L4 Prokaryotes eukaryotes and onion cheek preps
... Much simpler in structure, lack membrane bound organelles (mitochondria, chloroplasts). Lack complex structures such as Golgi bodies, cytoskeleton and lysosomes. • Nucleotide (or Nuclear Zone). The region of the cytoplasm that contains DNA. It is not surrounded by a nuclear membrane. • DNA. Always c ...
... Much simpler in structure, lack membrane bound organelles (mitochondria, chloroplasts). Lack complex structures such as Golgi bodies, cytoskeleton and lysosomes. • Nucleotide (or Nuclear Zone). The region of the cytoplasm that contains DNA. It is not surrounded by a nuclear membrane. • DNA. Always c ...
Centrioles are self-replicating organelles made up
... network of sacs that manufactures, processes, and transports chemical compounds for use inside and outside of the cell. It is connected to the double-layered nuclear envelope, providing a connection between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. Golgi Apparatus - The Golgi apparatus is the distribution and ...
... network of sacs that manufactures, processes, and transports chemical compounds for use inside and outside of the cell. It is connected to the double-layered nuclear envelope, providing a connection between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. Golgi Apparatus - The Golgi apparatus is the distribution and ...
Microbiology Slides - Welcome to Cherokee High School
... • Small size ( 0.5 to 2um) • Large surface area to volume ratio • A variety of shapes • Outer cell wall- very thick made of specialized molecules • Cell membranes may have a different constituency of molecules from eukaryote cells • Ribosomes smaller ...
... • Small size ( 0.5 to 2um) • Large surface area to volume ratio • A variety of shapes • Outer cell wall- very thick made of specialized molecules • Cell membranes may have a different constituency of molecules from eukaryote cells • Ribosomes smaller ...
Chapter 4 and 5 Tests
... What is “freezer burn” Where are lysosomes made and what are they? What are cilia? What effect do acids and bases have on the performance of enzymes? (Hint: enzymes can only perform properly within a narrow pH range) The Central Vacuole The Fluid Mosaic Model The phospholipid bi-layer Blood Types an ...
... What is “freezer burn” Where are lysosomes made and what are they? What are cilia? What effect do acids and bases have on the performance of enzymes? (Hint: enzymes can only perform properly within a narrow pH range) The Central Vacuole The Fluid Mosaic Model The phospholipid bi-layer Blood Types an ...
Cell Theory
... All cells come from pre-existing cells. Important organelles in a cell Nucleus: Contains the cell’s DNA. ‘Brain’ of the cell. Mitochondrion: Site of respiration. Provides the energy for the cell to function. Ribosomes: Site where proteins are made (including enzymes) Vacuole: Storage. Cytoplasm: W ...
... All cells come from pre-existing cells. Important organelles in a cell Nucleus: Contains the cell’s DNA. ‘Brain’ of the cell. Mitochondrion: Site of respiration. Provides the energy for the cell to function. Ribosomes: Site where proteins are made (including enzymes) Vacuole: Storage. Cytoplasm: W ...
Each of your cells is a miniature marvel
... Each of your cells is a miniature marvel. Consider taking a complex machine with millions of parts—say a jumbo jet—and shrinking it to microscopic size while keeping everything in working order. It would still seem simple compared to a living cell. Everything you do, every action and every thought, ...
... Each of your cells is a miniature marvel. Consider taking a complex machine with millions of parts—say a jumbo jet—and shrinking it to microscopic size while keeping everything in working order. It would still seem simple compared to a living cell. Everything you do, every action and every thought, ...
CELL FLIP NOTES - blog part 1
... • A prokaryotic cell is enclosed by a plasma membrane and is usually encased in a rigid cell wall –The cell wall may be covered by a sticky capsule –Inside the cell are its DNA and other parts ...
... • A prokaryotic cell is enclosed by a plasma membrane and is usually encased in a rigid cell wall –The cell wall may be covered by a sticky capsule –Inside the cell are its DNA and other parts ...
Cells
... Cell is the smallest unit that has all of the basic properties of life. Cells come from preexisting cells. ...
... Cell is the smallest unit that has all of the basic properties of life. Cells come from preexisting cells. ...
Cell Surface 1.Cell wall: of the plant cells
... secreted by the cells: collagen, fibronectin which bind to integrins receptor protein. Integrins bind to microfilaments on the cytoplasmic side. Thus integrins transmit changes in the ECM to cytoskeleton and vice versa. ...
... secreted by the cells: collagen, fibronectin which bind to integrins receptor protein. Integrins bind to microfilaments on the cytoplasmic side. Thus integrins transmit changes in the ECM to cytoskeleton and vice versa. ...
Cell theory + structure
... Describe the contributions of the following scientists: Robert Hooke – Anton van Leeuwenhoek – Matthias Schleiden – Theodor Schwann – Rudolph Virchow – All cells come from pre-existing cells The Cell Theory State the three components of the cell theory: 1. ___________________________________________ ...
... Describe the contributions of the following scientists: Robert Hooke – Anton van Leeuwenhoek – Matthias Schleiden – Theodor Schwann – Rudolph Virchow – All cells come from pre-existing cells The Cell Theory State the three components of the cell theory: 1. ___________________________________________ ...
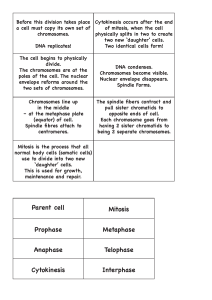
Parent cell Mitosis Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase
... DNA replicates! Two identical cells form! The cell begins to physically divide. The chromosomes are at the poles of the cell. The nuclear envelope reforms around the two sets of chromosomes. Chromosomes line up in the middle – at the metaphase plate (equator) of cell. centromeres. ...
