BIOLOGY 2a SUMMARY SHEET - Downlands Community School
... gradient) Oxygen for respiration passes through cell membranes by diffusion. ...
... gradient) Oxygen for respiration passes through cell membranes by diffusion. ...
Review Sheet Answers
... A cell is the basic unit of structure and function. Unicellular organisms are singlecelled organisms. Multicellular organisms are composed of many cells. 3. What are the three parts of cell theory? All living things are composed of cells, cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living ...
... A cell is the basic unit of structure and function. Unicellular organisms are singlecelled organisms. Multicellular organisms are composed of many cells. 3. What are the three parts of cell theory? All living things are composed of cells, cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living ...
112-lesson-3 - Macmillan Academy
... of the respiratory tract 2. Name two target tissues for insulin 3. Botulinum toxin binds to the ends of nerves and stops them from releasing chemicals that normally cause muscles to contract. There are 8 different boltulinum toxins, some stronger than others. Suggest why some are more potent than ot ...
... of the respiratory tract 2. Name two target tissues for insulin 3. Botulinum toxin binds to the ends of nerves and stops them from releasing chemicals that normally cause muscles to contract. There are 8 different boltulinum toxins, some stronger than others. Suggest why some are more potent than ot ...
Slide
... Electron micrographs of tangential sections through the cribriform TM region. (A) The cribriform cell (CR) was attached to BM-like material (BM) at places where the cribriform elastic fibers (EL) were connected to the cell by cross-banded connecting fibrils (CFs; arrows). The cell membrane was undul ...
... Electron micrographs of tangential sections through the cribriform TM region. (A) The cribriform cell (CR) was attached to BM-like material (BM) at places where the cribriform elastic fibers (EL) were connected to the cell by cross-banded connecting fibrils (CFs; arrows). The cell membrane was undul ...
UNIT 2 : Cells - Loudoun County Public Schools
... 1. Explain why cells are called the basic units of life. a) All living things are made of one or more cells. b) All cells come from pre-existing cells. c) Cells are very small to make it easy for nutrients to enter the cell and wastes to exit the cell. d) Scientist Associated with the Cell Theory (h ...
... 1. Explain why cells are called the basic units of life. a) All living things are made of one or more cells. b) All cells come from pre-existing cells. c) Cells are very small to make it easy for nutrients to enter the cell and wastes to exit the cell. d) Scientist Associated with the Cell Theory (h ...
Flushing High School
... 1. The process by which an organism keeps internal conditions fairly constant is _________________ . 2. A(An) _______________________________ is a procedure that changes only one variable at a time and keeps the others constant. 3. The information you gather from observations makes up your _________ ...
... 1. The process by which an organism keeps internal conditions fairly constant is _________________ . 2. A(An) _______________________________ is a procedure that changes only one variable at a time and keeps the others constant. 3. The information you gather from observations makes up your _________ ...
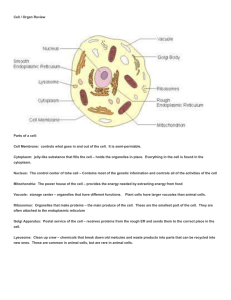
Cell / Organ Review Parts of a cell: Cell Membrane: controls what
... Ground Tissue (where photosynthesis takes palce)Observe and distinguish the cell wall, cell membrane, nucleus, chloroplast, and cytoplasm of cells. ...
... Ground Tissue (where photosynthesis takes palce)Observe and distinguish the cell wall, cell membrane, nucleus, chloroplast, and cytoplasm of cells. ...
Document
... We see cells in our fridge. Example: eggs Most expensive egg cell: caviar (Human sperm cells cost: 1 cent for 20,000 cells) Eggs are the largest and most expensive cells in the world. ...
... We see cells in our fridge. Example: eggs Most expensive egg cell: caviar (Human sperm cells cost: 1 cent for 20,000 cells) Eggs are the largest and most expensive cells in the world. ...
Chapter 21 Presentation-The Genetic Basis of Development
... encoded region is part of the protein that functions as a transcription regulator. The shape of the encoded region allows it to bind to any DNA segment, but by itself, it cannot select a specific sequence. The variable regions within the whole protein allow it to interact with other transcription ...
... encoded region is part of the protein that functions as a transcription regulator. The shape of the encoded region allows it to bind to any DNA segment, but by itself, it cannot select a specific sequence. The variable regions within the whole protein allow it to interact with other transcription ...
Cells: Chapter 2
... • Uses host cells enzymes and ribosomes for replication • Lysogenic phase: viruses may remain dormant inside host cells for long periods. There is no obvious change in their host cells • Can enter the lytic phase: new viruses are produced, assemble, and burst out of the host cell. • The cell is kill ...
... • Uses host cells enzymes and ribosomes for replication • Lysogenic phase: viruses may remain dormant inside host cells for long periods. There is no obvious change in their host cells • Can enter the lytic phase: new viruses are produced, assemble, and burst out of the host cell. • The cell is kill ...
