Cells – How to accelerate their aging
... This study was designed to find a way of accelerating the aging process of those cells. Here something bad was used for the good. The Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria syndrome, caused by a genetic defect, lets patients age faster. We introduced the same genetic defects in stem cells and generated differe ...
... This study was designed to find a way of accelerating the aging process of those cells. Here something bad was used for the good. The Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria syndrome, caused by a genetic defect, lets patients age faster. We introduced the same genetic defects in stem cells and generated differe ...
Cell Review
... 9. Distinguish between active and passive transport (all three types). Provide examples to support your explanation. 10. Distinguish between endocytosis and exocytosis. Give examples of types of cells or organisms that use these processes. 11. Describe the different phases of the cell cycle. What is ...
... 9. Distinguish between active and passive transport (all three types). Provide examples to support your explanation. 10. Distinguish between endocytosis and exocytosis. Give examples of types of cells or organisms that use these processes. 11. Describe the different phases of the cell cycle. What is ...
BIOLOGY
... 16. What is the function of Chloroplasts? 17. What characteristic do Mitochondria and Chloroplasts share that make them different than other organelles? ...
... 16. What is the function of Chloroplasts? 17. What characteristic do Mitochondria and Chloroplasts share that make them different than other organelles? ...
Ch.1 Notes - Green Local Schools
... Doing it all means not doing any one thing really well. Example of tradeoff Fully-featured Swiss Army knife does many jobs, but each tool can be awkward to use. ...
... Doing it all means not doing any one thing really well. Example of tradeoff Fully-featured Swiss Army knife does many jobs, but each tool can be awkward to use. ...
The Need for Cell Division
... • Cells also need a constant supply of nutrients and waste must be removed • Molecules enter into and out of cells through the cell membrane • The more cell membrane there is compared with the volume of a cell, the more efficiently the cell can take in nutrients and eliminate waste ...
... • Cells also need a constant supply of nutrients and waste must be removed • Molecules enter into and out of cells through the cell membrane • The more cell membrane there is compared with the volume of a cell, the more efficiently the cell can take in nutrients and eliminate waste ...
Epithelial Cells
... Epithelia are tissue cells formed that line the cavities in the body and also cover flat surfaces. For example, outer skin covering, lining of the stomach, lining of the liver, lining of the kidneys, and even lining of the uterus. The epithelia cells are the most abundant tissue in the body. ...
... Epithelia are tissue cells formed that line the cavities in the body and also cover flat surfaces. For example, outer skin covering, lining of the stomach, lining of the liver, lining of the kidneys, and even lining of the uterus. The epithelia cells are the most abundant tissue in the body. ...
Name - DiBiasioScience
... d. active transport Short Answer In complete sentences, write the answers to the questions on the lines provided. 14. How do prokaryotes and eukaryotes differ? ...
... d. active transport Short Answer In complete sentences, write the answers to the questions on the lines provided. 14. How do prokaryotes and eukaryotes differ? ...
Science review for final test on cells and systems
... No. Some cells in your body are larger than others. Cells in fat tissue are bigger than cells in muscle tissue. Cells that must do a lot of work are usually smaller than cells that are less active. The more active a cell is, the more nutrients it needs and the ...
... No. Some cells in your body are larger than others. Cells in fat tissue are bigger than cells in muscle tissue. Cells that must do a lot of work are usually smaller than cells that are less active. The more active a cell is, the more nutrients it needs and the ...
Comparing Bacteria, Plants, and Animals Directions: U
... 12) some can make their own food, some cannot 3) cells have a nucleus 13) cells have mitochondria, ER, and vacuoles 4) cells do not have a nucleus 5) cells have DNA, cell membrane, and cytoplasm 6) cells have a cell wall 7) cells can have chloroplasts 8) organism made of many cells 9) organism made ...
... 12) some can make their own food, some cannot 3) cells have a nucleus 13) cells have mitochondria, ER, and vacuoles 4) cells do not have a nucleus 5) cells have DNA, cell membrane, and cytoplasm 6) cells have a cell wall 7) cells can have chloroplasts 8) organism made of many cells 9) organism made ...
Cells and tissues - questions
... 1 The drawing shows a group of three cells. Make an outline drawing to show how the cells would appear under the microscope if a thin section A-A was cut and mounted on a slide. ...
... 1 The drawing shows a group of three cells. Make an outline drawing to show how the cells would appear under the microscope if a thin section A-A was cut and mounted on a slide. ...
