3 types of protein transport
... the initial ”start transfer signal” followed by a signal peptidase recognition site ...
... the initial ”start transfer signal” followed by a signal peptidase recognition site ...
Cells
... cell membrane by diffusion) or a water channel pathway (when the water cannot cross the lipid barriers, the water crosses these channels through either diffusion or filtration). Describe the control of the movement of molecules across the cell membraneDiffusion causes movement of molecules from a re ...
... cell membrane by diffusion) or a water channel pathway (when the water cannot cross the lipid barriers, the water crosses these channels through either diffusion or filtration). Describe the control of the movement of molecules across the cell membraneDiffusion causes movement of molecules from a re ...
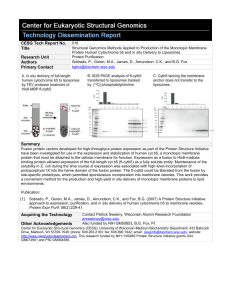
Center for Eukaryotic Structural Genomics (CESG)
... Fusion protein vectors developed for high-throughput protein expression as part of the Protein Structure Initiative have been investigated for use in the expression and stabilization of human cyt b5, a monotopic membrane protein that must be attached to the cellular membrane for function. Expression ...
... Fusion protein vectors developed for high-throughput protein expression as part of the Protein Structure Initiative have been investigated for use in the expression and stabilization of human cyt b5, a monotopic membrane protein that must be attached to the cellular membrane for function. Expression ...
illuminating life`s building blocks
... scurry off to a particular part of the cell membrane. That means that they no longer carry any information about the target molecule’s position, but they are in a position where Xiao can count them precisely and thus get an exact tally of the proteins produced, while the proteins themselves are free ...
... scurry off to a particular part of the cell membrane. That means that they no longer carry any information about the target molecule’s position, but they are in a position where Xiao can count them precisely and thus get an exact tally of the proteins produced, while the proteins themselves are free ...
Biochemistry Test w/Answers
... 10. Which of the following is a function of a protein? (9A) A. Forms the cell wall B. Insulation C. Gene expression D. Regulates enzymes 11. Enzymes are proteins that help increase the rate of chemical reactions inside cells. These proteins are composed of many simpler molecules called amino acids. ...
... 10. Which of the following is a function of a protein? (9A) A. Forms the cell wall B. Insulation C. Gene expression D. Regulates enzymes 11. Enzymes are proteins that help increase the rate of chemical reactions inside cells. These proteins are composed of many simpler molecules called amino acids. ...
Transport Across Cell Membrane
... the tails face each other forming a hydrophobic barrier which keeps water dissolved contents inside. Proteins may be Intrinsic – embedded in the lipid double layer and Extrinsic associated outside the lipid double layer. Proteins are gate keepers of cell and make the cell membrane selectively permea ...
... the tails face each other forming a hydrophobic barrier which keeps water dissolved contents inside. Proteins may be Intrinsic – embedded in the lipid double layer and Extrinsic associated outside the lipid double layer. Proteins are gate keepers of cell and make the cell membrane selectively permea ...
Chemistry for Biotech
... • Chemicallly very different from carbohydrates • Hydrophobic • 3 groups: – Triglycerides—animal fats & plant oils • Energy storage ...
... • Chemicallly very different from carbohydrates • Hydrophobic • 3 groups: – Triglycerides—animal fats & plant oils • Energy storage ...
Set of ideas for iGEM 2009
... • Bacteriophage based scaffold for tissue engineering. Bacteriophages are evolvable construction units that can be functionalized with many useful materials, such as RGD peptides. They also can be evolve to change their mechanical properties or the way they act to differentiate stem cells. In short: ...
... • Bacteriophage based scaffold for tissue engineering. Bacteriophages are evolvable construction units that can be functionalized with many useful materials, such as RGD peptides. They also can be evolve to change their mechanical properties or the way they act to differentiate stem cells. In short: ...
Are All Cells Alike?
... •For example, Paramecium, a protist, is hypertonic when compared to the pond water in which it lives. –In spite of a cell membrane that is less permeable to water than other cells, water still continually enters the Paramecium cell. –To solve this problem, Paramecium have a specialized organelle, t ...
... •For example, Paramecium, a protist, is hypertonic when compared to the pond water in which it lives. –In spite of a cell membrane that is less permeable to water than other cells, water still continually enters the Paramecium cell. –To solve this problem, Paramecium have a specialized organelle, t ...
Neurotransmission
... High-frequency stimulation leads to a more general increase in Ca2+, causing the release of peptide neuro transmitters from large densecore vesicles as well as smallmolecule neurotransmitters from small clear-core vesicles. ...
... High-frequency stimulation leads to a more general increase in Ca2+, causing the release of peptide neuro transmitters from large densecore vesicles as well as smallmolecule neurotransmitters from small clear-core vesicles. ...
Neurobiology of the Senses
... • Three other types of neurons contribute to information processing in the retina – Ganglion cells, horizontal cells, and ...
... • Three other types of neurons contribute to information processing in the retina – Ganglion cells, horizontal cells, and ...
Analytical Questions 1
... 5. Eukaryotic cells have an extensive and complex cytoskeleton, yet prokaryotic organisms lack a cytoskeleton. Identify 2 functions of eukaryotic cells that are dependent upon the cytoskeleton, and explain why each function are not important to prokaryotes. Why not important in prokaryotes 1. _____ ...
