Cells
... – Develop special features to carry out specific functions – Different functions can be performed at the same time ...
... – Develop special features to carry out specific functions – Different functions can be performed at the same time ...
02. Organizing principles of human body
... Made up of cells and cellular organelles (molecules) Cells can be eukaryotic or prokaryotic ...
... Made up of cells and cellular organelles (molecules) Cells can be eukaryotic or prokaryotic ...
Study Guide for Chapter 4 - Cells: Basic Unit of Life
... You are not required to answer these questions. But can you answer them? If not, make sure you find the answer before the day of the test. NOTE: Please understand that these are only general questions. Any information you read, took notes on, saw in a movie, practiced in an activity, answered on a w ...
... You are not required to answer these questions. But can you answer them? If not, make sure you find the answer before the day of the test. NOTE: Please understand that these are only general questions. Any information you read, took notes on, saw in a movie, practiced in an activity, answered on a w ...
Cells - SawyerScience
... 2. Most one-celled organisms are prokaryotic. 3. Plants and animals have eukaryotic cells. 4. Animal cells are enclosed in a cell wall. ...
... 2. Most one-celled organisms are prokaryotic. 3. Plants and animals have eukaryotic cells. 4. Animal cells are enclosed in a cell wall. ...
RUNX1 Modulates TGF-β1-Induced Myofibroblast Differentiation in
... Reactive stroma in prostate cancer is typified by the co-evolution of myofibroblasts. This reactive stroma is associated with most human carcinoma and more reactive stroma is predictive of aggressive disease progression. TGFβ1 is a key factor in regulating reactive stroma biology. However, the origi ...
... Reactive stroma in prostate cancer is typified by the co-evolution of myofibroblasts. This reactive stroma is associated with most human carcinoma and more reactive stroma is predictive of aggressive disease progression. TGFβ1 is a key factor in regulating reactive stroma biology. However, the origi ...
Cell: basic unit of structure and function of life. Prokaryotic: cells that
... Mitochondria: use oxygen to transfer energy in food to a form that the cell can use to carry out its activities. Endoplasmic reticulum: produce important products for the cell, including proteins and lipids. Golgi bodies: Help package products from the endoplasmic reticulum and distribute them aroun ...
... Mitochondria: use oxygen to transfer energy in food to a form that the cell can use to carry out its activities. Endoplasmic reticulum: produce important products for the cell, including proteins and lipids. Golgi bodies: Help package products from the endoplasmic reticulum and distribute them aroun ...
Slide ()
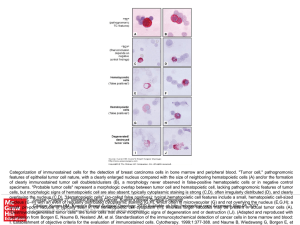
... Categorization of immunostained cells for the detection of breast carcinoma cells in bone marrow and peripheral blood. "Tumor cell," pathognomonic features of epithelial tumor cell nature, with a clearly enlarged nucleus compared with the size of neighboring hematopoietic cells (A) and/or the format ...
... Categorization of immunostained cells for the detection of breast carcinoma cells in bone marrow and peripheral blood. "Tumor cell," pathognomonic features of epithelial tumor cell nature, with a clearly enlarged nucleus compared with the size of neighboring hematopoietic cells (A) and/or the format ...
Biology – Wilson
... 16. Because cells are hypertonic in relation to fresh water, ___________________________ produces a net movement of water into the cell. If that happens, the cell will become ____________________________ and can even burst. 17. In plant and bacteria cells, what keeps them from bursting due to osmoti ...
... 16. Because cells are hypertonic in relation to fresh water, ___________________________ produces a net movement of water into the cell. If that happens, the cell will become ____________________________ and can even burst. 17. In plant and bacteria cells, what keeps them from bursting due to osmoti ...
Directed Reading A
... ______19. Chloroplasts are organelles that are found in the cells of a. animals. c. mitochondria. b. plants and algae. d. all eukaryotic cells. ______20. Which process happens inside a chloroplast? a. production of ATP c. photosynthesis b. production of DNA d. formation of animal cells ______21. Chl ...
... ______19. Chloroplasts are organelles that are found in the cells of a. animals. c. mitochondria. b. plants and algae. d. all eukaryotic cells. ______20. Which process happens inside a chloroplast? a. production of ATP c. photosynthesis b. production of DNA d. formation of animal cells ______21. Chl ...
Cells - Wsfcs
... 28. In what part of a cell are organelles found? 29. What is cytosol & what does it contain? 30. Name 3 organelles found in plant, but not animal cells. (See bottom of table ...