Biology Chapter 7
... Biology Chapter 7 Study Guide for Test Know the following Vocab: Cell wall Nucleus Chromatin Endoplasmic Reticulum Chlorophyll Cytoskeleton Transport Protein Cillia Mitochondria Pro vs. Eukaryotic Cell Plasma Membrane Organelles Ribosomes Lysosomes ...
... Biology Chapter 7 Study Guide for Test Know the following Vocab: Cell wall Nucleus Chromatin Endoplasmic Reticulum Chlorophyll Cytoskeleton Transport Protein Cillia Mitochondria Pro vs. Eukaryotic Cell Plasma Membrane Organelles Ribosomes Lysosomes ...
Cell Vocabulary
... protein synthesis and break down to carry it from one part to the other. Both Cells 11. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum- Both Cells- Transfer system which helps so carry substances throughout the cell. 12. Ribosomes- Like Factories that produce protein. May be attached to Rough ER or float freely. Both ...
... protein synthesis and break down to carry it from one part to the other. Both Cells 11. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum- Both Cells- Transfer system which helps so carry substances throughout the cell. 12. Ribosomes- Like Factories that produce protein. May be attached to Rough ER or float freely. Both ...
Plant and Animal Cells www
... diagram. If you are not sure of the name of an organelle, click on it to find out. ...
... diagram. If you are not sure of the name of an organelle, click on it to find out. ...
Botany review What adaptive advantage does the large surface area
... What adaptive advantage does the large surface area of leaves provide to plants? Know the various structural features unique to dicots and monocots. Ie. Leaf venation, flower arrangement, vascular tissue, etc. What tissue is found in leaf veins? In which layer of cells in a leaf does most photosynth ...
... What adaptive advantage does the large surface area of leaves provide to plants? Know the various structural features unique to dicots and monocots. Ie. Leaf venation, flower arrangement, vascular tissue, etc. What tissue is found in leaf veins? In which layer of cells in a leaf does most photosynth ...
Microbodies
... functions to help the body break down large molecules and detoxify hazardous substances It contains oxidative enzymes and catalysts. ...
... functions to help the body break down large molecules and detoxify hazardous substances It contains oxidative enzymes and catalysts. ...
The cell is the smallest unit of life
... The ________ ________ is a rigid layer of non-living material that surrounds the cells of plants and some other organisms. The cell wall is made of a tough, yet flexible, material called __________________. The function of the ____________ ____________is to support and protect the plant cell. The ce ...
... The ________ ________ is a rigid layer of non-living material that surrounds the cells of plants and some other organisms. The cell wall is made of a tough, yet flexible, material called __________________. The function of the ____________ ____________is to support and protect the plant cell. The ce ...
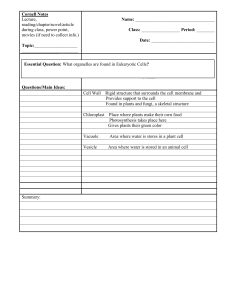
Organelle Notes #2
... Cornell Notes Lecture, reading/chapter/novel/article during class, power point, movies (if need to collect info.) ...
... Cornell Notes Lecture, reading/chapter/novel/article during class, power point, movies (if need to collect info.) ...
Slide 1
... Cell wall – distinguishes plant cells from animal cells; metabolically active and/or structural Plasma membrane - surrounding the ...
... Cell wall – distinguishes plant cells from animal cells; metabolically active and/or structural Plasma membrane - surrounding the ...
Cell Theory, Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic Cells
... Prokaryotic Cells – They are cells that have a cell membrane and cytoplasm, but do not contain a nucleus. (bacteria) ...
... Prokaryotic Cells – They are cells that have a cell membrane and cytoplasm, but do not contain a nucleus. (bacteria) ...
Cell encapsulation

Cell microencapsulation technology involves immobilization of the cells within a polymeric semi-permeable membrane that permits the bidirectional diffusion of molecules such as the influx of oxygen, nutrients, growth factors etc. essential for cell metabolism and the outward diffusion of waste products and therapeutic proteins. At the same time, the semi-permeable nature of the membrane prevents immune cells and antibodies from destroying the encapsulated cells regarding them as foreign invaders.The main motive of cell encapsulation technology is to overcome the existing problem of graft rejection in tissue engineering applications and thus reduce the need for long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs after an organ transplant to control side effects.