The Nature of Evolution - Western Washington University
... irreversibly. Thus every moment in the history of the universe is unique. What we need to recognize from this, in order to understand the universal nature of evolution, is that our universe is a dynamic place that is constantly changing irreversibly on the largest and smallest of scales. Natural Pro ...
... irreversibly. Thus every moment in the history of the universe is unique. What we need to recognize from this, in order to understand the universal nature of evolution, is that our universe is a dynamic place that is constantly changing irreversibly on the largest and smallest of scales. Natural Pro ...
Results from the AMANDA Neutrino Telescope
... There are more hits in UHE single muons, due to the after-pulsing in the photomultipliers. Background events are produced mainly vertically downwards and signal events are expected to be horizontal. Different residual time distributions (because of afterpulsing) Center of gravity of hits pulled away ...
... There are more hits in UHE single muons, due to the after-pulsing in the photomultipliers. Background events are produced mainly vertically downwards and signal events are expected to be horizontal. Different residual time distributions (because of afterpulsing) Center of gravity of hits pulled away ...
Early Universe Cosmology Advanced String School 2014 Puri, India
... • Pressure free matter/dust, w = 0. Ordinary baryonic matter as well as dark matter fall into this category. Their energy density simply scales inversely to the volume of a given region of space, ρ ∝ a−3 , as expected. • Relativistic particles/radiation, w = 13 . The energy density of radiation or a ...
... • Pressure free matter/dust, w = 0. Ordinary baryonic matter as well as dark matter fall into this category. Their energy density simply scales inversely to the volume of a given region of space, ρ ∝ a−3 , as expected. • Relativistic particles/radiation, w = 13 . The energy density of radiation or a ...
From Subatomic Particles to the Cosmos Mark Oreglia
... – The Planck era. Quantum gravity is important; current theories are inadequate. We can't get any closer to the Big Bang at earlier times – Inflation. A temporary period of domination by a form of dark energy at an ultrahigh energy scale. A speculative theory. – Electroweak phase transition. At high ...
... – The Planck era. Quantum gravity is important; current theories are inadequate. We can't get any closer to the Big Bang at earlier times – Inflation. A temporary period of domination by a form of dark energy at an ultrahigh energy scale. A speculative theory. – Electroweak phase transition. At high ...
Chapter 17
... Protons and As the universe expanded, it cooled down as its energy spread out over neutrons form a larger volume. About four minutes after the Big Bang, the universe at 4 minutes had cooled enough that protons and neutrons could stick together to form the nuclei of atoms. Because atoms were still fl ...
... Protons and As the universe expanded, it cooled down as its energy spread out over neutrons form a larger volume. About four minutes after the Big Bang, the universe at 4 minutes had cooled enough that protons and neutrons could stick together to form the nuclei of atoms. Because atoms were still fl ...
Szalay
... There are several parameters used to specify the shape of the fluctuation spectrum. These include the amplitude 8, the root-mean-square value of the density fluctuations in a sphere of 8 Mpc radius, the shape parameter , the redshift-distortion parameter , the bias parameter b, and the baryon fra ...
... There are several parameters used to specify the shape of the fluctuation spectrum. These include the amplitude 8, the root-mean-square value of the density fluctuations in a sphere of 8 Mpc radius, the shape parameter , the redshift-distortion parameter , the bias parameter b, and the baryon fra ...
How is Light Made?
... stellar distances... distances... • Two otherwise identical stars (same radius, same temperature ⇒ same luminosity) will still appear vastly different in brightness if at different distances from Earth • Reason: intensity of light inversely proportional to the square of the distance the light has to ...
... stellar distances... distances... • Two otherwise identical stars (same radius, same temperature ⇒ same luminosity) will still appear vastly different in brightness if at different distances from Earth • Reason: intensity of light inversely proportional to the square of the distance the light has to ...
Review for final
... Tell the difference between redshift and blueshift Describe how the Doppler shift is used on Astronomy o Ex. Be able to apply Doppler effect to explain the redshift in astronomy for measuring speed away from Earth, as Hubble did while studying galaxies. ...