Stem Cells: Links to Human Cancer and Aging
... histone methylation marks of both transcriptionally active and silent promoters (9). These chromatin structures, called “bivalent domains”, have been suggested to comprise transcriptionally repressed chromatin that is poised for selective activation by, for example, differentiation-inducing signalin ...
... histone methylation marks of both transcriptionally active and silent promoters (9). These chromatin structures, called “bivalent domains”, have been suggested to comprise transcriptionally repressed chromatin that is poised for selective activation by, for example, differentiation-inducing signalin ...
eukaryotic cell worksheet
... IB drawing rules. Your annotations of functions should not be included on the drawing but put underneath or on another piece of paper. The description of the organelle functions should be brief – not to exceed 10 words. 1. Draw and label a diagram of the ultrastructure of an exocrine gland cell of t ...
... IB drawing rules. Your annotations of functions should not be included on the drawing but put underneath or on another piece of paper. The description of the organelle functions should be brief – not to exceed 10 words. 1. Draw and label a diagram of the ultrastructure of an exocrine gland cell of t ...
File - Dr. Kamhi`s Science Website
... This is a brief expanded outline some of the material covered the first two quarters. The outline is to be used as a tool to help you further organize your studying and in no way is to be confused as a substitute for studying. SCIENTIFIC METHOD Observations The use of some, or all of the senses to p ...
... This is a brief expanded outline some of the material covered the first two quarters. The outline is to be used as a tool to help you further organize your studying and in no way is to be confused as a substitute for studying. SCIENTIFIC METHOD Observations The use of some, or all of the senses to p ...
NGSSS: Big Idea 14: Organization and
... SC.6.L.14.1 Describe and identify patterns in the hierarchical organization of from atoms to molecules and cells to tissues to organs to organ systems to organisms. SC.6.L.14.2 Investigate and explain the components of the scientific theory of cells (cell theory): all organisms are composed of cells ...
... SC.6.L.14.1 Describe and identify patterns in the hierarchical organization of from atoms to molecules and cells to tissues to organs to organ systems to organisms. SC.6.L.14.2 Investigate and explain the components of the scientific theory of cells (cell theory): all organisms are composed of cells ...
Document
... 8. What are the six elements essential to all of life? 9. What are the subatomic particles? Which ones are found in the nucleus of the atom? 10. How many electrons are found in each energy level (for the first 20 elements)? 11. Describe each type of bond: ionic, covalent, nonpolar covalent, polar co ...
... 8. What are the six elements essential to all of life? 9. What are the subatomic particles? Which ones are found in the nucleus of the atom? 10. How many electrons are found in each energy level (for the first 20 elements)? 11. Describe each type of bond: ionic, covalent, nonpolar covalent, polar co ...
BELL WORK: Answer the following questions:
... b) Allows the total number of bases in a DNA sequence to remain the same c) Replaces a base with its complementary base d) Produces a codon that codes for the same amino acid as the original codon ...
... b) Allows the total number of bases in a DNA sequence to remain the same c) Replaces a base with its complementary base d) Produces a codon that codes for the same amino acid as the original codon ...
Study Questions for Unit 1 (Chemistry and Cell Biology)
... 12. Describe the process of glycolysis. At one time, glycolysis was referred to as “anaerobic respiration”—in what sense is this a good name for glycolysis? Not such a good name? 13. How is the rate of glycolysis regulated by enzymes? 14. What is the relationship between the Krebs cycle and glycolys ...
... 12. Describe the process of glycolysis. At one time, glycolysis was referred to as “anaerobic respiration”—in what sense is this a good name for glycolysis? Not such a good name? 13. How is the rate of glycolysis regulated by enzymes? 14. What is the relationship between the Krebs cycle and glycolys ...
Chapter 4 Guided Reading
... 7. For each of the structures below – note the specific structure and the function of the organelle or part of the organelle. The important concept is to note how the specific structure allows for the specific function to be accomplished. a. Nucleus ...
... 7. For each of the structures below – note the specific structure and the function of the organelle or part of the organelle. The important concept is to note how the specific structure allows for the specific function to be accomplished. a. Nucleus ...
Cell Anatomy and Physiology Web Learning Adventure Purpose
... explaining the function of the organelle. 7- You may either write in your own words or copy and paste. [Remember you must give credit for your quote.] ...
... explaining the function of the organelle. 7- You may either write in your own words or copy and paste. [Remember you must give credit for your quote.] ...
Cell Theory Timeline
... • The bigger the cell, the smaller the surface area-to-volume ratio. • If a cell is too large, there is not enough surface area to allow materials to pass through quickly enough. ...
... • The bigger the cell, the smaller the surface area-to-volume ratio. • If a cell is too large, there is not enough surface area to allow materials to pass through quickly enough. ...
Cell Theory, Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
... DNA chain in a circle NO Membrane-bound organelles Cells are small Cells are simple Unicellular Ex. Bacteria ...
... DNA chain in a circle NO Membrane-bound organelles Cells are small Cells are simple Unicellular Ex. Bacteria ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.