Slide 1
... 3) Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and other materials from the ER for storage in the cell or release outside the cell. 4) From the Golgi apparatus, proteins > “shipped” to their final destination inside or outside the cell. ...
... 3) Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and other materials from the ER for storage in the cell or release outside the cell. 4) From the Golgi apparatus, proteins > “shipped” to their final destination inside or outside the cell. ...
Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic
... 3. Allows bacteria to adhere to various surfaces Streptococcus mutans - enamel on teeth to cause dental carries Klebseilla pneumoniae - attaches to respiratory tract ...
... 3. Allows bacteria to adhere to various surfaces Streptococcus mutans - enamel on teeth to cause dental carries Klebseilla pneumoniae - attaches to respiratory tract ...
Final Tech Project
... It's the rapping story of the living cell. It's a happy tune that's sort of cheery. About a real tough topic called the cell theory. All animals, plants, and protists too, Are made of cells with different jobs to do. They're the basic units of all organisms, And I hope by now you got the rhythm. It ...
... It's the rapping story of the living cell. It's a happy tune that's sort of cheery. About a real tough topic called the cell theory. All animals, plants, and protists too, Are made of cells with different jobs to do. They're the basic units of all organisms, And I hope by now you got the rhythm. It ...
How Do Muscles Work?
... The binding of ACh to the receptors increases the membrane permeability to sodium ions. Sodium ions then rush into the cell. ...
... The binding of ACh to the receptors increases the membrane permeability to sodium ions. Sodium ions then rush into the cell. ...
CELL BIOLOGY
... They have a nuclear membrane around their DNA and organelles surrounded by membranes inside ...
... They have a nuclear membrane around their DNA and organelles surrounded by membranes inside ...
Eukaryotes
... cell which perform specific tasks for the overall success and well being of the cell. The specific funtions of organelles vary widely and typically depend on their proximity within the cell as well as their physical characteristics. For example, specialized digestive organelles called lysosomes perf ...
... cell which perform specific tasks for the overall success and well being of the cell. The specific funtions of organelles vary widely and typically depend on their proximity within the cell as well as their physical characteristics. For example, specialized digestive organelles called lysosomes perf ...
Use the information in the book
... __________________________ by controlling what substances may enter or leave cells B. Some substances can cross the cell membrane without any input of energy by the cell C. The movement of such substances across the membrane is known as __________________________________ D. To stay alive, a ce ...
... __________________________ by controlling what substances may enter or leave cells B. Some substances can cross the cell membrane without any input of energy by the cell C. The movement of such substances across the membrane is known as __________________________________ D. To stay alive, a ce ...
Principles of physiologic function
... that allow ions and other small molecules to cross the membrane. • Because AQP is always open, cells must regulate their water permeability by adding or removing AQP from the membrane. ...
... that allow ions and other small molecules to cross the membrane. • Because AQP is always open, cells must regulate their water permeability by adding or removing AQP from the membrane. ...
Chapter 5
... unicellular organisms. Almost all carry out basic functions. Ex: Not all tree cells perform photosynthesis, only those with chlorophyll. Specialized cells like blood cells are dependent upon one another. ...
... unicellular organisms. Almost all carry out basic functions. Ex: Not all tree cells perform photosynthesis, only those with chlorophyll. Specialized cells like blood cells are dependent upon one another. ...
Cell based biosensor approach to characterize
... The work presented is aimed developing a QCM based platform for the characterisation of interactions between bio-nano interface and its cell binding partners using Attana label free cell based biosensor system2 This new biosensor system is based on the quartz crystal microbalance technology (QCM ...
... The work presented is aimed developing a QCM based platform for the characterisation of interactions between bio-nano interface and its cell binding partners using Attana label free cell based biosensor system2 This new biosensor system is based on the quartz crystal microbalance technology (QCM ...
Modulation of excitability and olfactory responses in mouse vomeronasal sensory... estrogen Suraj Cherian, Ian McDaniels, Chun Yang, Rona J. Delay
... Aggression and parental care are behaviors that are often mediated by chemical cues. Many of these chemical responses occur in the vomeronasal organ (VNO). Vomeronasal sensory neurons (VSNs) are the chemical sensors of the VNO and express specific odor receptors that are G protein coupled and linked ...
... Aggression and parental care are behaviors that are often mediated by chemical cues. Many of these chemical responses occur in the vomeronasal organ (VNO). Vomeronasal sensory neurons (VSNs) are the chemical sensors of the VNO and express specific odor receptors that are G protein coupled and linked ...
