Prions tunnel between cells Hans
... epithelial cell layer and are then transported by bone marrow-derived dendritic cells (DCs) to lymphoid tissues such as the spleen. From these tissues, prions are thought to enter the peripheral nervous system and spread in a retrograde direction along the peripheral nerve fibres towards the CNS. H ...
... epithelial cell layer and are then transported by bone marrow-derived dendritic cells (DCs) to lymphoid tissues such as the spleen. From these tissues, prions are thought to enter the peripheral nervous system and spread in a retrograde direction along the peripheral nerve fibres towards the CNS. H ...
7 3-3SR - Groupfusion.net
... 5. Making Inferences Why can multicellular organisms be more complex than single-cell organisms? Use the three advantages of being multicellular to help explain your answer. _______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ...
... 5. Making Inferences Why can multicellular organisms be more complex than single-cell organisms? Use the three advantages of being multicellular to help explain your answer. _______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ...
Life Science Semester Review Part 2 NAME
... 36. Which of the following correctly matches an organelle with its “Cell City” function? a. Golgi Apparatus to Post office b. Cell wall to Mayer c. Mitochondria to solar panel 37. How are plant cells different from animal cells? a. Plant cells have cell walls. b. Animal cells have cell membranes. c. ...
... 36. Which of the following correctly matches an organelle with its “Cell City” function? a. Golgi Apparatus to Post office b. Cell wall to Mayer c. Mitochondria to solar panel 37. How are plant cells different from animal cells? a. Plant cells have cell walls. b. Animal cells have cell membranes. c. ...
Plant and animal cells AP MAKE UP
... Procedure – Prepare a wet mount of one small elodea leaflet. Use fresh water. Sketch 2 or 3 cells next to each other. Enlarge to show structure. Label nucleus, cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, chloroplasts and total magnification Title sketch ...
... Procedure – Prepare a wet mount of one small elodea leaflet. Use fresh water. Sketch 2 or 3 cells next to each other. Enlarge to show structure. Label nucleus, cell wall, cell membrane, cytoplasm, chloroplasts and total magnification Title sketch ...
Cells Homework 1
... structural proteins; about twenty different enzymes and small quantities of many other substances. Cell walls are complex structures and this complexity must be important to plant life. Cell walls, therefore, must not be seen simply as “cardboard boxes”. Cell walls can be removed from plant cells by ...
... structural proteins; about twenty different enzymes and small quantities of many other substances. Cell walls are complex structures and this complexity must be important to plant life. Cell walls, therefore, must not be seen simply as “cardboard boxes”. Cell walls can be removed from plant cells by ...
5.1 Study Guide KEY
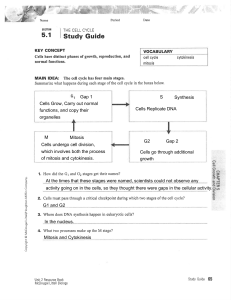
... The name given to the stage where cells carry out their normal functions but are unlikely to divide. ...
... The name given to the stage where cells carry out their normal functions but are unlikely to divide. ...
Chapter 2 notes
... • The ability to produce offspring that are similar to the parents • Sexual: requires 2 parents (most multicellular) • Asexual: requires 1 parent – one organism divides into two parts (bacteria, yeast, some plants) ...
... • The ability to produce offspring that are similar to the parents • Sexual: requires 2 parents (most multicellular) • Asexual: requires 1 parent – one organism divides into two parts (bacteria, yeast, some plants) ...
Collect-a-Cell! - Partnerships for Environmental Education and Rural
... levels of organization demonstrate the complementary nature of structure and function. The student is expected to: o recognize levels of organization in plants and animals, including cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms; o differentiate between structure and function in plant and ani ...
... levels of organization demonstrate the complementary nature of structure and function. The student is expected to: o recognize levels of organization in plants and animals, including cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms; o differentiate between structure and function in plant and ani ...
Cell Biology - Cloudfront.net
... molecules across concentration gradient –Very few molecules can do this –Proteins carry glucose molecules into red blood cells ...
... molecules across concentration gradient –Very few molecules can do this –Proteins carry glucose molecules into red blood cells ...
Match Success Criteria to Justification
... 4) I should be able to draw and and label 2 or 3 onion skin cells, seen on my slide. ...
... 4) I should be able to draw and and label 2 or 3 onion skin cells, seen on my slide. ...
A cell is like the bank
... Nuclear membrane • Is like the president of the banks office • Allows materials to pass in and out and lets people in his office ...
... Nuclear membrane • Is like the president of the banks office • Allows materials to pass in and out and lets people in his office ...