... Tell the difference between redshift and blueshift Describe how the Doppler shift is used on Astronomy o Ex. Be able to apply Doppler effect to explain the redshift in astronomy for measuring speed away from Earth, as Hubble did while studying galaxies. ...
ASTROPHYSICS AND COSMOLOGY
... geometry-mass relation, can be obtained in the quantum geometrodynamical approach. In terms of general relativity, its effective contribution to the field equations can be linked to the time evolution of the equation of state of matter caused by the processes of redistribution of the energy between ...
... geometry-mass relation, can be obtained in the quantum geometrodynamical approach. In terms of general relativity, its effective contribution to the field equations can be linked to the time evolution of the equation of state of matter caused by the processes of redistribution of the energy between ...
M - ASTRONOMY GROUP – University of St Andrews
... 1611: Galileo supports Copernicus (Planets orbit Sun, not Earth) COPERNICAN COSMOLOGY 1742: Maupertius identifies nebulae 1784: Messier catalogue (103 fuzzy objects) 1864: Huggins: first spectrum for a nebula 1908: Leavitt: Cepheids in LMC 1924: Hubble: Cepheids in Andromeda MODERN COSMOLOGY 1929: H ...
... 1611: Galileo supports Copernicus (Planets orbit Sun, not Earth) COPERNICAN COSMOLOGY 1742: Maupertius identifies nebulae 1784: Messier catalogue (103 fuzzy objects) 1864: Huggins: first spectrum for a nebula 1908: Leavitt: Cepheids in LMC 1924: Hubble: Cepheids in Andromeda MODERN COSMOLOGY 1929: H ...
Modification of Newton`s law of gravity at very large distances
... starts to dominate over gravity. This model contains basic features of MOND (at least roughly) but fails when confronting with gravitational lensing by clusters. To explain lensing this extra force must act like gravity and, in fact, be gravity. We note that if this additional potential cuts off at ...
... starts to dominate over gravity. This model contains basic features of MOND (at least roughly) but fails when confronting with gravitational lensing by clusters. To explain lensing this extra force must act like gravity and, in fact, be gravity. We note that if this additional potential cuts off at ...
Learning goals for Astronomy`s Final 2013
... Tell the difference between redshift and blueshift Describe how the Doppler shift is used on Astronomy o Ex. Be able to apply Doppler effect to explain the redshift in astronomy for measuring speed away from Earth, as Hubble did while studying galaxies. ...
... Tell the difference between redshift and blueshift Describe how the Doppler shift is used on Astronomy o Ex. Be able to apply Doppler effect to explain the redshift in astronomy for measuring speed away from Earth, as Hubble did while studying galaxies. ...
ppt
... ….. detailed analysis & background understand underway “ don’t know what to expect & what are expected .” ...
... ….. detailed analysis & background understand underway “ don’t know what to expect & what are expected .” ...
Can Gravity Explain the Pioneer 10-11 Anomaly
... • A fully relativistic modified gravity (MOG) called Scalar-TensorVector-Gravity (STVG) leads to a self-consistent, stable gravity theory that can describe solar system, astrophysical and cosmological data. The theory has an extra degree of freedom, a vector field called a “phion” field whose curl i ...
... • A fully relativistic modified gravity (MOG) called Scalar-TensorVector-Gravity (STVG) leads to a self-consistent, stable gravity theory that can describe solar system, astrophysical and cosmological data. The theory has an extra degree of freedom, a vector field called a “phion” field whose curl i ...
R. Bender (ESO)
... assembly of galaxies and dust-enshrouded violent star formation processes that may have produced a large fraction of all stars in the universe, especially those in spheroids. ALMA will allow to probe the collapse of the first massive galaxy fragments before they have largely turned into stars. A ...
... assembly of galaxies and dust-enshrouded violent star formation processes that may have produced a large fraction of all stars in the universe, especially those in spheroids. ALMA will allow to probe the collapse of the first massive galaxy fragments before they have largely turned into stars. A ...
