26.5 The Expanding Universe
... In 1965, Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson, using a radio telescope, noticed a faint distant glow in every direction. • Today this glow is called the cosmic microwave background radiation. • This glow is energy produced during the big bang, still traveling throughout the universe. ...
... In 1965, Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson, using a radio telescope, noticed a faint distant glow in every direction. • Today this glow is called the cosmic microwave background radiation. • This glow is energy produced during the big bang, still traveling throughout the universe. ...
WRL3659.tmp - U of L Class Index
... 6. What evidence suggests that the universe is expanding? 7. What is the ‘Hubble time’? 8. Why does Rees think that intelligent life may be rare in the universe? 9. What do we mean when we ask whether the universe is open, closed, or flat? 10. What is a neutron star? 11. What did Penzias and Wilson ...
... 6. What evidence suggests that the universe is expanding? 7. What is the ‘Hubble time’? 8. Why does Rees think that intelligent life may be rare in the universe? 9. What do we mean when we ask whether the universe is open, closed, or flat? 10. What is a neutron star? 11. What did Penzias and Wilson ...
wk11noQ
... • Highest temperature and lowest density of the three gaseous phases (hot, tenuous phase of the ISM): T ~ 103 to 106 K; n ~ 10-5 to 10-3 ions/cm3 • Weak degree of concentration to the plane of the Galactic disk: scale height z is a few kpc. Also seen in dense knots known as “HII regions” marking are ...
... • Highest temperature and lowest density of the three gaseous phases (hot, tenuous phase of the ISM): T ~ 103 to 106 K; n ~ 10-5 to 10-3 ions/cm3 • Weak degree of concentration to the plane of the Galactic disk: scale height z is a few kpc. Also seen in dense knots known as “HII regions” marking are ...
Lecture
... Cosmic Background Radiation • In 1965, Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson were using a very sensitive radio telescope to study radio emission from the sky. – They found a background source of noise with a temperature of 3 K that they could not explain. – After discussing the observations with other ast ...
... Cosmic Background Radiation • In 1965, Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson were using a very sensitive radio telescope to study radio emission from the sky. – They found a background source of noise with a temperature of 3 K that they could not explain. – After discussing the observations with other ast ...
ppt
... Correlation disappears when including lower energy cosmic rays (pointing accuracy) or farther away galaxies (GZK). While an accumulation of showers point to nearby galaxies, in particular to the Centaurus A region, others point to voids, far away from any matter. Present statistics do not allow for ...
... Correlation disappears when including lower energy cosmic rays (pointing accuracy) or farther away galaxies (GZK). While an accumulation of showers point to nearby galaxies, in particular to the Centaurus A region, others point to voids, far away from any matter. Present statistics do not allow for ...
Part II, page 129 (instructions on page 127)
... Distances of farthest galaxies are measured from redshifts ...
... Distances of farthest galaxies are measured from redshifts ...
The Cosmos & the Bible - Access Research Network
... must go into woods to see only tree trunks all around. • To have a dark sky, universe must not be deep enough to see only star surfaces in all directions. • Thus the universe is of finite age, or finite size, or average star density = 0. ...
... must go into woods to see only tree trunks all around. • To have a dark sky, universe must not be deep enough to see only star surfaces in all directions. • Thus the universe is of finite age, or finite size, or average star density = 0. ...
chapter 13 cosmology
... We measure the radial velocity for each cluster of galaxies to be vr = D/t, where t is the time it takes to move the measured change in distance, D. In the diagram above, the top part represents the universe 2 years ago. The different clusters are identified as A, B, etc. and are spaced 1 Mpc apar ...
... We measure the radial velocity for each cluster of galaxies to be vr = D/t, where t is the time it takes to move the measured change in distance, D. In the diagram above, the top part represents the universe 2 years ago. The different clusters are identified as A, B, etc. and are spaced 1 Mpc apar ...
Mapping the Universe - Tufts Institute of Cosmology
... is to determine how the initial power spectrum evolved into the spectrum observed today. Only in the past several years have observations, such as those of galaxy distribution and of the cosmic microwave background radiation, acquired enough data to put theories to the test. So-called cold dark matt ...
... is to determine how the initial power spectrum evolved into the spectrum observed today. Only in the past several years have observations, such as those of galaxy distribution and of the cosmic microwave background radiation, acquired enough data to put theories to the test. So-called cold dark matt ...
Test 2 - Physics@Brock
... (a) a high concentration of swimming pools, sports cars, and affected accents. (b) more than one million galaxies. (c) more than one thousand galaxies. (d) more than one hundred galaxies. 18. A common result of a galaxy collision is (a) the creation of several “child” galaxies. (b) the formation of ...
... (a) a high concentration of swimming pools, sports cars, and affected accents. (b) more than one million galaxies. (c) more than one thousand galaxies. (d) more than one hundred galaxies. 18. A common result of a galaxy collision is (a) the creation of several “child” galaxies. (b) the formation of ...