Interesting facts: • Many cells in the body use exocytosis to release
... Many cells in the body use exocytosis to release enzymes or other proteins that act in other areas of the body like secretion of the hormones glucagon and insulin, or to release molecules that help cells communicate with one another more directly through the products that they secrete like neurotran ...
... Many cells in the body use exocytosis to release enzymes or other proteins that act in other areas of the body like secretion of the hormones glucagon and insulin, or to release molecules that help cells communicate with one another more directly through the products that they secrete like neurotran ...
Document
... Two teams of scientists reported yesterday that they had turned human skin cells into what appear to be embryonic stem cells without having to make or destroy an embryo — a feat that could quell the ethical debate troubling the field. All they had to do, the scientists said, was add four genes.” ...
... Two teams of scientists reported yesterday that they had turned human skin cells into what appear to be embryonic stem cells without having to make or destroy an embryo — a feat that could quell the ethical debate troubling the field. All they had to do, the scientists said, was add four genes.” ...
Fun Hippo - snellbiology
... Eukaryotes have a much larger genome which is sequester in a nucleus to increase efficiency. In addition, eukaryotes have membrane bound organelles that increase the surface area of the cell to further increase efficiency of the eukaryotic cell. ...
... Eukaryotes have a much larger genome which is sequester in a nucleus to increase efficiency. In addition, eukaryotes have membrane bound organelles that increase the surface area of the cell to further increase efficiency of the eukaryotic cell. ...
Stem Cells
... Blastocyst – hollow ball of cells; early embryo Pluripotent – inside blastocyst; can develop into most types of cells (not the tissue around embryo) ...
... Blastocyst – hollow ball of cells; early embryo Pluripotent – inside blastocyst; can develop into most types of cells (not the tissue around embryo) ...
Overview of the cell structure Bacteria, animals and plants
... Basic properties of cells • Order and complexity – surrounded by a semi-permeable membrane, similar in composition and function – Similar chemical composition: similarity of structural patterns of macromolecules and their functions – Similar biochemical and regulatory processes – hierarchal complexi ...
... Basic properties of cells • Order and complexity – surrounded by a semi-permeable membrane, similar in composition and function – Similar chemical composition: similarity of structural patterns of macromolecules and their functions – Similar biochemical and regulatory processes – hierarchal complexi ...
Eukaryotic Cell Organelles
... Rough ER – covered in ribosomes; packages proteins made by the ribosomes into vesicles (small sacs containing materials) that are transported to the golgi complex Smooth ER – no ribosomes; make lipids and break down toxic substances ...
... Rough ER – covered in ribosomes; packages proteins made by the ribosomes into vesicles (small sacs containing materials) that are transported to the golgi complex Smooth ER – no ribosomes; make lipids and break down toxic substances ...
Cellular Level of Organization
... Name: ____________________________________________________ Date: ______________ Period: ________ Use book/internet/handouts to fill in the information about cell organelles. Color back side diagram of parts. Memory clue: reminder of function Cell Organelle/ Location and Function How will you remembe ...
... Name: ____________________________________________________ Date: ______________ Period: ________ Use book/internet/handouts to fill in the information about cell organelles. Color back side diagram of parts. Memory clue: reminder of function Cell Organelle/ Location and Function How will you remembe ...
Pre-Lesson 10: Bacterial Diseases I
... disease. But, it can be an ________________ pathogen when introduced into the body by a puncture or other wound, a medical treatment, or it grows where it should not in an immunocompromised patient, such as with Aids. ...
... disease. But, it can be an ________________ pathogen when introduced into the body by a puncture or other wound, a medical treatment, or it grows where it should not in an immunocompromised patient, such as with Aids. ...
Small groups - SID Evangelism
... Christ instructed them to go They were to go out two by two (Mark 6:7..) Brother was sent out with brother (friends) ...
... Christ instructed them to go They were to go out two by two (Mark 6:7..) Brother was sent out with brother (friends) ...
Cell encapsulation

Cell microencapsulation technology involves immobilization of the cells within a polymeric semi-permeable membrane that permits the bidirectional diffusion of molecules such as the influx of oxygen, nutrients, growth factors etc. essential for cell metabolism and the outward diffusion of waste products and therapeutic proteins. At the same time, the semi-permeable nature of the membrane prevents immune cells and antibodies from destroying the encapsulated cells regarding them as foreign invaders.The main motive of cell encapsulation technology is to overcome the existing problem of graft rejection in tissue engineering applications and thus reduce the need for long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs after an organ transplant to control side effects.