Gravitational Lensing, SZ Effects, and Large
... However, around real clusters, the probability of high noise peaks can be higher than average ...
... However, around real clusters, the probability of high noise peaks can be higher than average ...
KTH, astro experiments
... Some short circuits in the gaps appeared during and after installation in ATLAS.These shorts are assumed to be due to dust between the electrodes. A short circuit results in one side of a group of anodes being inactive, giving only half the signal in 32 readout channels, i.e. increaing the noise. ...
... Some short circuits in the gaps appeared during and after installation in ATLAS.These shorts are assumed to be due to dust between the electrodes. A short circuit results in one side of a group of anodes being inactive, giving only half the signal in 32 readout channels, i.e. increaing the noise. ...
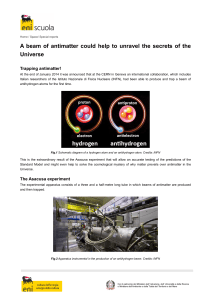
A beam of antimatter could help to unravel the secrets of
... Why are we made of matter? This question does not have a commonly accepted answer yet. To answer this question one must go back in time to when the Universe was formed, to the Big Bang. A few moments after the Big Bang, around 14 billion years ago, the Universe was in a phase of extremely rapid expa ...
... Why are we made of matter? This question does not have a commonly accepted answer yet. To answer this question one must go back in time to when the Universe was formed, to the Big Bang. A few moments after the Big Bang, around 14 billion years ago, the Universe was in a phase of extremely rapid expa ...
Static, Infinite, Etern and Auto sustentable Universe
... galaxies do around its own center (where its density of matter could be infinite due to the presence of a super massive black hole [15, 16]. According with our hypothesis, hierarchic levels finish here, and we think that this grouped matter reach its maximum level and has a common rotation center, n ...
... galaxies do around its own center (where its density of matter could be infinite due to the presence of a super massive black hole [15, 16]. According with our hypothesis, hierarchic levels finish here, and we think that this grouped matter reach its maximum level and has a common rotation center, n ...
File - INFN-LNF
... scenarios related to possible science from the Moon; To study the Solar System scenario; To correlate the identified scenarios with other scientific and technological activities on going on the Earth and in the space; To identify the scientific objectives and translate them into scientific requireme ...
... scenarios related to possible science from the Moon; To study the Solar System scenario; To correlate the identified scenarios with other scientific and technological activities on going on the Earth and in the space; To identify the scientific objectives and translate them into scientific requireme ...
Article 8
... The second line of evidence is the Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation (CMB) that was discovered in 1965 by Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson from Bell Labs. They were working with a microwave receiver, but were getting noise from every direction they pointed the receiver. It was coming from all over ...
... The second line of evidence is the Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation (CMB) that was discovered in 1965 by Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson from Bell Labs. They were working with a microwave receiver, but were getting noise from every direction they pointed the receiver. It was coming from all over ...
Lecture 3: Interstellar Dust, Radiative Transfer and Thermal Radiation
... •Mean intensity Jν, i.e. the average of Iν over all directions: ...
... •Mean intensity Jν, i.e. the average of Iν over all directions: ...
Hubble`s Law
... The Big Bang • Big Bang has no center • Happened everywhere! • Wherever you go, there was the big bang! • So as we talk about the very dense early universe, remember that we are talking about what happened not just far away at the edge of the Universe, but right here! ...smooshed up small, but stil ...
... The Big Bang • Big Bang has no center • Happened everywhere! • Wherever you go, there was the big bang! • So as we talk about the very dense early universe, remember that we are talking about what happened not just far away at the edge of the Universe, but right here! ...smooshed up small, but stil ...
ppt
... Looking into a star at any angle, we always look back to an optical depth of about t l = 2/3 as measured straight back along the line of sight Photon’s at a distance of less than 1 mean free path from the surface are likely to escape Star’s photosphere is defined to be the layer from which visible l ...
