APB Unit 2 Outline - Westminster Public Schools Wiki
... What is the current model of the molecular architecture of membranes? ...
... What is the current model of the molecular architecture of membranes? ...
Name - Net Start Class
... Week 18 CCA Study Guide Remember this worksheet is meant only to be a guide to help you prepare for the up coming test. You should also access the online textbook, study your journal, and cell diagrams. ...
... Week 18 CCA Study Guide Remember this worksheet is meant only to be a guide to help you prepare for the up coming test. You should also access the online textbook, study your journal, and cell diagrams. ...
"Cell Structures" notes guide
... 19. All cells have ______________ which contains the “instructions” for all the cell’s activities. ...
... 19. All cells have ______________ which contains the “instructions” for all the cell’s activities. ...
S100: Science: a foundation course S100/17: Genetic code Executive Producer: Nat Taylor
... remember that this film is speeded up a great deal so that condensed into a few moments is a process which will last a whole day. Here’s the Interphase cell with little structure visible. And we’ll jump, yes, into Prophase. Chromosomes are distinct, and now they’re free in the cell substance. Rememb ...
... remember that this film is speeded up a great deal so that condensed into a few moments is a process which will last a whole day. Here’s the Interphase cell with little structure visible. And we’ll jump, yes, into Prophase. Chromosomes are distinct, and now they’re free in the cell substance. Rememb ...
File
... Cell Structure Unit 2: Cells Learning Target (7.12DEF) Differentiate between structure and function in plant and animal cell organelles, including cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondrion, chloroplast, and vacuole ...
... Cell Structure Unit 2: Cells Learning Target (7.12DEF) Differentiate between structure and function in plant and animal cell organelles, including cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondrion, chloroplast, and vacuole ...
Cellular Biology Formal Lab #1 Observing Cells
... What is cytoplasmic streaming? What is the purpose? ...
... What is cytoplasmic streaming? What is the purpose? ...
BIO STUDY GUIDE - Biochemistry and Cells
... 1. Which of the four main types of organic molecules are polymers? 2. What does the term organic mean? 3. What is the valence number of electrons for Carbon? 4. Proteins are made of what? 5. Enzymes fall into which of the four main classes of organic molecules? 6. Bases have what pH? Acids have what ...
... 1. Which of the four main types of organic molecules are polymers? 2. What does the term organic mean? 3. What is the valence number of electrons for Carbon? 4. Proteins are made of what? 5. Enzymes fall into which of the four main classes of organic molecules? 6. Bases have what pH? Acids have what ...
cell jeopardy
... These cell parts are visible under a microscope in plants or animals What are the Nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane? ...
... These cell parts are visible under a microscope in plants or animals What are the Nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane? ...
Organelles
... Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum • Ribosomes attached to the membranes give a “rough” appearance • Proteins are produced on the ribosomes and then transferred through the rough e.r. membranes ...
... Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum • Ribosomes attached to the membranes give a “rough” appearance • Proteins are produced on the ribosomes and then transferred through the rough e.r. membranes ...
Nucleus and Ribosomes?!
... •contain DNA and some RNA. • found in eukaryotes (animal and plant). • can cause down syndrome among many others. •are much like nurses because they help deliver/care for babies who are basically big bundles of genetic info <3 •AND much like nurses work in hospitals which are like eukaryotic cells b ...
... •contain DNA and some RNA. • found in eukaryotes (animal and plant). • can cause down syndrome among many others. •are much like nurses because they help deliver/care for babies who are basically big bundles of genetic info <3 •AND much like nurses work in hospitals which are like eukaryotic cells b ...
Presentation
... 1. provides cellular "blueprint" that controls the functions of the cell 2. In the form of DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) 3. DNA is universal for all cells, an all living things - evidence of common ancestry 4. Chromatin is the complex of proteins and DNA, it condenses into chromosomes before cell divi ...
... 1. provides cellular "blueprint" that controls the functions of the cell 2. In the form of DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) 3. DNA is universal for all cells, an all living things - evidence of common ancestry 4. Chromatin is the complex of proteins and DNA, it condenses into chromosomes before cell divi ...
Test Date:______ Essential Concepts and Skills READINGS 1
... cell because of diffusion or transport (homeostasis) . This membrane is flexible j) Cilia – hair-like structures that help in food capture & movement of the organism. k) Flagella - flagella is one long "whip-like" structure used only for movement. l) Cytoplasm – Jelly like substance that surrounds o ...
... cell because of diffusion or transport (homeostasis) . This membrane is flexible j) Cilia – hair-like structures that help in food capture & movement of the organism. k) Flagella - flagella is one long "whip-like" structure used only for movement. l) Cytoplasm – Jelly like substance that surrounds o ...
Tissues
... B) Varying vascularity C) Extracellular matrix 2. Structural components A) Ground substance – fills space between cells and contains the protein fibers B) Protein fibers – provide support & flexibility 1) Collagen fibers 2) Elastic fibers 3) Reticular fibers C) Cells 1) Fibroblasts – connective tiss ...
... B) Varying vascularity C) Extracellular matrix 2. Structural components A) Ground substance – fills space between cells and contains the protein fibers B) Protein fibers – provide support & flexibility 1) Collagen fibers 2) Elastic fibers 3) Reticular fibers C) Cells 1) Fibroblasts – connective tiss ...
