The Death of a Star - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... is why the planet alternates between burning and freezing temperatures. Mercury is also a dense planet and is composed of mostly iron and nickel. Venus is also a terrestrial planet and has a thick toxic atmosphere, which traps the heat making it the hottest planet in the Solar System. It is nearly t ...
... is why the planet alternates between burning and freezing temperatures. Mercury is also a dense planet and is composed of mostly iron and nickel. Venus is also a terrestrial planet and has a thick toxic atmosphere, which traps the heat making it the hottest planet in the Solar System. It is nearly t ...
speech on dark matter
... anything through my lectures and reading, it is that there are STILL some major problems with our comprehension of the universe that we exist in. Before my studies I (somewhat naively perhaps) assumed that after the existence and findings of great minds such as Aristotle, Galileo, and Einstein, that ...
... anything through my lectures and reading, it is that there are STILL some major problems with our comprehension of the universe that we exist in. Before my studies I (somewhat naively perhaps) assumed that after the existence and findings of great minds such as Aristotle, Galileo, and Einstein, that ...
“Breakthroughs” of the 20th Century
... spectroscopic and photometric data collection, leading to such cornerstones as the Hertzprung-Russell diagram and the mass-luminosity relationship, and to the realization that the Universe contained a multitude of galaxies and was expanding. Radio astronomy was introduced and the advent of the space ...
... spectroscopic and photometric data collection, leading to such cornerstones as the Hertzprung-Russell diagram and the mass-luminosity relationship, and to the realization that the Universe contained a multitude of galaxies and was expanding. Radio astronomy was introduced and the advent of the space ...
The First Stars in the Universe
... found evidence for the final stages of this ionization process. The researchers observed strong absorption of ultraviolet light in the spectra of quasars that date from about 900 million years after the big bang. The results suggest that the last patches of neutral hydrogen gas were being ionized at ...
... found evidence for the final stages of this ionization process. The researchers observed strong absorption of ultraviolet light in the spectra of quasars that date from about 900 million years after the big bang. The results suggest that the last patches of neutral hydrogen gas were being ionized at ...
PART 1 - Berrigasteiz
... or she helps Ss to understand what they are supposed to do (see ideas for the teacher on h.1.1) Step 3: T tells Ss to spell their name, town, continent, planet, etc… next, they fill in a “space address” to add to their scrapbook. Step 4: Ss are requested to assemble their scrapbooks, let space for t ...
... or she helps Ss to understand what they are supposed to do (see ideas for the teacher on h.1.1) Step 3: T tells Ss to spell their name, town, continent, planet, etc… next, they fill in a “space address” to add to their scrapbook. Step 4: Ss are requested to assemble their scrapbooks, let space for t ...
Structure of the Universe
... How are distances in the universe measured? • Distances between most objects in the universe are so large that astronomers measure distances using the speed of light. • A light-year is the distance that light travels through space in one year. • Light travels through space at about 300,000 km/s, or ...
... How are distances in the universe measured? • Distances between most objects in the universe are so large that astronomers measure distances using the speed of light. • A light-year is the distance that light travels through space in one year. • Light travels through space at about 300,000 km/s, or ...
Expanding Universe Lab
... In Figure 2 are spectra of five relatively nearby galaxies. Distances to these galaxies have been derived by other methods and are given in the middle column of Figure 2. The spectra show two separate sets of spectral features. Notice that the copy here is a positive so that absorption lines appear ...
... In Figure 2 are spectra of five relatively nearby galaxies. Distances to these galaxies have been derived by other methods and are given in the middle column of Figure 2. The spectra show two separate sets of spectral features. Notice that the copy here is a positive so that absorption lines appear ...
constraints on primordial magnetic fields with cmb anisotropies
... The tensor passive mode is the dominant contribution to the large scale angular power spectrum for scale invariant PMF (nB=-2.9). We have considered the magnetized passive tensor bispectrum for l<500 and the squeezed limit configuration in which the passive bispectrum is amplified. The magnetized bi ...