... Looking into a star at any angle, we always look back to an optical depth of about t l = 2/3 as measured straight back along the line of sight Photon’s at a distance of less than 1 mean free path from the surface are likely to escape Star’s photosphere is defined to be the layer from which visible l ...
Cosmic microwave background
The cosmic microwave background (CMB) is the thermal radiation left over from the time of recombination in Big Bang cosmology. In older literature, the CMB is also variously known as cosmic microwave background radiation (CMBR) or ""relic radiation."" The CMB is a cosmic background radiation that is fundamental to observational cosmology because it is the oldest light in the universe, dating to the epoch of recombination. With a traditional optical telescope, the space between stars and galaxies (the background) is completely dark. However, a sufficiently sensitive radio telescope shows a faint background glow, almost exactly the same in all directions, that is not associated with any star, galaxy, or other object. This glow is strongest in the microwave region of the radio spectrum. The accidental discovery of CMB in 1964 by American radio astronomers Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson was the culmination of work initiated in the 1940s, and earned the discoverers the 1978 Nobel Prize.The CMB is a snapshot of the oldest light in our Universe, imprinted on the sky when the Universe was just 380,000 years old. It shows tiny temperature fluctuations that correspond to regions of slightly different densities, representing the seeds of all future structure: the stars and galaxies of today.The CMB is well explained as radiation left over from an early stage in the development of the universe, and its discovery is considered a landmark test of the Big Bang model of the universe. When the universe was young, before the formation of stars and planets, it was denser, much hotter, and filled with a uniform glow from a white-hot fog of hydrogen plasma. As the universe expanded, both the plasma and the radiation filling it grew cooler. When the universe cooled enough, protons and electrons combined to form neutral atoms. These atoms could no longer absorb the thermal radiation, and so the universe became transparent instead of being an opaque fog. Cosmologists refer to the time period when neutral atoms first formed as the recombination epoch, and the event shortly afterwards when photons started to travel freely through space rather than constantly being scattered by electrons and protons in plasma is referred to as photon decoupling. The photons that existed at the time of photon decoupling have been propagating ever since, though growing fainter and less energetic, since the expansion of space causes their wavelength to increase over time (and wavelength is inversely proportional to energy according to Planck's relation). This is the source of the alternative term relic radiation. The surface of last scattering refers to the set of points in space at the right distance from us so that we are now receiving photons originally emitted from those points at the time of photon decoupling.Precise measurements of the CMB are critical to cosmology, since any proposed model of the universe must explain this radiation. The CMB has a thermal black body spectrum at a temperature of 7000272548000000000♠2.72548±0.00057 K. The spectral radiance dEν/dν peaks at 160.2 GHz, in the microwave range of frequencies. (Alternatively if spectral radiance is defined as dEλ/dλ then the peak wavelength is 1.063 mm.) The glow is very nearly uniform in all directions, but the tiny residual variations show a very specific pattern, the same as that expected of a fairly uniformly distributed hot gas that has expanded to the current size of the universe. In particular, the spectral radiance at different angles of observation in the sky contains small anisotropies, or irregularities, which vary with the size of the region examined. They have been measured in detail, and match what would be expected if small thermal variations, generated by quantum fluctuations of matter in a very tiny space, had expanded to the size of the observable universe we see today. This is a very active field of study, with scientists seeking both better data (for example, the Planck spacecraft) and better interpretations of the initial conditions of expansion. Although many different processes might produce the general form of a black body spectrum, no model other than the Big Bang has yet explained the fluctuations. As a result, most cosmologists consider the Big Bang model of the universe to be the best explanation for the CMB.The high degree of uniformity throughout the observable universe and its faint but measured anisotropy lend strong support for the Big Bang model in general and the ΛCDM (""Lambda Cold Dark Matter"") model in particular. Moreover, the fluctuations are coherent on angular scales that are larger than the apparent cosmological horizon at recombination. Either such coherence is acausally fine-tuned, or cosmic inflation occurred.