... DNA replicates! Two identical cells form! The cell begins to physically divide. The chromosomes are at the poles of the cell. The nuclear envelope reforms around the two sets of chromosomes. Chromosomes line up in the middle – at the metaphase plate (equator) of cell. centromeres. ...
Cell/Microscope Review - Union Beach School District
... have the ability to reproduce move grow and develop ...
... have the ability to reproduce move grow and develop ...
Unit 2- Topic One - St. John Paul II Collegiate
... *Know the names of the organisms on pg 115, Figure 2.5 Amoeba – like “the blob” a unicellular organism that eats by flowing around it and absorbing it. It reproduces by splitting into two amoebas. Parts of a cell Cytoplasm: jelly-like material in which other parts of the cell float ...
... *Know the names of the organisms on pg 115, Figure 2.5 Amoeba – like “the blob” a unicellular organism that eats by flowing around it and absorbing it. It reproduces by splitting into two amoebas. Parts of a cell Cytoplasm: jelly-like material in which other parts of the cell float ...
Introduction: Apoptosis – programmed cell death significantly
... Apoptosis – programmed cell death significantly participates in maintaining of tissue homeostasis. Its alteration is leading to cancer disease. Inositolhexaphosphate (IP6) is naturally occurring substance that is present in most legumes, cereals and seems. IP6 and its lower phosphorylated forms are ...
... Apoptosis – programmed cell death significantly participates in maintaining of tissue homeostasis. Its alteration is leading to cancer disease. Inositolhexaphosphate (IP6) is naturally occurring substance that is present in most legumes, cereals and seems. IP6 and its lower phosphorylated forms are ...
Cell Diversity
... Cells are limited in size by the ratio between their outer surface area and their volume. This means that if a cell keeps the same shape as it grows, its volume will increase more rapidly than its surface area At some point, its surface area becomes too small to allow nutrients, oxygen, and other ma ...
... Cells are limited in size by the ratio between their outer surface area and their volume. This means that if a cell keeps the same shape as it grows, its volume will increase more rapidly than its surface area At some point, its surface area becomes too small to allow nutrients, oxygen, and other ma ...
doc 3.2.1.1 eukaryotes checklist
... The structure of eukaryotic cells, restricted to the structure and function of: •• cell-surface membrane ...
... The structure of eukaryotic cells, restricted to the structure and function of: •• cell-surface membrane ...
The Cell - SNC2PSylvia2011
... Most cells can be seen with the naked eye All living things are made of cells. Plant cells and animal cells are the same. Humans are made up of trillions of cells. New cells come from cells that were already ...
... Most cells can be seen with the naked eye All living things are made of cells. Plant cells and animal cells are the same. Humans are made up of trillions of cells. New cells come from cells that were already ...
Biology EOC Review 6 Cell Cycle, Transport and Differentiation
... D. facilitated diffusion. 5. Water moves out of a cell when the concentration surrounding the cell is A. hypertonic. B. isotonic. C. hypotonic. 6. Cells use active transport to A. obtain molecules they need. B. break down molecules. C. engulf large particles. D. detect the charge of molecules. 7. A ...
... D. facilitated diffusion. 5. Water moves out of a cell when the concentration surrounding the cell is A. hypertonic. B. isotonic. C. hypotonic. 6. Cells use active transport to A. obtain molecules they need. B. break down molecules. C. engulf large particles. D. detect the charge of molecules. 7. A ...
01A004 - Proliferated Cell Lines and Uses Thereof
... Despite the promising potential of cellular therapies, one fundamental problem that has long hindered implementation is the fact that most cells are only capable of replicating a finite number of times. As this technique can be employed on virtually any adult cell type, potential applications where ...
... Despite the promising potential of cellular therapies, one fundamental problem that has long hindered implementation is the fact that most cells are only capable of replicating a finite number of times. As this technique can be employed on virtually any adult cell type, potential applications where ...
Cell culture on high-extension surfaces
... Cell culture on high-extension surfaces: Novel technology in support of regenerative medicine Thomas M. Quinn and Derek H. Rosenzweig While seeking ways for improved culture of chondrocytes for cartilage tissue engineering, we have developed novel technology for cell culture on extendable surfaces. ...
... Cell culture on high-extension surfaces: Novel technology in support of regenerative medicine Thomas M. Quinn and Derek H. Rosenzweig While seeking ways for improved culture of chondrocytes for cartilage tissue engineering, we have developed novel technology for cell culture on extendable surfaces. ...
cell Basic unit of structure and function of all living things. All liv
... Particles of a substance move from an area where there are a lot of particles of a substance to an area where there are fewer particles of a substance. More to less ...
... Particles of a substance move from an area where there are a lot of particles of a substance to an area where there are fewer particles of a substance. More to less ...
Cell encapsulation

Cell microencapsulation technology involves immobilization of the cells within a polymeric semi-permeable membrane that permits the bidirectional diffusion of molecules such as the influx of oxygen, nutrients, growth factors etc. essential for cell metabolism and the outward diffusion of waste products and therapeutic proteins. At the same time, the semi-permeable nature of the membrane prevents immune cells and antibodies from destroying the encapsulated cells regarding them as foreign invaders.The main motive of cell encapsulation technology is to overcome the existing problem of graft rejection in tissue engineering applications and thus reduce the need for long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs after an organ transplant to control side effects.