... The tensor passive mode is the dominant contribution to the large scale angular power spectrum for scale invariant PMF (nB=-2.9). We have considered the magnetized passive tensor bispectrum for l<500 and the squeezed limit configuration in which the passive bispectrum is amplified. The magnetized bi ...
Document
... tCR~107 yr, LCR ~ uCR Vgal / tCR ~ 1041 erg/sec, is ~10% of the kinetic energy rate of galactic supernovae. However, there are still problems with this standard interpretation: Upper limits on -ray fluxes from supernova remnants are below predictions from interactions of accelerated cosmic rays wit ...
... tCR~107 yr, LCR ~ uCR Vgal / tCR ~ 1041 erg/sec, is ~10% of the kinetic energy rate of galactic supernovae. However, there are still problems with this standard interpretation: Upper limits on -ray fluxes from supernova remnants are below predictions from interactions of accelerated cosmic rays wit ...
Cosmic - ScienceA2Z.com
... • Big Bang Theory: (cont) – As the universe expanded, the wave stretched-out, much like a phone cord is stretched as you walk away from the base – The stretched-out wave would be very long and have very low energy – Two scientists, A. Penzias and R. Wilson, discovered this radiation, experimental ve ...
... • Big Bang Theory: (cont) – As the universe expanded, the wave stretched-out, much like a phone cord is stretched as you walk away from the base – The stretched-out wave would be very long and have very low energy – Two scientists, A. Penzias and R. Wilson, discovered this radiation, experimental ve ...
Unit 11: Dark Energy
... determine what these pinwheel-like objects were because they did not know whether they were nearby small systems where one star was forming or distant large objects as big as the whole Milky Way. Distance measurements in astronomy are notoriously difficult and full of subtle errors. We can judge the ...
... determine what these pinwheel-like objects were because they did not know whether they were nearby small systems where one star was forming or distant large objects as big as the whole Milky Way. Distance measurements in astronomy are notoriously difficult and full of subtle errors. We can judge the ...
File
... $400 Answer from H1 Galaxies appear to be red, which means their lightwaves are stretched out, which means they are moving away from us. Everything appears to be moving away from everything. This means the universe is expanding. This means that everything must have been together at one point. ...
... $400 Answer from H1 Galaxies appear to be red, which means their lightwaves are stretched out, which means they are moving away from us. Everything appears to be moving away from everything. This means the universe is expanding. This means that everything must have been together at one point. ...
PowerPoint-Präsentation - Max-Planck
... High-energy gamma rays allow us to explore some of the most extreme, and most interesting objects in the Universe. Most of the radiation we detect is thermal radiation, created by hot bodies such as our Sun. The hotter the source, the higher is the frequency of the radiation. However, very basic con ...
... High-energy gamma rays allow us to explore some of the most extreme, and most interesting objects in the Universe. Most of the radiation we detect is thermal radiation, created by hot bodies such as our Sun. The hotter the source, the higher is the frequency of the radiation. However, very basic con ...
http://lambda.gsfc.nasa.gov/product/map/dr1/pub_papers/firstyear/basic/wmap_basic_results.pdf
... WMAP is intriguing. WMAP continues to operate, so results will improve. ...
... WMAP is intriguing. WMAP continues to operate, so results will improve. ...
ska - Astrophysics
... Hydrogen (right). Weak gravitational lensing will allow the measurement of the dark matter power spectrum, while extragalactic masers will allow the precise determination of H0. Combined with Planck and other CMB data, SKA will remove the degeneracies in all the Cosmological Parameters and reduce th ...
... Hydrogen (right). Weak gravitational lensing will allow the measurement of the dark matter power spectrum, while extragalactic masers will allow the precise determination of H0. Combined with Planck and other CMB data, SKA will remove the degeneracies in all the Cosmological Parameters and reduce th ...
83. Expanding the Universe on a Balloon
... away from each other. Students will observe that some dots move more or farther apart than others, but they will see that no dots get closer together. Most astronomers believe that the galaxies in the universe are moving away from each other in a similar fashion to the dots on the balloon. Also simi ...