... 5. Eukaryotic cells have an extensive and complex cytoskeleton, yet prokaryotic organisms lack a cytoskeleton. Identify 2 functions of eukaryotic cells that are dependent upon the cytoskeleton, and explain why each function are not important to prokaryotes. Why not important in prokaryotes 1. _____ ...
Cell Transport
... If molecules are too large to fit through cell membrane or protein channels ______ will diffuse ____ _____ _____of the cell to maintain equilibrium ...
... If molecules are too large to fit through cell membrane or protein channels ______ will diffuse ____ _____ _____of the cell to maintain equilibrium ...
Study Guide
... group, carboxyl group, and an R-group b. R-groups are different between amino acids c. Proteins are used in cells to form structures, fight disease, and to catalyze chemical reactions ...
... group, carboxyl group, and an R-group b. R-groups are different between amino acids c. Proteins are used in cells to form structures, fight disease, and to catalyze chemical reactions ...
Lizzie Yasewicz Date: 2/23/12 Student Conference Abstract
... therapeutic approaches and effective new strategies are desperately needed (Shukla et al.). cAMP response element binding protein (CREB) is a cellular transcription factor which has previously been linked to cell proliferation, fibrogenesis and cell transformation in other cancers (Shukla et al.). S ...
... therapeutic approaches and effective new strategies are desperately needed (Shukla et al.). cAMP response element binding protein (CREB) is a cellular transcription factor which has previously been linked to cell proliferation, fibrogenesis and cell transformation in other cancers (Shukla et al.). S ...
AP Biology Ch. 43 Immunity
... Helper T cells and cytotoxic T cells are the main effectors of the cell-mediated immune response. When a helper T cell encounters an antigen-presenting cell, it releases signals that activate itself and cytotoxic T cells and help to stimulate B cells. Cytotoxic T cells attack infected body cells tha ...
... Helper T cells and cytotoxic T cells are the main effectors of the cell-mediated immune response. When a helper T cell encounters an antigen-presenting cell, it releases signals that activate itself and cytotoxic T cells and help to stimulate B cells. Cytotoxic T cells attack infected body cells tha ...
Review Packet: Cell Transport 2> .The diagram below represents a
... of potassium than the surrounding blood plasma does. This higher concentration is maintained by the process of ...
... of potassium than the surrounding blood plasma does. This higher concentration is maintained by the process of ...
AP Biology Reading Guide Chapter 6
... 18. The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) makes up more than half the total membrane system in many eukaryotic cells.Refer to figure 6.12 on make 105 in your textbook and explain the lumen, transport vesicles, and the difference between smooth and rough ER. ...
... 18. The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) makes up more than half the total membrane system in many eukaryotic cells.Refer to figure 6.12 on make 105 in your textbook and explain the lumen, transport vesicles, and the difference between smooth and rough ER. ...
1-cell structure
... A dark stained mass of chromatin, usually adherent to the inner aspect of the nuclear envelope of female somatic cells e.g. Buccal epithelial cells. A drumstick mass protruding from the nucleus of neutrophils. Represents one of the two X chromosomes which is inactive (condensed) in normal female . S ...
... A dark stained mass of chromatin, usually adherent to the inner aspect of the nuclear envelope of female somatic cells e.g. Buccal epithelial cells. A drumstick mass protruding from the nucleus of neutrophils. Represents one of the two X chromosomes which is inactive (condensed) in normal female . S ...
Cell Unit Review Worksheet | Part I | KEY
... polar, making them attracted to water and thus hydrophilic. The tails phospholipids face inward, towards each other, because they are nonpolar making them hydrophobic. Because of these characteristics this causes the phospholipids to be arranged in two layers. Answer the following questions abo ...
... polar, making them attracted to water and thus hydrophilic. The tails phospholipids face inward, towards each other, because they are nonpolar making them hydrophobic. Because of these characteristics this causes the phospholipids to be arranged in two layers. Answer the following questions abo ...
Plasma_Membrane2
... with the plasma membrane. This is how many hormones are secreted and how nerve ...
... with the plasma membrane. This is how many hormones are secreted and how nerve ...
Evans-Day-Abstract-2015
... Objectives: Gene-expression profiling offers functional insight into the molecular changes underlying the presence and progression of disease. Importantly, these profiles can be assessed for the functional connections between disease states and the effects of therapeutic compounds, as shown by the C ...
... Objectives: Gene-expression profiling offers functional insight into the molecular changes underlying the presence and progression of disease. Importantly, these profiles can be assessed for the functional connections between disease states and the effects of therapeutic compounds, as shown by the C ...
Control of Gene Expression 3 - Dr. Kordula
... D. The combinatorial complexity of transcriptional control. The human genome encodes about 2000 transcription factors. Because of the (1) multiplicity of promoter elements, (2) the ability of the group of transcription factors to work cooperatively, (3) the possibility for various combinations ...
... D. The combinatorial complexity of transcriptional control. The human genome encodes about 2000 transcription factors. Because of the (1) multiplicity of promoter elements, (2) the ability of the group of transcription factors to work cooperatively, (3) the possibility for various combinations ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.