2012/2013 AP Biology Midterm Review Sheet
... o Proteins - structure, transport, defense, enzymes, amino acids, dipeptides, polypeptides, proteins, peptide bonds, 1°, 2°, 3°, 4° levels of structure o Lipids - energy storage, structure, hormones, groups: triglycerides (fats, saturated C-C, unsaturated/kinky C=C), phospholipids, steroids, (choles ...
... o Proteins - structure, transport, defense, enzymes, amino acids, dipeptides, polypeptides, proteins, peptide bonds, 1°, 2°, 3°, 4° levels of structure o Lipids - energy storage, structure, hormones, groups: triglycerides (fats, saturated C-C, unsaturated/kinky C=C), phospholipids, steroids, (choles ...
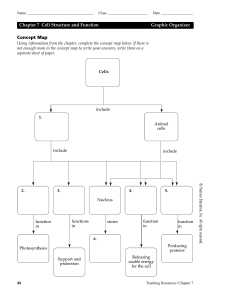
Concept Map Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function Graphic
... Using information from the chapter, complete the concept map below. If there is not enough room in the concept map to write your answers, write them on a separate sheet of paper. ...
... Using information from the chapter, complete the concept map below. If there is not enough room in the concept map to write your answers, write them on a separate sheet of paper. ...
Chapter 6: Concept 6.6
... fibers extending throughout the cytoplasm. Unlike your body's skeleton, the skeleton of most cells does not keep the same structural pattern all the time. It is always changing, with new extensions building at the same time that others are breaking apart. Different kinds of fibers make up the cytosk ...
... fibers extending throughout the cytoplasm. Unlike your body's skeleton, the skeleton of most cells does not keep the same structural pattern all the time. It is always changing, with new extensions building at the same time that others are breaking apart. Different kinds of fibers make up the cytosk ...
How are Plant and Animal Cells Different Similar.indd
... • Chloroplast • Mitochondria • Makes own food • Obtains food from the environment Directions: Compare and contrast plant and animals cells by completing the Venn Diagram using the terms from the word bank. Then answer the questions. Cell Wall and Chloroplast 1. What does the plant cell have that the ...
... • Chloroplast • Mitochondria • Makes own food • Obtains food from the environment Directions: Compare and contrast plant and animals cells by completing the Venn Diagram using the terms from the word bank. Then answer the questions. Cell Wall and Chloroplast 1. What does the plant cell have that the ...
You Light Up My Life
... • Smallest unit of life • Can survive on its own or has potential to do so • Is highly organized for metabolism ...
... • Smallest unit of life • Can survive on its own or has potential to do so • Is highly organized for metabolism ...
a molecule necessary and complementary to life. What elements are
... This is a phospholipid molecule. Which area is hydrophilic? In terms of its role in the cell membrane, which area would be found inside the membrane? Which area would face the inside of the cell? facing outside of the cell membrane? ...
... This is a phospholipid molecule. Which area is hydrophilic? In terms of its role in the cell membrane, which area would be found inside the membrane? Which area would face the inside of the cell? facing outside of the cell membrane? ...
Cell Structure and Function
... • Cell’s “garbage disposal” containing very reactive enzymes • Used by immune system cells (macrophages) to capture and process ...
... • Cell’s “garbage disposal” containing very reactive enzymes • Used by immune system cells (macrophages) to capture and process ...
Document
... Surrounded by double membrane and contain own DNA, but codes for very few proteins! (a few dozen) Instead, most genes from prokaryotic ancestor have been transferred to the nucleus, so proteins must be imported ...
... Surrounded by double membrane and contain own DNA, but codes for very few proteins! (a few dozen) Instead, most genes from prokaryotic ancestor have been transferred to the nucleus, so proteins must be imported ...
Chapter 1 (Sections 1-3) Study Guide: Cell Structure and
... cell theory all organisms are made of one or more cells, the cell is the smallest unit of life, all new cells come from preexisting cells. homeostasis to keep internal conditions within certain limits. cell basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. cell membrane a flexible covering that ...
... cell theory all organisms are made of one or more cells, the cell is the smallest unit of life, all new cells come from preexisting cells. homeostasis to keep internal conditions within certain limits. cell basic structural and functional unit of all organisms. cell membrane a flexible covering that ...
Cell Membrane
... Co-transport and counter transport: is transport of one or more solutes against an electrochemical gradient, coupled to the transport of another solute down an ...
... Co-transport and counter transport: is transport of one or more solutes against an electrochemical gradient, coupled to the transport of another solute down an ...
Cell Membrane
... Co-transport and counter transport: is transport of one or more solutes against an electrochemical gradient, coupled to the transport of another solute down an ...
... Co-transport and counter transport: is transport of one or more solutes against an electrochemical gradient, coupled to the transport of another solute down an ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.