The Basic Unit - missmbrougham
... The functions of living things are performed by the cells they are made of ...
... The functions of living things are performed by the cells they are made of ...
Study guide: Microscopes and Cells Study the
... Cell membrane Lipid bilayer that surrounds all cells; has lots of proteins embedded in it that help control what materials are allowed in or out Cell wall Structure that surrounds cells in plants and some protists; cellulose is an important component of plant cell walls Lysosome An organelle which c ...
... Cell membrane Lipid bilayer that surrounds all cells; has lots of proteins embedded in it that help control what materials are allowed in or out Cell wall Structure that surrounds cells in plants and some protists; cellulose is an important component of plant cell walls Lysosome An organelle which c ...
Cells_Review cell parts and people-blank
... 5. Who was the 1st person to see cells? 6. Who was the first person to observe the nucleus? 7. Are bacteria prokaryotes or eukaryotes? 8. Organisms whose cells contain nuclei are called what? 9. Organisms whose cells lack nuclei are called what? 10. What are the 3 parts of the cell theory? 11. A sma ...
... 5. Who was the 1st person to see cells? 6. Who was the first person to observe the nucleus? 7. Are bacteria prokaryotes or eukaryotes? 8. Organisms whose cells contain nuclei are called what? 9. Organisms whose cells lack nuclei are called what? 10. What are the 3 parts of the cell theory? 11. A sma ...
Cell Structure Guided Notes
... 3. 1838 - Mathias Schleiden concluded that all _______________ were composed of cells. 4. 1839 – Theodor Schwann concluded that all __________________ tissues are composed of cells. 5. What did Rudolph Virchow observe under the microscope in 1858? 6. What conclusion did Virchow make from this observ ...
... 3. 1838 - Mathias Schleiden concluded that all _______________ were composed of cells. 4. 1839 – Theodor Schwann concluded that all __________________ tissues are composed of cells. 5. What did Rudolph Virchow observe under the microscope in 1858? 6. What conclusion did Virchow make from this observ ...
Cell Notes - Marshall Middle
... Cells I. Looking at Cells A. Cells are the smallest, most basic unit of life. B. There are approximately 60 to 100 trillion cells in the average adult human. C. The microscope is a tool that helps us to look inside of cells. D. Discovery of Cells 1. 1665 - Robert Hooke used a primitive microscope to ...
... Cells I. Looking at Cells A. Cells are the smallest, most basic unit of life. B. There are approximately 60 to 100 trillion cells in the average adult human. C. The microscope is a tool that helps us to look inside of cells. D. Discovery of Cells 1. 1665 - Robert Hooke used a primitive microscope to ...
9 cells - WordPress.com
... • Anton van Leeuwenhoek (1675): was the first person to observe living cells. ...
... • Anton van Leeuwenhoek (1675): was the first person to observe living cells. ...
Cells
... the inside of the cell from the surrounding environment. These are found in BOTH plant and animal cells. ...
... the inside of the cell from the surrounding environment. These are found in BOTH plant and animal cells. ...
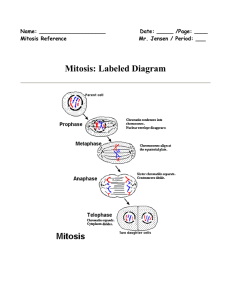
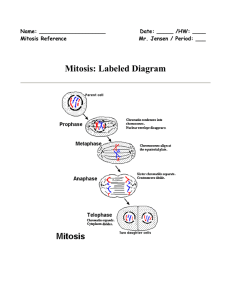
1. Describe two functions of centromere during mitosis. 2. a) Look at
... a) Micro propagation is the process where plant cell from any tissue specially the fast growing is taken and placed in nutrient medium. The cell will start dividing and give rise to the new cells which eventually produces the whole plant body. Suggest four advantages of producing plants by the micro ...
... a) Micro propagation is the process where plant cell from any tissue specially the fast growing is taken and placed in nutrient medium. The cell will start dividing and give rise to the new cells which eventually produces the whole plant body. Suggest four advantages of producing plants by the micro ...
Section 7.3
... Provides support and protection Made of cellulose Allows materials to pass through it but not selectively like plasma membrane ...
... Provides support and protection Made of cellulose Allows materials to pass through it but not selectively like plasma membrane ...
Institute for Genetics of the University of Cologne Christoph Möhl
... a severe limitation. A promising strategy to extract information on generalized cell architecture more objectively is averaging microscopic data over time and various cells. However, since migrating cells usually perform a random walk by constantly changing their location, shape and cytoskeletal org ...
... a severe limitation. A promising strategy to extract information on generalized cell architecture more objectively is averaging microscopic data over time and various cells. However, since migrating cells usually perform a random walk by constantly changing their location, shape and cytoskeletal org ...
Chapter 3/Lesson 1 Part 2 Notes
... •A diploid cell contains pairs of chromosomes that equal the chromosome number of that organism’s species. •For example, a diploid human cell has 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes or 46 total. •Homologous chromosomes are similar but not identical. Creating Haploid Cells •A haploid cell is a cell th ...
... •A diploid cell contains pairs of chromosomes that equal the chromosome number of that organism’s species. •For example, a diploid human cell has 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes or 46 total. •Homologous chromosomes are similar but not identical. Creating Haploid Cells •A haploid cell is a cell th ...
Characteristics of Cancer Cells
... Characteristics of Cancer Cells - How do they differ from “normal” cells ...
... Characteristics of Cancer Cells - How do they differ from “normal” cells ...
Study Guide for Microscope and Cell Test
... b. Cytoplasm – makes up 2/3 of a cell, it is a gel like substance that fills the cell c. Cell membrane – surrounds the cell ...
... b. Cytoplasm – makes up 2/3 of a cell, it is a gel like substance that fills the cell c. Cell membrane – surrounds the cell ...
Cell encapsulation

Cell microencapsulation technology involves immobilization of the cells within a polymeric semi-permeable membrane that permits the bidirectional diffusion of molecules such as the influx of oxygen, nutrients, growth factors etc. essential for cell metabolism and the outward diffusion of waste products and therapeutic proteins. At the same time, the semi-permeable nature of the membrane prevents immune cells and antibodies from destroying the encapsulated cells regarding them as foreign invaders.The main motive of cell encapsulation technology is to overcome the existing problem of graft rejection in tissue engineering applications and thus reduce the need for long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs after an organ transplant to control side effects.