... away from each other. Students will observe that some dots move more or farther apart than others, but they will see that no dots get closer together. Most astronomers believe that the galaxies in the universe are moving away from each other in a similar fashion to the dots on the balloon. Also simi ...
The First Stars in the Universe
... universe of 13.7 billion years). Researchers will need better telescopes to see more distant objects dating from still earlier times. Cosmologists, however, can make deductions about the early universe based on the cosmic microwave background radiation, which was emitted about 400,000 years after th ...
... universe of 13.7 billion years). Researchers will need better telescopes to see more distant objects dating from still earlier times. Cosmologists, however, can make deductions about the early universe based on the cosmic microwave background radiation, which was emitted about 400,000 years after th ...
The First Stars in the Universe - Scientific American
... have recently found evidence for the final stages of this ionization process. The researchers observed strong absorption of ultraviolet light in the spectra of quasars that date from about 900 million years after the big bang. The results suggest that the last patches of neutral hydrogen gas were be ...
... have recently found evidence for the final stages of this ionization process. The researchers observed strong absorption of ultraviolet light in the spectra of quasars that date from about 900 million years after the big bang. The results suggest that the last patches of neutral hydrogen gas were be ...
Moffat
... • A fully relativistic modified gravity (MOG) called Scalar-TensorVector-Gravity (STVG or MSTG) leads to a self-consistent, stable gravity theory that can describe solar system, astrophysical and cosmological data. The theory has an extra degree of freedom, a vector field called a “phion” field whos ...
... • A fully relativistic modified gravity (MOG) called Scalar-TensorVector-Gravity (STVG or MSTG) leads to a self-consistent, stable gravity theory that can describe solar system, astrophysical and cosmological data. The theory has an extra degree of freedom, a vector field called a “phion” field whos ...
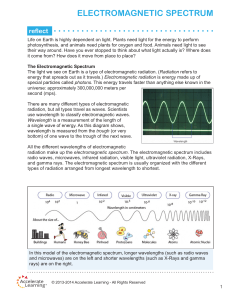
electromagnetic spectrum
... universe exploded and expanded out of a single including people! point during a single event about 13.7 billion years ago. This massive explosion of energy and matter must have given off electromagnetic radiation. Scientists have been able to detect some of this radiation left over from the Big Bang ...
... universe exploded and expanded out of a single including people! point during a single event about 13.7 billion years ago. This massive explosion of energy and matter must have given off electromagnetic radiation. Scientists have been able to detect some of this radiation left over from the Big Bang ...
A. Big Bang Theory: A Failure from the Beginning
... abundances of the lightest elements: hydrogen, deuterium, and helium ... Detailed calculations predicted that the present Universe should contain about 75% of its mass in the form of hydrogen and 25% as helium-4 with about one part in a million ending up in the form of all the other elements. ... Th ...
... abundances of the lightest elements: hydrogen, deuterium, and helium ... Detailed calculations predicted that the present Universe should contain about 75% of its mass in the form of hydrogen and 25% as helium-4 with about one part in a million ending up in the form of all the other elements. ... Th ...
Electromagnetic Spectrum
... Doppler effect together. Sound waves are not a part of the electromagnetic spectrum. However, they are shifted by the Doppler effect the same way that electromagnetic waves are. The unaided human eye is not capable of directly observing the Doppler shift of light on Earth, but the unaided ear can ea ...
... Doppler effect together. Sound waves are not a part of the electromagnetic spectrum. However, they are shifted by the Doppler effect the same way that electromagnetic waves are. The unaided human eye is not capable of directly observing the Doppler shift of light on Earth, but the unaided ear can ea ...
Coupling and Collapse
... Conclusions • Naturally if the perturbation is smaller than the mean free path the photons diffuse istantaneously and no perturbation can survive for smaller scale lengths (or masses). • Assuming a scale length for which the scale length corresponds to the travel carried out in a random walk by a p ...