The Universe - Cloudfront.net
... violent explosion from which the universe continues to expand, evolve, and cool The big bang theory states that at one time, the entire universe was confined to a dense, hot, supermassive ball. Then, about 13.7 billion years ago, a violent explosion occurred, hurling this material in all directions ...
... violent explosion from which the universe continues to expand, evolve, and cool The big bang theory states that at one time, the entire universe was confined to a dense, hot, supermassive ball. Then, about 13.7 billion years ago, a violent explosion occurred, hurling this material in all directions ...
Last time we left off at hydrogen and helium, because that`s all that
... If we agree that uniformly spread stuff isn’t alive, we need some way to cause it to clump. Our understanding of how the clumping happens depends on the content of the universe, so let’s survey that briefly. As you probably know, in the past several years it has become clear that the stuff that we a ...
... If we agree that uniformly spread stuff isn’t alive, we need some way to cause it to clump. Our understanding of how the clumping happens depends on the content of the universe, so let’s survey that briefly. As you probably know, in the past several years it has become clear that the stuff that we a ...
AWG recommendation on Cosmic Vision
... most noticeably the WMAP results. However, the physical mechanism driving inflation is unclear at present and competing physical theories exist. Since they differ in their predictions about the amplitude and shape of the primordial gravitational wave spectrum, determining those provides the key for ...
... most noticeably the WMAP results. However, the physical mechanism driving inflation is unclear at present and competing physical theories exist. Since they differ in their predictions about the amplitude and shape of the primordial gravitational wave spectrum, determining those provides the key for ...
the nuclear, plasma, and radiation universe
... values of energy are involved. This force of nature expresses itself the process of radioactivity, where isotopes of different elements, either naturally occurring, or artificially created transform into other isotopes. It is the dream of the ancient alchemists come true. Radioisotopes can have dele ...
... values of energy are involved. This force of nature expresses itself the process of radioactivity, where isotopes of different elements, either naturally occurring, or artificially created transform into other isotopes. It is the dream of the ancient alchemists come true. Radioisotopes can have dele ...
What are your ideas about The Universe? - Harvard
... which is the exact order of age? Current theories of moon formation suggest it was formed by a collision of a Mars-sized object with the Earth, making it slightly younger than the Earth and planets. On the other hand, an astronomer reviewing this activity noted that our picture of Saturn shows well ...
... which is the exact order of age? Current theories of moon formation suggest it was formed by a collision of a Mars-sized object with the Earth, making it slightly younger than the Earth and planets. On the other hand, an astronomer reviewing this activity noted that our picture of Saturn shows well ...
Inflation and the Cosmic Microwave Background
... enough to allow the points in opposite sides of the sky (A and B in Fig. 4) to be in causal contact. The exponential expansion of in ation produces an event horizon at a constant proper distance which is equivalent to a shrinking comoving horizon. A shrinking comoving horizon is the key to the in at ...
... enough to allow the points in opposite sides of the sky (A and B in Fig. 4) to be in causal contact. The exponential expansion of in ation produces an event horizon at a constant proper distance which is equivalent to a shrinking comoving horizon. A shrinking comoving horizon is the key to the in at ...
There are billions of galaxies, many containing
... seems to be as observed from the earth. This apparent brightness allows us to determine its distance. The farther it is from the sun, the dimmer it will appear. If we know any two of the three—absolute brightness, apparent brightness, and distance—we can compute the third, distance in this case. It ...
... seems to be as observed from the earth. This apparent brightness allows us to determine its distance. The farther it is from the sun, the dimmer it will appear. If we know any two of the three—absolute brightness, apparent brightness, and distance—we can compute the third, distance in this case. It ...
Lesson 55 – The Structure of the Universe - science
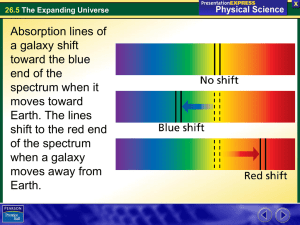
... comparison spectrum of an element on Earth, at rest compared with the observer, is shown above and below each galactic spectrum. For very high speeds the simple formula cannot be used and the effects of special relativity have to be allowed for. It is important to realise that the Doppler shift will ...
... comparison spectrum of an element on Earth, at rest compared with the observer, is shown above and below each galactic spectrum. For very high speeds the simple formula cannot be used and the effects of special relativity have to be allowed for. It is important to realise that the Doppler shift will ...
Unweaving the Fabric of the Universe: The Interplay between
... equations considering Einstein’s theory as an effective theory valid at lower energy scales. Moreover, it is hoped that Quantum Gravity may shed some light on the nature of the inflaton field. Note that there are unresolved puzzles of the Hot Big Bang model, referring to the initial singularity, bar ...
... equations considering Einstein’s theory as an effective theory valid at lower energy scales. Moreover, it is hoped that Quantum Gravity may shed some light on the nature of the inflaton field. Note that there are unresolved puzzles of the Hot Big Bang model, referring to the initial singularity, bar ...
