Chapter 3 Section 2 - Blue Earth Area Schools
... Determine why cells must be relatively small Compare the structure of prokaryotic cells with that of eukaryotic cells Describe the structure of cell membranes Differentiate between the membrane proteins structures and functions ...
... Determine why cells must be relatively small Compare the structure of prokaryotic cells with that of eukaryotic cells Describe the structure of cell membranes Differentiate between the membrane proteins structures and functions ...
Cell Structure Notes - Center Grove Schools
... – For cells with cell walls – cell membrane is inside the cell wall – A cell membrane allows food and oxygen into the cell and waste out of the cell (semipermeable) ...
... – For cells with cell walls – cell membrane is inside the cell wall – A cell membrane allows food and oxygen into the cell and waste out of the cell (semipermeable) ...
Unit 1
... What are the insides of cell like? • There are types of cells: – Procaryotic: cells where the nucleus isn´t separated from the rest of the cell. – Eucaryotic: cells where the nucleus is separated from the rest of the cell. ...
... What are the insides of cell like? • There are types of cells: – Procaryotic: cells where the nucleus isn´t separated from the rest of the cell. – Eucaryotic: cells where the nucleus is separated from the rest of the cell. ...
Microtubules and Microfilaments
... cytoplasm • The location of cellular chemical reactions • Found in Both types of cells • Rough ER – contains ribosomes that are attached to the surface, it is involved in the transport, storage, making and modifying of proteins. • Smooth ER- production and storage of lipids, contains NO ribosomes ...
... cytoplasm • The location of cellular chemical reactions • Found in Both types of cells • Rough ER – contains ribosomes that are attached to the surface, it is involved in the transport, storage, making and modifying of proteins. • Smooth ER- production and storage of lipids, contains NO ribosomes ...
Biology – Wilson
... 1. In some respects, the _________________________________ is like a factory. 2. These structures are known as "little organs." _____________________________. 3. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic cell into 2 major parts: _________________ & ____________________. 4. See Figure 7-7. What part of t ...
... 1. In some respects, the _________________________________ is like a factory. 2. These structures are known as "little organs." _____________________________. 3. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic cell into 2 major parts: _________________ & ____________________. 4. See Figure 7-7. What part of t ...
Cheek Cell Lab
... 7. Once you think you have located a cell, switch to high power and refocus. (Remember, do NOT use the coarse adjustment knob at this point) ...
... 7. Once you think you have located a cell, switch to high power and refocus. (Remember, do NOT use the coarse adjustment knob at this point) ...
Plant and Animal Cells Study Sheet
... Students will be able to identify the following parts of animal cell and plant cells: cell membrane, cell wall, cytoplasm, nucleus, chloroplasts Students will be able to determine the function of the following organelles: cell membrane, cell wall, cytoplasm, nucleus, chloroplasts Students will be ab ...
... Students will be able to identify the following parts of animal cell and plant cells: cell membrane, cell wall, cytoplasm, nucleus, chloroplasts Students will be able to determine the function of the following organelles: cell membrane, cell wall, cytoplasm, nucleus, chloroplasts Students will be ab ...
Power Point
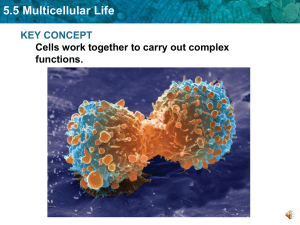
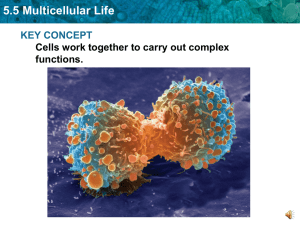
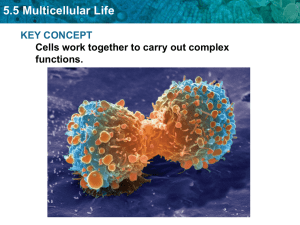
... 5.5 Multicellular Life Specialized cells perform specific functions. • Cells develop into their mature forms through the process of cell differentiation. • Cells differ because different combinations of genes are expressed. • A cell’s location in an embryo helps determine how it will differentiate. ...
... 5.5 Multicellular Life Specialized cells perform specific functions. • Cells develop into their mature forms through the process of cell differentiation. • Cells differ because different combinations of genes are expressed. • A cell’s location in an embryo helps determine how it will differentiate. ...
5.5 Multicellular Life KEY CONCEPT Cells work together to carry out complex functions.
... 5.5 Multicellular Life Specialized cells perform specific functions. • Cells develop into their mature forms through the process of cell differentiation. • Cells differ because different combinations of genes are expressed. • A cell’s location in an embryo helps determine how it will differentiate. ...
... 5.5 Multicellular Life Specialized cells perform specific functions. • Cells develop into their mature forms through the process of cell differentiation. • Cells differ because different combinations of genes are expressed. • A cell’s location in an embryo helps determine how it will differentiate. ...
Plant Parts and Cells Plants are living things that are made of many
... The main parts of a plant are the roots, stems, leaves and flowers, each with its own function. The roots anchor the plant to the soil and absorb water and minerals (including nitrogen, phosphorus, calcium, potassium, & magnesium that the plant needs. The stems hold the leaves up high, exposing them ...
... The main parts of a plant are the roots, stems, leaves and flowers, each with its own function. The roots anchor the plant to the soil and absorb water and minerals (including nitrogen, phosphorus, calcium, potassium, & magnesium that the plant needs. The stems hold the leaves up high, exposing them ...
Cellular Hierarchy - Bibb County Schools
... S7L2c Explain that cells are organized into tissues, tissues into organs, organs into systems and systems into organisms. ...