... Conclusions • Naturally if the perturbation is smaller than the mean free path the photons diffuse istantaneously and no perturbation can survive for smaller scale lengths (or masses). • Assuming a scale length for which the scale length corresponds to the travel carried out in a random walk by a p ...
Cosmic microwave background
The cosmic microwave background (CMB) is the thermal radiation left over from the time of recombination in Big Bang cosmology. In older literature, the CMB is also variously known as cosmic microwave background radiation (CMBR) or ""relic radiation."" The CMB is a cosmic background radiation that is fundamental to observational cosmology because it is the oldest light in the universe, dating to the epoch of recombination. With a traditional optical telescope, the space between stars and galaxies (the background) is completely dark. However, a sufficiently sensitive radio telescope shows a faint background glow, almost exactly the same in all directions, that is not associated with any star, galaxy, or other object. This glow is strongest in the microwave region of the radio spectrum. The accidental discovery of CMB in 1964 by American radio astronomers Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson was the culmination of work initiated in the 1940s, and earned the discoverers the 1978 Nobel Prize.The CMB is a snapshot of the oldest light in our Universe, imprinted on the sky when the Universe was just 380,000 years old. It shows tiny temperature fluctuations that correspond to regions of slightly different densities, representing the seeds of all future structure: the stars and galaxies of today.The CMB is well explained as radiation left over from an early stage in the development of the universe, and its discovery is considered a landmark test of the Big Bang model of the universe. When the universe was young, before the formation of stars and planets, it was denser, much hotter, and filled with a uniform glow from a white-hot fog of hydrogen plasma. As the universe expanded, both the plasma and the radiation filling it grew cooler. When the universe cooled enough, protons and electrons combined to form neutral atoms. These atoms could no longer absorb the thermal radiation, and so the universe became transparent instead of being an opaque fog. Cosmologists refer to the time period when neutral atoms first formed as the recombination epoch, and the event shortly afterwards when photons started to travel freely through space rather than constantly being scattered by electrons and protons in plasma is referred to as photon decoupling. The photons that existed at the time of photon decoupling have been propagating ever since, though growing fainter and less energetic, since the expansion of space causes their wavelength to increase over time (and wavelength is inversely proportional to energy according to Planck's relation). This is the source of the alternative term relic radiation. The surface of last scattering refers to the set of points in space at the right distance from us so that we are now receiving photons originally emitted from those points at the time of photon decoupling.Precise measurements of the CMB are critical to cosmology, since any proposed model of the universe must explain this radiation. The CMB has a thermal black body spectrum at a temperature of 7000272548000000000♠2.72548±0.00057 K. The spectral radiance dEν/dν peaks at 160.2 GHz, in the microwave range of frequencies. (Alternatively if spectral radiance is defined as dEλ/dλ then the peak wavelength is 1.063 mm.) The glow is very nearly uniform in all directions, but the tiny residual variations show a very specific pattern, the same as that expected of a fairly uniformly distributed hot gas that has expanded to the current size of the universe. In particular, the spectral radiance at different angles of observation in the sky contains small anisotropies, or irregularities, which vary with the size of the region examined. They have been measured in detail, and match what would be expected if small thermal variations, generated by quantum fluctuations of matter in a very tiny space, had expanded to the size of the observable universe we see today. This is a very active field of study, with scientists seeking both better data (for example, the Planck spacecraft) and better interpretations of the initial conditions of expansion. Although many different processes might produce the general form of a black body spectrum, no model other than the Big Bang has yet explained the fluctuations. As a result, most cosmologists consider the Big Bang model of the universe to be the best explanation for the CMB.The high degree of uniformity throughout the observable universe and its faint but measured anisotropy lend strong support for the Big Bang model in general and the ΛCDM (""Lambda Cold Dark Matter"") model in particular. Moreover, the fluctuations are coherent on angular scales that are larger than the apparent cosmological horizon at recombination. Either such coherence is acausally fine-tuned, or cosmic inflation occurred.