Lesson 2 Bacteria.notebook
... Chemoautotroph: use chemicals to produce their own energy/food Obligate Aerobe: must have O2 to live Obligate Anaerobe: dies in the presence of O2 Faculative Anaerobe: can live with or without O2 5. Explain the difference between binary fission and conjugatio ...
... Chemoautotroph: use chemicals to produce their own energy/food Obligate Aerobe: must have O2 to live Obligate Anaerobe: dies in the presence of O2 Faculative Anaerobe: can live with or without O2 5. Explain the difference between binary fission and conjugatio ...
Chapter 01
... • Identify a particular aspect of it that can be stated as a problem • Produce an hypothesis that explains the event • Test the hypothesis by experiment ...
... • Identify a particular aspect of it that can be stated as a problem • Produce an hypothesis that explains the event • Test the hypothesis by experiment ...
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
... name _ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ...
... name _ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ...
Test Date:______ Essential Concepts and Skills READINGS 1
... a) All living things are made of one or more cells. b) All cells come from pre-existing cells. c) Cells are the basic unit of life. d) Scientist Associated with the Cell Theory (Hooke/Leeuwenhoek/Schlieden & Schwan / Virchow) (use foldable) 2. Describe specific examples that illustrate the relations ...
... a) All living things are made of one or more cells. b) All cells come from pre-existing cells. c) Cells are the basic unit of life. d) Scientist Associated with the Cell Theory (Hooke/Leeuwenhoek/Schlieden & Schwan / Virchow) (use foldable) 2. Describe specific examples that illustrate the relations ...
Producing new cells - Clydebank High School
... chromosomes during mitosis going from the parent cell to daughter cells? A. the number of chromosomes stays ...
... chromosomes during mitosis going from the parent cell to daughter cells? A. the number of chromosomes stays ...
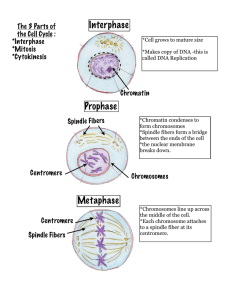
Interphase Prophase Metaphase
... *the centromeres split and the 2 chromatids separate. *the chromatids move along the spindle fibers to opposite ends of the cell. * the cell is stretched out as the opposite ends pull apart. ...
... *the centromeres split and the 2 chromatids separate. *the chromatids move along the spindle fibers to opposite ends of the cell. * the cell is stretched out as the opposite ends pull apart. ...
Cell Lab
... 6. Switch to medium power. Cells should be visible, but they will be small and look like nearly clear purplish blobs. If you are looking at something dark purple, it is probably not a cell 7. Once you think you have located a cell, switch to high power and refocus. (Remember, do NOT use the coarse a ...
... 6. Switch to medium power. Cells should be visible, but they will be small and look like nearly clear purplish blobs. If you are looking at something dark purple, it is probably not a cell 7. Once you think you have located a cell, switch to high power and refocus. (Remember, do NOT use the coarse a ...
Do you know that most living things start out as a single cell
... All cells are made from other cells. New cells are made when an old cell divides in two. Each of these two cells can then divide to make two more cells. This process is called cell division. As long as each new cell continues to divide, a single cell can become many cells. Cell division begins insid ...
... All cells are made from other cells. New cells are made when an old cell divides in two. Each of these two cells can then divide to make two more cells. This process is called cell division. As long as each new cell continues to divide, a single cell can become many cells. Cell division begins insid ...
Ch. 7 Cells - dublin.k12.ca.us
... tono - = stretched; - plast = molded (tonoplast: the membrane that encloses a large central vacuole in a mature plant cell) trans - = across; - port = a harbor (transport vesicle: a membranous compartment used to enclose and transport materials from one part of a cell to another) ultra - = beyond (u ...
... tono - = stretched; - plast = molded (tonoplast: the membrane that encloses a large central vacuole in a mature plant cell) trans - = across; - port = a harbor (transport vesicle: a membranous compartment used to enclose and transport materials from one part of a cell to another) ultra - = beyond (u ...
caenorhabditis elegans
... endodermal, mesodermal, and germ-line precursors. Gastrulation occurs when small groups of cells ingress at various times into the small blastocoel space. The blastocoel space forms when specific surfaces of cells separate from one another in the interior of the embryo. Cells acquire an apical-basal ...
... endodermal, mesodermal, and germ-line precursors. Gastrulation occurs when small groups of cells ingress at various times into the small blastocoel space. The blastocoel space forms when specific surfaces of cells separate from one another in the interior of the embryo. Cells acquire an apical-basal ...
Cells from Cells - Upper Grand District School Board
... area until a scab forms. This scab restores the skin’s continuity, preventing bacteria from entering the body. Then the skin cells underneath can undergo cell division to produce new cells that fill in the gap. Once the skin layer is restored, the scab falls off. ...