... S7L2c Explain that cells are organized into tissues, tissues into organs, organs into systems and systems into organisms. ...
Document
... ____ 9.What is the genetic material contained inside a cell’s nucleus? a. protein c. DNA b. lipids d. nucleolus _____ 10. The function of proteins in a cell is to a. control chemical reactions. c. cover the nucleus. b. store genetic information. d. copy messages from DNA. _____ 11. What is the nucle ...
... ____ 9.What is the genetic material contained inside a cell’s nucleus? a. protein c. DNA b. lipids d. nucleolus _____ 10. The function of proteins in a cell is to a. control chemical reactions. c. cover the nucleus. b. store genetic information. d. copy messages from DNA. _____ 11. What is the nucle ...
Document
... Cell – smallest unit that can live and reproduce on its own or as part of a multicelled organism. It has an outer membrane, DNA, and other components called organelles. Tissue – cells form tissues. It is an organized group of similar cells that perform the same task. For example, muscle is a tissue ...
... Cell – smallest unit that can live and reproduce on its own or as part of a multicelled organism. It has an outer membrane, DNA, and other components called organelles. Tissue – cells form tissues. It is an organized group of similar cells that perform the same task. For example, muscle is a tissue ...
CELL RESPIRATION: uses GLUCOSE to produce energy (ATP)
... What to study - Cells Exam CELL THEORY 3 parts: 1. Cells are the basic unit of FUNCTION of all living things. 2. Cells are the basic unit of STRUCTURE of all living things. 3. All cells come from preexisting cells. Exceptions: viruses are not made up of cells (only a protein coat and DNA) BUT th ...
... What to study - Cells Exam CELL THEORY 3 parts: 1. Cells are the basic unit of FUNCTION of all living things. 2. Cells are the basic unit of STRUCTURE of all living things. 3. All cells come from preexisting cells. Exceptions: viruses are not made up of cells (only a protein coat and DNA) BUT th ...
OLD BIO Cell
... B. It is selectively permeable so only certain molecules can pass through it. C. It acts more like a fluid than a solid because its molecules are constantly moving. D. Cell membranes surround all animal, plant, and bacterial cells. E. It is a bilayer composed mainly of phospholipids and proteins Cel ...
... B. It is selectively permeable so only certain molecules can pass through it. C. It acts more like a fluid than a solid because its molecules are constantly moving. D. Cell membranes surround all animal, plant, and bacterial cells. E. It is a bilayer composed mainly of phospholipids and proteins Cel ...
Review Session: Name: ______ Use your Unit 3 Notes to complete
... 1) Gather – slide, cover slip, specimen (must be translucent), water, (stain) dropper 2) Place specimen on slide 3) Place 3 drops of water (approx.) on top of the specimen 4) Place cover slip over slide – MUST be done at an angle to prevent bubbles! 13. Write levels of organization from the simplest ...
... 1) Gather – slide, cover slip, specimen (must be translucent), water, (stain) dropper 2) Place specimen on slide 3) Place 3 drops of water (approx.) on top of the specimen 4) Place cover slip over slide – MUST be done at an angle to prevent bubbles! 13. Write levels of organization from the simplest ...
Parts of a Cell Note Sheet:
... Surrounds the nucleus. Controls what enters and exits the nucleus. ...
... Surrounds the nucleus. Controls what enters and exits the nucleus. ...
Cell Organelles - MBBS Students Club
... usually in plant cells Many smaller vacuoles in animal cells Storage container for water, food, enzymes, wastes, pigments, etc. What type of microscope may have been used to take this picture? ...
... usually in plant cells Many smaller vacuoles in animal cells Storage container for water, food, enzymes, wastes, pigments, etc. What type of microscope may have been used to take this picture? ...
Cell Organelles
... usually in plant cells Many smaller vacuoles in animal cells Storage container for water, food, enzymes, wastes, pigments, etc. What type of microscope may have been used to take this picture? ...
... usually in plant cells Many smaller vacuoles in animal cells Storage container for water, food, enzymes, wastes, pigments, etc. What type of microscope may have been used to take this picture? ...
Prokaryotes - AP Biology Overview
... Capsule – covers outer cell wall – sticky protection from host cells Fimbriae – short numerous hairs that attach prokaryotes to one another Pili – longer hair – can be used for conjugation – DNA transfer from one bacteria to another ...
... Capsule – covers outer cell wall – sticky protection from host cells Fimbriae – short numerous hairs that attach prokaryotes to one another Pili – longer hair – can be used for conjugation – DNA transfer from one bacteria to another ...
Cell Organelles - Fall River Public Schools
... usually in plant cells Many smaller vacuoles in animal cells Storage container for water, food, enzymes, wastes, pigments, etc. What type of microscope may have been used to take this picture? ...
... usually in plant cells Many smaller vacuoles in animal cells Storage container for water, food, enzymes, wastes, pigments, etc. What type of microscope may have been used to take this picture? ...
Cell encapsulation

Cell microencapsulation technology involves immobilization of the cells within a polymeric semi-permeable membrane that permits the bidirectional diffusion of molecules such as the influx of oxygen, nutrients, growth factors etc. essential for cell metabolism and the outward diffusion of waste products and therapeutic proteins. At the same time, the semi-permeable nature of the membrane prevents immune cells and antibodies from destroying the encapsulated cells regarding them as foreign invaders.The main motive of cell encapsulation technology is to overcome the existing problem of graft rejection in tissue engineering applications and thus reduce the need for long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs after an organ transplant to control side effects.