tiniest bacteria cells are only 0.2 micrometers. Typical cells range from 5-50 micrometers. ...
... Basic Cell Structures Micrometer (1,000 times smaller than a millimeter) The tiniest bacteria cells are only 0.2 micrometers. Typical cells range from 5-50 micrometers. ...
Chapter 6
... However cones also respond in varying degrees to other wavelengths Color vision depends on the three cone types various ratios of stimulation in response to different wavelengths Phototransduction - conversion of light in to electrical signals Photoreceptors hyperpolarize on light absorption! Opposi ...
... However cones also respond in varying degrees to other wavelengths Color vision depends on the three cone types various ratios of stimulation in response to different wavelengths Phototransduction - conversion of light in to electrical signals Photoreceptors hyperpolarize on light absorption! Opposi ...
Chapter 3 Worksheet #1 - Part 1 Cells Name: :______ Part 1 Cells 1
... molecules are formed (cellular respiration). These special molecules are the basic energy source for all cells. 13. ribosome: What are they composed of? Ribosomes are the actual sites of ______________________ _______________________. 14. Endoplasmic reticulum: provides a network of channels for ___ ...
... molecules are formed (cellular respiration). These special molecules are the basic energy source for all cells. 13. ribosome: What are they composed of? Ribosomes are the actual sites of ______________________ _______________________. 14. Endoplasmic reticulum: provides a network of channels for ___ ...
R24Summary Statement - University of Illinois Archives
... cell, albeit a big one. This provides a conceptual and a practical approach to working out complex information processing pathways. Since it is now well demonstrated that dendrites not only contain enzymes that modify existing proteins but also the machinery for protein synthesis, several aspects of ...
... cell, albeit a big one. This provides a conceptual and a practical approach to working out complex information processing pathways. Since it is now well demonstrated that dendrites not only contain enzymes that modify existing proteins but also the machinery for protein synthesis, several aspects of ...
Gastrulation
... Pattern formation typically involves: Some initial spatial differences in molecular (inc. mRNA) distribution or gene expression of a few patterning molecules is set up: •location of maternal transcription factors in early Drosophila •location of maternal growth factors in the frog Xenopus Concentrat ...
... Pattern formation typically involves: Some initial spatial differences in molecular (inc. mRNA) distribution or gene expression of a few patterning molecules is set up: •location of maternal transcription factors in early Drosophila •location of maternal growth factors in the frog Xenopus Concentrat ...
Chapter 2 – Cell Processes and Energy
... a. What is a compound? b. What is an ORGANIC compound? c. Types of Organic Molecules and their function to the cell 1. Proteins 2. Carbohydrates 3. Lipids 4. Nucleic Acids d. Examples of each type of organic molecule e. Role of water in the cell f. Vocabulary – element, atom, compound, molecule, org ...
... a. What is a compound? b. What is an ORGANIC compound? c. Types of Organic Molecules and their function to the cell 1. Proteins 2. Carbohydrates 3. Lipids 4. Nucleic Acids d. Examples of each type of organic molecule e. Role of water in the cell f. Vocabulary – element, atom, compound, molecule, org ...
The Cell in Its Environment
... • How do most small molecules cross the cell membrane? • What types of molecules need to cross the cell membrane? • What is the difference between passive transport and active transport? ...
... • How do most small molecules cross the cell membrane? • What types of molecules need to cross the cell membrane? • What is the difference between passive transport and active transport? ...
Biological membranes: the basics and why they are
... and waste products (channels) • Acquired the ability to achieve these functions against a concentration gradient (transporters) • Later developments: conversion of membrane potential to do work; signalling from outside to inside; cell recognition; movement of molecules in eukaryotic vesicles; compar ...
... and waste products (channels) • Acquired the ability to achieve these functions against a concentration gradient (transporters) • Later developments: conversion of membrane potential to do work; signalling from outside to inside; cell recognition; movement of molecules in eukaryotic vesicles; compar ...
Cell Test 1 – Review Sheet
... What two organelles are only in a plant cell? Cell wall and chloroplasts ...
... What two organelles are only in a plant cell? Cell wall and chloroplasts ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.