... area until a scab forms. This scab restores the skin’s continuity, preventing bacteria from entering the body. Then the skin cells underneath can undergo cell division to produce new cells that fill in the gap. Once the skin layer is restored, the scab falls off. ...
Cells
... • Some cells are complete organisms, such as the unicellular bacteria and protozoa • Other cells are specialized components of multi-cellular organisms (ex nerve, liver, and muscle cells) ...
... • Some cells are complete organisms, such as the unicellular bacteria and protozoa • Other cells are specialized components of multi-cellular organisms (ex nerve, liver, and muscle cells) ...
AP Biology Cell Lab
... ____ 12. Which of the following is one of the two main functions of the nuclear envelope? a. provides residence for ribosomes b. allows separation of DNA from cytoplasm machinery c. provides total isolation of nuclear components d. enables faster cell division e. enables larger cell size ____ 13. Wh ...
... ____ 12. Which of the following is one of the two main functions of the nuclear envelope? a. provides residence for ribosomes b. allows separation of DNA from cytoplasm machinery c. provides total isolation of nuclear components d. enables faster cell division e. enables larger cell size ____ 13. Wh ...
Section 5.2 - Cells: The Basic Unit of Life ANIMAL CELL
... Cell Membrane - entire cell is covered with the cell membrane. - acts like a gatekeeper, controlling the movement of materials into and out of the cell. Nucleus - acts as the control centre, directing all of the cell's activities. - genetic information is organized into threadlike structures called ...
... Cell Membrane - entire cell is covered with the cell membrane. - acts like a gatekeeper, controlling the movement of materials into and out of the cell. Nucleus - acts as the control centre, directing all of the cell's activities. - genetic information is organized into threadlike structures called ...
Chapter 5 review questions
... 22. Which type of cells would have more mitochondria & why? 23. ___________ like glucose are burned in the mitochondria to release cellular energy known as __________. 24. What surrounds the outside of all cells? 25. In plant cells, a __________ surrounds the cell membrane for extra support. 26. Wha ...
... 22. Which type of cells would have more mitochondria & why? 23. ___________ like glucose are burned in the mitochondria to release cellular energy known as __________. 24. What surrounds the outside of all cells? 25. In plant cells, a __________ surrounds the cell membrane for extra support. 26. Wha ...
Science - Rainhill High School
... As an organism develops, cells differentiate to form different types of cells. Most types of animal cell differentiate at an early stage whereas many types of plant cells retain the ability to differentiate throughout life. In mature animals, cell division is mainly restricted to repair and replacem ...
... As an organism develops, cells differentiate to form different types of cells. Most types of animal cell differentiate at an early stage whereas many types of plant cells retain the ability to differentiate throughout life. In mature animals, cell division is mainly restricted to repair and replacem ...
Cells Compared to Manhattan Beach, CA
... Cell City Manhattan Beach, CA Cells, the basic unit of life, can be compared to a pizza parlor, a factory, and even Manhattan Beach, CA. These cells are busy building and breaking down macromolecules. They are at work releasing energy from foods, and then using that energy to make needed cell parts. ...
... Cell City Manhattan Beach, CA Cells, the basic unit of life, can be compared to a pizza parlor, a factory, and even Manhattan Beach, CA. These cells are busy building and breaking down macromolecules. They are at work releasing energy from foods, and then using that energy to make needed cell parts. ...
Parts of the Cell
... 2. Cytoplasm – liquid gel that fills the cell. Site of all chemical activities and keeps the organelles from drying out. 3. Nucleus – “brain” of the cell. Contains the genetic (DNA,RNA) material that instructs the cell what to do. 4. Ribosome – site of protein synthesis. Found along the Endoplasmic ...
... 2. Cytoplasm – liquid gel that fills the cell. Site of all chemical activities and keeps the organelles from drying out. 3. Nucleus – “brain” of the cell. Contains the genetic (DNA,RNA) material that instructs the cell what to do. 4. Ribosome – site of protein synthesis. Found along the Endoplasmic ...
Name: Pd.: ____ Chapter 10. Cell Growth and Division Section 10.1
... The formula for finding the surface area of a sphere, such as a baseball or basketball, is A=4πr2. where r is the radius. The formula for finding the volume of a sphere is V=4/3πr3 a. Calculate the surface area and the volume of a basketball that has a radius of 12.2 cm and a baseball that has a rad ...
... The formula for finding the surface area of a sphere, such as a baseball or basketball, is A=4πr2. where r is the radius. The formula for finding the volume of a sphere is V=4/3πr3 a. Calculate the surface area and the volume of a basketball that has a radius of 12.2 cm and a baseball that has a rad ...
Cells
... Organism that has a well defined nucleus Contains membrane-bound organelles Some Specialized cells can function without a nucleus, Ex. Red blood cells Ex. Plants, Fungi, Animals, Humans ...
... Organism that has a well defined nucleus Contains membrane-bound organelles Some Specialized cells can function without a nucleus, Ex. Red blood cells Ex. Plants, Fungi, Animals, Humans ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.