... 28. In what part of a cell are organelles found? 29. What is cytosol & what does it contain? 30. Name 3 organelles found in plant, but not animal cells. (See bottom of table ...
Cell Organelles Review Package
... 23. Why are many membranes that are present in cells interchangeable? Give an example in your explanation. __________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 24. Which organelles will probably be more abundant than others in an active eukary ...
... 23. Why are many membranes that are present in cells interchangeable? Give an example in your explanation. __________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 24. Which organelles will probably be more abundant than others in an active eukary ...
The Origin of Eukaryotic Cells
... prokaryotic cell membrane folded inward (invaginated) to enclose copies of its genetic material. This invagination resulted in the formation of several doublemembrane-bound entities (organelles) in a single cell. These entities could then have evolved into the eukaryotic mitochondrion, nucleus and c ...
... prokaryotic cell membrane folded inward (invaginated) to enclose copies of its genetic material. This invagination resulted in the formation of several doublemembrane-bound entities (organelles) in a single cell. These entities could then have evolved into the eukaryotic mitochondrion, nucleus and c ...
High hydrostatic pressure induces immunogenic cell
... Fučíková, Ph.D., Department of Immunology Abstract Recent studies have identified molecular events characteristic of immunogenic cell death (ICD), including surface exposure of calreticulin (CRT), the heat shock proteins HSP70 and HSP90, the release of highmobility group box protein 1 (HMGB1) and th ...
... Fučíková, Ph.D., Department of Immunology Abstract Recent studies have identified molecular events characteristic of immunogenic cell death (ICD), including surface exposure of calreticulin (CRT), the heat shock proteins HSP70 and HSP90, the release of highmobility group box protein 1 (HMGB1) and th ...
Ch. 7-Cells Lecture #1 blanks
... A. ____- The basic unit of living organisms B. The ______ was developed by several scientists including Hooke, Schleiden andSchwann. ...
... A. ____- The basic unit of living organisms B. The ______ was developed by several scientists including Hooke, Schleiden andSchwann. ...
Cell Organelle Table
... carbohydrates to specific locations Single membrane bound structure that comes from Golgi body – contain enzymes to digest Play an important role in cell division (guide the chromosomes to proper places) The backbone of the cell – supports the cell shape, anchors the organelle, provides highway syst ...
... carbohydrates to specific locations Single membrane bound structure that comes from Golgi body – contain enzymes to digest Play an important role in cell division (guide the chromosomes to proper places) The backbone of the cell – supports the cell shape, anchors the organelle, provides highway syst ...
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells on PDF File
... eukaryote. Which structure is present in both organisms? A. a nucleus that controls the actions of the cell B. a mitochondria that provides the cell with energy C. a cell wall that maintains a rigid structure for the cell D. a cell membrane that holds in the contents of the cell ...
... eukaryote. Which structure is present in both organisms? A. a nucleus that controls the actions of the cell B. a mitochondria that provides the cell with energy C. a cell wall that maintains a rigid structure for the cell D. a cell membrane that holds in the contents of the cell ...
DNA THE BASICS AND BEYOND Name Per
... 8. Give a way the two are similar. 9. Give a way that they are different Somatic Nuclear Transfer 10. Somatic cell nuclear transfer (_________), also called _________ transfer, uses a different approach than artificial embryo twinning but it __________ the same ____________ Somatic Cell 11. A ______ ...
... 8. Give a way the two are similar. 9. Give a way that they are different Somatic Nuclear Transfer 10. Somatic cell nuclear transfer (_________), also called _________ transfer, uses a different approach than artificial embryo twinning but it __________ the same ____________ Somatic Cell 11. A ______ ...
Cellular Structure Notes Part 1
... 3. Cytoplasm – gelatin-like substance inside cell membrane a. Cytoskeleton - scaffolding-like structure in cytoplasm which helps cell keep its shape b. In the cytoplasm, eukaryotic cells (cells with a defined nucleus) have organelles which help with cell life processes. 4. Nucleus – contains instruc ...
... 3. Cytoplasm – gelatin-like substance inside cell membrane a. Cytoskeleton - scaffolding-like structure in cytoplasm which helps cell keep its shape b. In the cytoplasm, eukaryotic cells (cells with a defined nucleus) have organelles which help with cell life processes. 4. Nucleus – contains instruc ...
Cells and Cell Processes Review
... Name ____________________________________ Cells and Cell Processes Review Sheet ...
... Name ____________________________________ Cells and Cell Processes Review Sheet ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.