NAME DATE ______ PERIOD _____
... 23, A signal to which an organism responds ___________________________ 24. Another name for a living thing is ______________________ 25. The “science of life” that studies all living things is called _____________ 26. The process by which organisms as a group change over time; Process by which moder ...
... 23, A signal to which an organism responds ___________________________ 24. Another name for a living thing is ______________________ 25. The “science of life” that studies all living things is called _____________ 26. The process by which organisms as a group change over time; Process by which moder ...
the discovery of cells
... - Organisms with a cell that lacks internal structures surrounded by membranes - Most are single celled organisms Eukaryote/ Eukaryotic: - Organisms that have cells containing internal, membrane bound structures - Organelles = a structure that has a membrane surrounding it. - Organelles isolate the ...
... - Organisms with a cell that lacks internal structures surrounded by membranes - Most are single celled organisms Eukaryote/ Eukaryotic: - Organisms that have cells containing internal, membrane bound structures - Organelles = a structure that has a membrane surrounding it. - Organelles isolate the ...
Inner life of a cell http://www.aimediaserver.com
... • The nonpolar (water hating) tails make up the interior of the bilayer, and the polar (water loving) heads make up the outer layer. ...
... • The nonpolar (water hating) tails make up the interior of the bilayer, and the polar (water loving) heads make up the outer layer. ...
Unit 2
... I. The Key Roles of Cell Division A. Cell division functions in reproduction, growth, and repair B. Cell division distributes identical sets of chromosomes to daughter cells II. The Mitotic Cell Cycle A. The mitotic phase alternates with interphase in the cell cycle: an overview B. The mitotic spind ...
... I. The Key Roles of Cell Division A. Cell division functions in reproduction, growth, and repair B. Cell division distributes identical sets of chromosomes to daughter cells II. The Mitotic Cell Cycle A. The mitotic phase alternates with interphase in the cell cycle: an overview B. The mitotic spind ...
RIDDLES - Mexico Central School District
... • Two types: 1. Rough-with ribosomes on them (RER) 2. Smooth- no ribosomes on them (SER) ...
... • Two types: 1. Rough-with ribosomes on them (RER) 2. Smooth- no ribosomes on them (SER) ...
MITOSIS COLORING HOMEWORK
... and performing cell activities like cellular respiration, osmosis, and for plant cells, photosynthesis. During interphase, DNA and other cell materials are copied. While in interphase, the DNA is shaped like uncoiled strands that look like spaghetti. When it is in this shape, it is called chromatin. ...
... and performing cell activities like cellular respiration, osmosis, and for plant cells, photosynthesis. During interphase, DNA and other cell materials are copied. While in interphase, the DNA is shaped like uncoiled strands that look like spaghetti. When it is in this shape, it is called chromatin. ...
Tanner`s Presentation - University of Toronto Physics
... •High pressure and cold temperatures at the poles cause air to sink. ...
... •High pressure and cold temperatures at the poles cause air to sink. ...
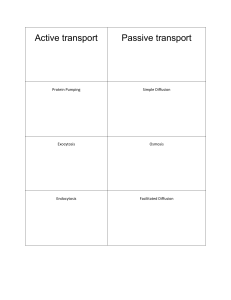
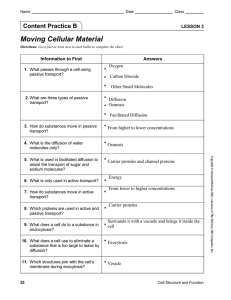
Comparing Organelles to Body Systems
... • A barrier between the cytoplasm and the outside of the cell • Pulls needed matter through the membrane • Controls what enters and leaves the cell ...
... • A barrier between the cytoplasm and the outside of the cell • Pulls needed matter through the membrane • Controls what enters and leaves the cell ...
Supplemental File S5. Predisposition to Cancer
... Description of how a BRCA1+/BRCA1- individual can have a cell with no functional BRCA1 alleles. Patients with inherited forms of breast cancer inherit one normal allele and one mutant allele of a gene (ex. BRCA1+/BRCA1-). Then, subsequent somatic changes lead to a cell with no functional BRCA1 allel ...
... Description of how a BRCA1+/BRCA1- individual can have a cell with no functional BRCA1 alleles. Patients with inherited forms of breast cancer inherit one normal allele and one mutant allele of a gene (ex. BRCA1+/BRCA1-). Then, subsequent somatic changes lead to a cell with no functional BRCA1 allel ...
printer-friendly sample test questions
... A. two daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. B. two daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell. C. four daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. D. four daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the ...
... A. two daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. B. two daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell. C. four daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. D. four daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the ...
Chapter 15: The Cell - Heritage Christian School
... The books of the bible are like individual chromosomes: there are many of them, each one contains huge storehouses of information, but are divided into groups. The chapters of each book are like genes: every chromosome is like a beaded necklace of genes in a special order, every chapter must be in i ...
... The books of the bible are like individual chromosomes: there are many of them, each one contains huge storehouses of information, but are divided into groups. The chapters of each book are like genes: every chromosome is like a beaded necklace of genes in a special order, every chapter must be in i ...
Useful fundamental numbers in molecular biology The numbers
... in molecular biology The numbers quoted here were extracted from the literature. They should only serve as “rule of thumb” values. Consult the full references to learn about the specific system under study, growth conditions, measurement method etc. Full references at: www.bioNumbers.org Cell sizes: ...
... in molecular biology The numbers quoted here were extracted from the literature. They should only serve as “rule of thumb” values. Consult the full references to learn about the specific system under study, growth conditions, measurement method etc. Full references at: www.bioNumbers.org Cell sizes: ...
7th Grade Science
... 1) do not have to wait for a mate 2.) makes more offspring Disadvantage) if a mutation or problem occurs, since offspring are genetically identical, then the problem could cause a population to become extinct. 5. Tell 1 advantage and 1 disadvantage of sexual reproduction Sexual= Advantage) allows fo ...
... 1) do not have to wait for a mate 2.) makes more offspring Disadvantage) if a mutation or problem occurs, since offspring are genetically identical, then the problem could cause a population to become extinct. 5. Tell 1 advantage and 1 disadvantage of sexual reproduction Sexual= Advantage) allows fo ...
Prokaryotic cell
... 7. Mitochondria harvest chemical energy from food – Mitochondria carry out cellular respiration which uses the chemical energy in food to make ATP for cellular work Mitochondrion ...
... 7. Mitochondria harvest chemical energy from food – Mitochondria carry out cellular respiration which uses the chemical energy in food to make ATP for cellular work Mitochondrion ...
BIOLOGY 1: FIRST SEMESTER FINAL EXAM
... 26. Which organic molecules belong in the same category as lipids? 27. What type of fatty acids make up oils (liquid fats)? 28. Name some conditions that can affect the function of enzymes? 29. What are enzymes? What do they do? ...
... 26. Which organic molecules belong in the same category as lipids? 27. What type of fatty acids make up oils (liquid fats)? 28. Name some conditions that can affect the function of enzymes? 29. What are enzymes? What do they do? ...
Biology 11
... • Site of photosynthesis, found in plants only • Uses chlorophyll to convert light energy into chemical energy (glucose) ...
... • Site of photosynthesis, found in plants only • Uses chlorophyll to convert light energy into chemical energy (glucose) ...
The Cell Theory
... It is amazing to think that the cells that make up our bodies are just as alive as we are. Humans are just an intricately designed community of cells, which must work together to survive. ...
... It is amazing to think that the cells that make up our bodies are just as alive as we are. Humans are just an intricately designed community of cells, which must work together to survive. ...
The Cell Key Concept Builder
... Directions: Complete the paragraphs by choosing terms from the word bank and writing them in the correct spaces. Terms may be used only once. ...
... Directions: Complete the paragraphs by choosing terms from the word bank and writing them in the correct spaces. Terms may be used only once. ...
Cell cycle
The cell cycle or cell-division cycle is the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its division and duplication (replication) that produces two daughter cells. In prokaryotes which lack a cell nucleus, the cell cycle occurs via a process termed binary fission. In cells with a nucleus, as in eukaryotes, the cell cycle can be divided into three periods: interphase, the mitotic (M) phase, and cytokinesis. During interphase, the cell grows, accumulating nutrients needed for mitosis, preparing it for cell division and duplicating its DNA. During the mitotic phase, the cell splits itself into two distinct daughter cells. During the final stage, cytokinesis, the new cell is completely divided. To ensure the proper division of the cell, there are control mechanisms known as cell cycle checkpoints.The cell-division cycle is a vital process by which a single-celled fertilized egg develops into a mature organism, as well as the process by which hair, skin, blood cells, and some internal organs are renewed. After cell division, each of the daughter cells begin the interphase of a new cycle. Although the various stages of interphase are not usually morphologically distinguishable, each phase of the cell cycle has a distinct set of specialized biochemical processes that prepare the cell for initiation of cell division.