Cells, Photosynthesis, and Cellular Respiration
... 14. Draw the Golgi apparatus…be able to identify it on a diagram. 15. What is the function of the nucleolus? 16. What is the main function of the cell wall? 17. Which organelle can be found in the cytoplasm and on the surface of the endoplasmic reticulum? 18. Which organelle is a membrane-bound sac ...
... 14. Draw the Golgi apparatus…be able to identify it on a diagram. 15. What is the function of the nucleolus? 16. What is the main function of the cell wall? 17. Which organelle can be found in the cytoplasm and on the surface of the endoplasmic reticulum? 18. Which organelle is a membrane-bound sac ...
Hypertonic, Hypotonic and Isotonic
... • Facilitated diffusion is the process in which molecules that cannot directly diffuse across the membrane pass through special protein channels. o Examples: glucose and water ...
... • Facilitated diffusion is the process in which molecules that cannot directly diffuse across the membrane pass through special protein channels. o Examples: glucose and water ...
Diffusion and Osmosis
... Diffusion • Definition: movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to low concentration • What is concentration? • Concentration is an amount. • Example: What does it mean if a pool has a high concentration of chlorine? ...
... Diffusion • Definition: movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to low concentration • What is concentration? • Concentration is an amount. • Example: What does it mean if a pool has a high concentration of chlorine? ...
Document
... 2. Electron microscopes can enlarge images 100,000 times or more C. The cell theory describes how cells relate to living things. 1. All organisms are made of one or more cells 2. The cell is the smallest unit of life 3. All new cells come from pre-existing cells D. Scientists agree that all livings ...
... 2. Electron microscopes can enlarge images 100,000 times or more C. The cell theory describes how cells relate to living things. 1. All organisms are made of one or more cells 2. The cell is the smallest unit of life 3. All new cells come from pre-existing cells D. Scientists agree that all livings ...
Hast Cell Analogy
... We chose the students to represent the ribosomes because the ribosomes produce protein in the cell which in our case is knowledge because knowledge is was makes HAST what is is and the students are the one who produce the knowledge. ...
... We chose the students to represent the ribosomes because the ribosomes produce protein in the cell which in our case is knowledge because knowledge is was makes HAST what is is and the students are the one who produce the knowledge. ...
HBio Cell Parts
... HONORS BIOLOGY LAB: CELL PARTS Background Information: In this lab you will observe organelles found in certain plant and animal cells. Just as animals are made up of smaller parts called organs (heart, lungs, liver, etc.), cells are made up of smaller parts called organelles. If we wanted to observ ...
... HONORS BIOLOGY LAB: CELL PARTS Background Information: In this lab you will observe organelles found in certain plant and animal cells. Just as animals are made up of smaller parts called organs (heart, lungs, liver, etc.), cells are made up of smaller parts called organelles. If we wanted to observ ...
Pretest on Cell Theory, Microscopes, and Organelles
... 6. Cheetahs can run at speeds in excess of 60 mph, which requires a lot of energy. The cells of a cheetah might need to contain large numbers of which organelles? (What oganelle make energy from sugar?) a. nucleoli c. lysosomes b. mitochondria d. vacuoles 7. Which structure destroys worn out parts a ...
... 6. Cheetahs can run at speeds in excess of 60 mph, which requires a lot of energy. The cells of a cheetah might need to contain large numbers of which organelles? (What oganelle make energy from sugar?) a. nucleoli c. lysosomes b. mitochondria d. vacuoles 7. Which structure destroys worn out parts a ...
5 Homeostasis and Transport adn Cell Structure
... Osmosis is the movement of WATER from high to low concentration. Depends on the concentration of solutes inside and outside of the cell. ◦ Hypotonic Solution—solution outside the cell has a lower concentration of solute molecules than inside. Water moves into the cell. (Oh NO! She’s gonna blow!) ◦ H ...
... Osmosis is the movement of WATER from high to low concentration. Depends on the concentration of solutes inside and outside of the cell. ◦ Hypotonic Solution—solution outside the cell has a lower concentration of solute molecules than inside. Water moves into the cell. (Oh NO! She’s gonna blow!) ◦ H ...
Characteristics of Living Things and Cell Structure and Function PPT
... membrane bound organelles; found in bacteria and cyanobacteria 2) eukaryotic—do have an organized nucleus and membrane-bound organelles such as Golgi apparatus and mitochondria. All other organisms such as plants and animals have this kind of cell. ...
... membrane bound organelles; found in bacteria and cyanobacteria 2) eukaryotic—do have an organized nucleus and membrane-bound organelles such as Golgi apparatus and mitochondria. All other organisms such as plants and animals have this kind of cell. ...
Name: Cell City Introduction Floating around in the cytoplasm are
... Floating around in the cytoplasm are small structures called organelles. Like the organs in your own body, each one carries out a specific function necessary for the cell to survive. Imagine the cell as a miniature city. The organelles might represent companies, places or parts of the city because t ...
... Floating around in the cytoplasm are small structures called organelles. Like the organs in your own body, each one carries out a specific function necessary for the cell to survive. Imagine the cell as a miniature city. The organelles might represent companies, places or parts of the city because t ...
BIOREACTION AND BIOREACTOR - Universiti Malaysia Perlis
... • Growth rate, rg depends on the nutrient concentration (Cs) ...
... • Growth rate, rg depends on the nutrient concentration (Cs) ...