Essential Biology 02.3: Eukaryotes In the table below, compare
... Plant cells have a chloroplast, a cell wall and a vacuole while animal cells do not have these as they do not apply to their function because it does not do photosynthesis, need to keep a set shape or get rid of waste. ...
... Plant cells have a chloroplast, a cell wall and a vacuole while animal cells do not have these as they do not apply to their function because it does not do photosynthesis, need to keep a set shape or get rid of waste. ...
CRCT Jeopardy - Thomas County Schools
... Which structure supplies energy through aerobic respiration? • Nucleus • Ribosome • Endoplasmic reticulum • Mitochondrion ...
... Which structure supplies energy through aerobic respiration? • Nucleus • Ribosome • Endoplasmic reticulum • Mitochondrion ...
Ch. 11 Stem Notes
... 2. Three stages of cell signaling: Explain them. a. Reception b. Transduction ...
... 2. Three stages of cell signaling: Explain them. a. Reception b. Transduction ...
Edible Cell Food List (Write the list of food choices on the board for
... Square and Round baked pie crusts (5" diameter) (plant cell or animal cell base) 1 25oz jar applesauce (cytoplasm) 1 box Famous Amos cookies (nucleus) 1 bag of Twizzlers Pull N Peal (cell membrane) 1 12oz bag of stick pretzels (cell wall) 1 10oz bag of mini marshmallows (animal cell vacuoles) 1 10oz ...
... Square and Round baked pie crusts (5" diameter) (plant cell or animal cell base) 1 25oz jar applesauce (cytoplasm) 1 box Famous Amos cookies (nucleus) 1 bag of Twizzlers Pull N Peal (cell membrane) 1 12oz bag of stick pretzels (cell wall) 1 10oz bag of mini marshmallows (animal cell vacuoles) 1 10oz ...
Chapter 7 section 1,2 and 4- The Cell
... 10. Know these words from section 3 or from the power point.: cell wall, cell membrane, cellulose, flagella, cilia. 11. Know the levels of organization. 12. Know the order for smallest to largest for the cells. (animal and plant cells and prokaryotes. 13. understand why cells are specialized. 14. un ...
... 10. Know these words from section 3 or from the power point.: cell wall, cell membrane, cellulose, flagella, cilia. 11. Know the levels of organization. 12. Know the order for smallest to largest for the cells. (animal and plant cells and prokaryotes. 13. understand why cells are specialized. 14. un ...
753
... The small intestine achieves most of the nutrient absorption due to its characteristic morphology: a defined succession of villi and crypts that considerably increases the exchange area (human intestine presents a surface area of 300m2) . More in details, the intestinal epithelium consists of a cell ...
... The small intestine achieves most of the nutrient absorption due to its characteristic morphology: a defined succession of villi and crypts that considerably increases the exchange area (human intestine presents a surface area of 300m2) . More in details, the intestinal epithelium consists of a cell ...
100 Scientists Plant Cells Animal Cells & Cell Theory Organelles
... Which organelle is called “the power house” of the cell? Hint: It releases energy needed for the cell to function properly. ...
... Which organelle is called “the power house” of the cell? Hint: It releases energy needed for the cell to function properly. ...
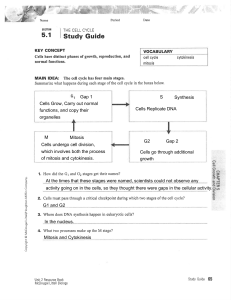
5.1 Study Guide KEY
... MAIN IDEA: Cells divide at different rates. E. Among different types of cells, which stage of the cell cycle varies G1 ...
... MAIN IDEA: Cells divide at different rates. E. Among different types of cells, which stage of the cell cycle varies G1 ...
Supplementary Materials and Methods
... Total RNA was prepared from treated cells using a Qiagen RNEasy mini kit with on column DNAse digestion. RNA sequencing and alignments were performed at Ocean Ridge Biosciences. For q-RTPCR, first strand cDNA was prepared using SuperScript III RT according to manufacturer’s instructions, and qPCR wa ...
... Total RNA was prepared from treated cells using a Qiagen RNEasy mini kit with on column DNAse digestion. RNA sequencing and alignments were performed at Ocean Ridge Biosciences. For q-RTPCR, first strand cDNA was prepared using SuperScript III RT according to manufacturer’s instructions, and qPCR wa ...
CELLS, CELLS, CELLS
... the cell (e.g. proteins) 6. MITOCHONDRIA- supply energy for the cell . "powerhouse" of the cell . convert energy from food (Glucose) into a form the body can use (ATP) through a process called CELLULAR RESPIRATION Chemical formula for Cellular Respiration is (C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + ATP) (T ...
... the cell (e.g. proteins) 6. MITOCHONDRIA- supply energy for the cell . "powerhouse" of the cell . convert energy from food (Glucose) into a form the body can use (ATP) through a process called CELLULAR RESPIRATION Chemical formula for Cellular Respiration is (C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + ATP) (T ...
Extracellular matrix

In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM) is a collection of extracellular molecules secreted by cells that provides structural and biochemical support to the surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM.The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest.The plant ECM includes cell wall components, like cellulose, in addition to more complex signaling molecules. Some single-celled organisms adopt multicelluar biofilms in which the cells are embedded in an ECM composed primarily of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS).