Cells specialize to carry out different jobs
... cell, it begins to divide. The single cell divides by mitosis until it forms a ball of cells called an embryo. At some early point in the life of this embryo, the cells begin to specialize. When cells specialize, they become equipped to take on different jobs in the body. For example, some of the ce ...
... cell, it begins to divide. The single cell divides by mitosis until it forms a ball of cells called an embryo. At some early point in the life of this embryo, the cells begin to specialize. When cells specialize, they become equipped to take on different jobs in the body. For example, some of the ce ...
Chapter 1 Eukaryotic Cells Section 1
... Nucleus – largest organelle in a eukaryotic cell, contains DNA that directs all cell activity Ribosomes – organelles that make protein Endoplasmic reticulum – folded membrane where cell materials are made (proteins, lipids) and moved to different places in the cell Mitochondria – power source of a c ...
... Nucleus – largest organelle in a eukaryotic cell, contains DNA that directs all cell activity Ribosomes – organelles that make protein Endoplasmic reticulum – folded membrane where cell materials are made (proteins, lipids) and moved to different places in the cell Mitochondria – power source of a c ...
LT2a, 1b size.
... LT2a, 1b Using scaling theory, explain why cells have an upper limit on their size. (Hint: “Surface area increases by the ______ of length while volume increases by the _____ of length.”) Equate the appropriate parts of the cell with surface area and volume to explain. ...
... LT2a, 1b Using scaling theory, explain why cells have an upper limit on their size. (Hint: “Surface area increases by the ______ of length while volume increases by the _____ of length.”) Equate the appropriate parts of the cell with surface area and volume to explain. ...
Cells and Structure
... Schleiden, Schwann and Virchow - 1800s The cell is the basic and smallest unit of life All cells arise from pre-existing cells The cell is the working unit of organisms ...
... Schleiden, Schwann and Virchow - 1800s The cell is the basic and smallest unit of life All cells arise from pre-existing cells The cell is the working unit of organisms ...
Ch 6: Cells
... Evidence: Chloroplasts and mitochondria each have their own separate DNA and can reproduce on their own ...
... Evidence: Chloroplasts and mitochondria each have their own separate DNA and can reproduce on their own ...
Assignment Discovery: Cells
... B) It produces food for the cell. C) Waste leaves the cell through the nucleus. D) It controls all the activities of the cell. ...
... B) It produces food for the cell. C) Waste leaves the cell through the nucleus. D) It controls all the activities of the cell. ...
Classifying Living Things A2-A11
... Nucleus= control center of cell (brain) Cytoplasm= fluid inside cell where all the parts float Mitochondria= releases energy into cell Cell membrane= holds the cell together ...
... Nucleus= control center of cell (brain) Cytoplasm= fluid inside cell where all the parts float Mitochondria= releases energy into cell Cell membrane= holds the cell together ...
Anatomy and development of the adult spinal cord neural stem cell
... Professor Kate Storey (co- supervisor Dr Paul Felts) Division of Cell & Developmental Biology College of Life Sciences, University of Dundee The aim of this project is to characterize the heterogeneous cell populations within the adult mouse spinal cord stem cell niche, investigate the regulation of ...
... Professor Kate Storey (co- supervisor Dr Paul Felts) Division of Cell & Developmental Biology College of Life Sciences, University of Dundee The aim of this project is to characterize the heterogeneous cell populations within the adult mouse spinal cord stem cell niche, investigate the regulation of ...
Comparing Plant and Animal Cells
... Comparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Integrated Science 1 N ame: ...
... Comparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Integrated Science 1 N ame: ...
Cell Theory and Scientists
... He saw what appeared to be thousands of tiny empty chambers. He called these chambers cells... and the term is still used today. 1674 - Anton van Leeuwenhoek used a single-lens microscope to observe pond water - and revealed a world of tiny living organisms. He drew illustrations of organisms he fou ...
... He saw what appeared to be thousands of tiny empty chambers. He called these chambers cells... and the term is still used today. 1674 - Anton van Leeuwenhoek used a single-lens microscope to observe pond water - and revealed a world of tiny living organisms. He drew illustrations of organisms he fou ...
Cells and Organelles Chart
... Science North is an agency of the Government of Ontario and a registered charity #10796 2979 RR0001. ...
... Science North is an agency of the Government of Ontario and a registered charity #10796 2979 RR0001. ...
Biology- ch. 7
... • All living things are composed of cells • Cells are the basic units of structure and organization in living things • New cells are produced from existing cells with cells passing copies of their genetic material down to their daughter cells ...
... • All living things are composed of cells • Cells are the basic units of structure and organization in living things • New cells are produced from existing cells with cells passing copies of their genetic material down to their daughter cells ...
By570PresAnimated
... Students will be able to calculate data from Punnett’s squares and determine probabilities of inheritance ...
... Students will be able to calculate data from Punnett’s squares and determine probabilities of inheritance ...
What is a Cell?
... Animal like Motile Feed Phagocytosis Algae Plant like Uses photosynthesis for its nutrients Some motile, some are not ...
... Animal like Motile Feed Phagocytosis Algae Plant like Uses photosynthesis for its nutrients Some motile, some are not ...
Cell Review Cell Theory Levels of Organization Organelle
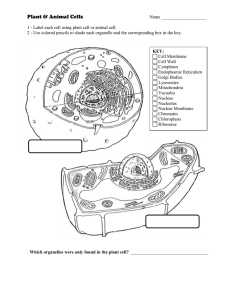
... 6. Cell Membrane – Barrier of protection for the cell (Allows nutrients in and waste out) 8. Vacuole – Stores water and waste. 4. Chloroplasts – Makes food for the plant cell. 2. Cell Wall – Only in plants to give a rigid structure and add barrier of protection. 7. Ribosome – Creates protein Plant C ...
... 6. Cell Membrane – Barrier of protection for the cell (Allows nutrients in and waste out) 8. Vacuole – Stores water and waste. 4. Chloroplasts – Makes food for the plant cell. 2. Cell Wall – Only in plants to give a rigid structure and add barrier of protection. 7. Ribosome – Creates protein Plant C ...
Name - Marissa Elementary School
... Look up the following answers in your Chapter 1 ISN notes. 1. What is a species? A group of organisms that have the same characteristics and produce offspring ...
... Look up the following answers in your Chapter 1 ISN notes. 1. What is a species? A group of organisms that have the same characteristics and produce offspring ...
Name - cloudfront.net
... saw CELLS. He was actually observing CORK TREE cell walls magnified only 30 times. D. Electron microscopes invented in 1928 using ELECTRONS instead of LIGHT passing through an object—can only use DEAD cells. (Transmission Electron Microscope 1 MILLION stronger than light microscope and Scanning Elec ...
... saw CELLS. He was actually observing CORK TREE cell walls magnified only 30 times. D. Electron microscopes invented in 1928 using ELECTRONS instead of LIGHT passing through an object—can only use DEAD cells. (Transmission Electron Microscope 1 MILLION stronger than light microscope and Scanning Elec ...
Eukaryotic cells Section review model answers Ribosomes are
... series of folded membranes on which lipids, proteins, and other materials are made, and through which those materials are delivered to other places in the cell. 4. Plant cells have cell walls, but animal cells do not. Plant cells have chloroplasts, which animal cells do not have. Plant cells do not ...
... series of folded membranes on which lipids, proteins, and other materials are made, and through which those materials are delivered to other places in the cell. 4. Plant cells have cell walls, but animal cells do not. Plant cells have chloroplasts, which animal cells do not have. Plant cells do not ...
Cell encapsulation

Cell microencapsulation technology involves immobilization of the cells within a polymeric semi-permeable membrane that permits the bidirectional diffusion of molecules such as the influx of oxygen, nutrients, growth factors etc. essential for cell metabolism and the outward diffusion of waste products and therapeutic proteins. At the same time, the semi-permeable nature of the membrane prevents immune cells and antibodies from destroying the encapsulated cells regarding them as foreign invaders.The main motive of cell encapsulation technology is to overcome the existing problem of graft rejection in tissue engineering applications and thus reduce the need for long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs after an organ transplant to control side effects.