Coupling and Collapse
... Conclusions • Naturally if the perturbation is smaller than the mean free path the photons diffuse instantaneously and no perturbation can survive for smaller scale lengths (or masses). • Assuming a scale length for which the scale length corresponds to the travel carried out in a random walk by a ...
... Conclusions • Naturally if the perturbation is smaller than the mean free path the photons diffuse instantaneously and no perturbation can survive for smaller scale lengths (or masses). • Assuming a scale length for which the scale length corresponds to the travel carried out in a random walk by a ...
PowerPoint No. 7 -- The Cosmological Argument (II)
... same rate is if, at some finite time in the past, the entire universe had been a single, infinitely dense point. – The initial expansion of this single, infinitely dense point is known as the “Big Bang.” – Scientists’ best estimates indicate the “Big Bang” happened 15 billion years ago. ...
... same rate is if, at some finite time in the past, the entire universe had been a single, infinitely dense point. – The initial expansion of this single, infinitely dense point is known as the “Big Bang.” – Scientists’ best estimates indicate the “Big Bang” happened 15 billion years ago. ...
Cosmic microwave background
The cosmic microwave background (CMB) is the thermal radiation left over from the time of recombination in Big Bang cosmology. In older literature, the CMB is also variously known as cosmic microwave background radiation (CMBR) or ""relic radiation."" The CMB is a cosmic background radiation that is fundamental to observational cosmology because it is the oldest light in the universe, dating to the epoch of recombination. With a traditional optical telescope, the space between stars and galaxies (the background) is completely dark. However, a sufficiently sensitive radio telescope shows a faint background glow, almost exactly the same in all directions, that is not associated with any star, galaxy, or other object. This glow is strongest in the microwave region of the radio spectrum. The accidental discovery of CMB in 1964 by American radio astronomers Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson was the culmination of work initiated in the 1940s, and earned the discoverers the 1978 Nobel Prize.The CMB is a snapshot of the oldest light in our Universe, imprinted on the sky when the Universe was just 380,000 years old. It shows tiny temperature fluctuations that correspond to regions of slightly different densities, representing the seeds of all future structure: the stars and galaxies of today.The CMB is well explained as radiation left over from an early stage in the development of the universe, and its discovery is considered a landmark test of the Big Bang model of the universe. When the universe was young, before the formation of stars and planets, it was denser, much hotter, and filled with a uniform glow from a white-hot fog of hydrogen plasma. As the universe expanded, both the plasma and the radiation filling it grew cooler. When the universe cooled enough, protons and electrons combined to form neutral atoms. These atoms could no longer absorb the thermal radiation, and so the universe became transparent instead of being an opaque fog. Cosmologists refer to the time period when neutral atoms first formed as the recombination epoch, and the event shortly afterwards when photons started to travel freely through space rather than constantly being scattered by electrons and protons in plasma is referred to as photon decoupling. The photons that existed at the time of photon decoupling have been propagating ever since, though growing fainter and less energetic, since the expansion of space causes their wavelength to increase over time (and wavelength is inversely proportional to energy according to Planck's relation). This is the source of the alternative term relic radiation. The surface of last scattering refers to the set of points in space at the right distance from us so that we are now receiving photons originally emitted from those points at the time of photon decoupling.Precise measurements of the CMB are critical to cosmology, since any proposed model of the universe must explain this radiation. The CMB has a thermal black body spectrum at a temperature of 7000272548000000000♠2.72548±0.00057 K. The spectral radiance dEν/dν peaks at 160.2 GHz, in the microwave range of frequencies. (Alternatively if spectral radiance is defined as dEλ/dλ then the peak wavelength is 1.063 mm.) The glow is very nearly uniform in all directions, but the tiny residual variations show a very specific pattern, the same as that expected of a fairly uniformly distributed hot gas that has expanded to the current size of the universe. In particular, the spectral radiance at different angles of observation in the sky contains small anisotropies, or irregularities, which vary with the size of the region examined. They have been measured in detail, and match what would be expected if small thermal variations, generated by quantum fluctuations of matter in a very tiny space, had expanded to the size of the observable universe we see today. This is a very active field of study, with scientists seeking both better data (for example, the Planck spacecraft) and better interpretations of the initial conditions of expansion. Although many different processes might produce the general form of a black body spectrum, no model other than the Big Bang has yet explained the fluctuations. As a result, most cosmologists consider the Big Bang model of the universe to be the best explanation for the CMB.The high degree of uniformity throughout the observable universe and its faint but measured anisotropy lend strong support for the Big Bang model in general and the ΛCDM (""Lambda Cold Dark Matter"") model in particular. Moreover, the fluctuations are coherent on angular scales that are larger than the apparent cosmological horizon at recombination. Either such coherence is acausally fine-tuned, or cosmic inflation occurred.