Ch. 2-2: The Organelles of the Cell ER, Golgi Complex, Lysosomes
... 1. Organelles are very _________ in size and can only be observed with a __________. 2. They each have a specific ___________and are found throughout the ____________. 3. ___________ takes part in nearly every cell _______________. 4. What makes these proteins? ___________________________ 5. Some ri ...
... 1. Organelles are very _________ in size and can only be observed with a __________. 2. They each have a specific ___________and are found throughout the ____________. 3. ___________ takes part in nearly every cell _______________. 4. What makes these proteins? ___________________________ 5. Some ri ...
Cell Transport
... • Descriptions for solutions on either side of a membrane: 1. Hypertonic –solute is in high concentration so water is low. 2. Hypotonic – solute is in low concentration so water is high. 3. Isotonic – solute concentration is equal on both sides. ...
... • Descriptions for solutions on either side of a membrane: 1. Hypertonic –solute is in high concentration so water is low. 2. Hypotonic – solute is in low concentration so water is high. 3. Isotonic – solute concentration is equal on both sides. ...
using animal-derived growth factors in stem cell
... Vesivirus 2117 in a bioreactor producing imiglucerase at Genzyme‘s manufacturing facility ...
... Vesivirus 2117 in a bioreactor producing imiglucerase at Genzyme‘s manufacturing facility ...
1. Eukaryotic Cell Structure Eukaryotic Organelles
... Prokaryotic Cell Shape One convenient characteristic with which to identify and classify prokaryotes is their size and shape as seen in the microscope. • the diameter of prokaryotic cells ranges from ~0.2 to 2.0 μm • prokaryotes are essentially unicellular and more or less maintain a constant shape ...
... Prokaryotic Cell Shape One convenient characteristic with which to identify and classify prokaryotes is their size and shape as seen in the microscope. • the diameter of prokaryotic cells ranges from ~0.2 to 2.0 μm • prokaryotes are essentially unicellular and more or less maintain a constant shape ...
2-3 outline answers
... Lesson Outline for Teaching Lesson 3: Moving Cellular Material A. Passive Transport 1. A cell membrane is semipermeable, which means that it allows only certain substances to enter or leave a cell. ...
... Lesson Outline for Teaching Lesson 3: Moving Cellular Material A. Passive Transport 1. A cell membrane is semipermeable, which means that it allows only certain substances to enter or leave a cell. ...
Supplementary information
... CFDA-AM. All results were related to 100 % viability concerning to water control. ...
... CFDA-AM. All results were related to 100 % viability concerning to water control. ...
Aug31-Sept11
... Things Video Activity and turn in Read and take notes on the “Cell Theory” article-DO NOT write on the article Complete Vocab Notebook using Frayer Model Finish Characteristics of Living Things HW assignment that is ...
... Things Video Activity and turn in Read and take notes on the “Cell Theory” article-DO NOT write on the article Complete Vocab Notebook using Frayer Model Finish Characteristics of Living Things HW assignment that is ...
Slide ()
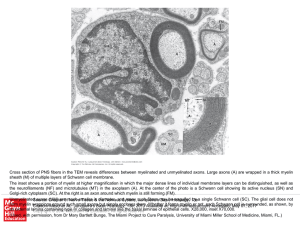
... Cross section of PNS fibers in the TEM reveals differences between myelinated and unmyelinated axons. Large axons (A) are wrapped in a thick myelin sheath (M) of multiple layers of Schwann cell membrane. The inset shows a portion of myelin at higher magnification in which the major dense lines of in ...
... Cross section of PNS fibers in the TEM reveals differences between myelinated and unmyelinated axons. Large axons (A) are wrapped in a thick myelin sheath (M) of multiple layers of Schwann cell membrane. The inset shows a portion of myelin at higher magnification in which the major dense lines of in ...
section_7-2_eukaryotic_cell_structure_assignment_value_50_2017
... c. When a cell divides, chromatin condenses to form into __________________________. d. The smooth ER produces a large amount of ___________________________. e. Vacuoles help maintain ________________________ in the cell. f. Chloroplast contains the green pigment _______________________. g. The func ...
... c. When a cell divides, chromatin condenses to form into __________________________. d. The smooth ER produces a large amount of ___________________________. e. Vacuoles help maintain ________________________ in the cell. f. Chloroplast contains the green pigment _______________________. g. The func ...
Essential Question: What is active and passive transport?
... substances is larger in the environment than in the cell. • Thus cell will loose water. The cell will shrink. Ex. Wilted celery, cooking meat. ...
... substances is larger in the environment than in the cell. • Thus cell will loose water. The cell will shrink. Ex. Wilted celery, cooking meat. ...
Cell cycle
The cell cycle or cell-division cycle is the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its division and duplication (replication) that produces two daughter cells. In prokaryotes which lack a cell nucleus, the cell cycle occurs via a process termed binary fission. In cells with a nucleus, as in eukaryotes, the cell cycle can be divided into three periods: interphase, the mitotic (M) phase, and cytokinesis. During interphase, the cell grows, accumulating nutrients needed for mitosis, preparing it for cell division and duplicating its DNA. During the mitotic phase, the cell splits itself into two distinct daughter cells. During the final stage, cytokinesis, the new cell is completely divided. To ensure the proper division of the cell, there are control mechanisms known as cell cycle checkpoints.The cell-division cycle is a vital process by which a single-celled fertilized egg develops into a mature organism, as well as the process by which hair, skin, blood cells, and some internal organs are renewed. After cell division, each of the daughter cells begin the interphase of a new cycle. Although the various stages of interphase are not usually morphologically distinguishable, each phase of the cell cycle has a distinct set of specialized biochemical processes that prepare the cell for initiation of cell division.