Chapter 6 guided reading handouts
... Recall the relationship of structure to function. Why is the inner membrane of the mitochondria highly folded? What role do all the individual thylakoid membranes serve? (Same answer for both questions.) Chloroplasts and mitochondria both have ribosomes and their own DNA. You will learn later about ...
... Recall the relationship of structure to function. Why is the inner membrane of the mitochondria highly folded? What role do all the individual thylakoid membranes serve? (Same answer for both questions.) Chloroplasts and mitochondria both have ribosomes and their own DNA. You will learn later about ...
Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell
... Recall the relationship of structure to function. Why is the inner membrane of the mitochondria highly folded? What role do all the individual thylakoid membranes serve? (Same answer for both questions.) Chloroplasts and mitochondria both have ribosomes and their own DNA. You will learn later about ...
... Recall the relationship of structure to function. Why is the inner membrane of the mitochondria highly folded? What role do all the individual thylakoid membranes serve? (Same answer for both questions.) Chloroplasts and mitochondria both have ribosomes and their own DNA. You will learn later about ...
Revision Sheet Quarter 1 2014-2015 Department:
... How does chlorophyll aid in the process of photosynthesis? A. Chlorophyll absorbs sunlight. B. Chlorophyll absorbs glucose. C. Chlorophyll releases carbon dioxide. D. Chlorophyll transfers water to the roots of the plant. 12.Eukaryotic cells undergo mitosis as part of the cell cycle. What does a cel ...
... How does chlorophyll aid in the process of photosynthesis? A. Chlorophyll absorbs sunlight. B. Chlorophyll absorbs glucose. C. Chlorophyll releases carbon dioxide. D. Chlorophyll transfers water to the roots of the plant. 12.Eukaryotic cells undergo mitosis as part of the cell cycle. What does a cel ...
Plant and Animal Cells Lab: A Comparison
... Objectives: Students will discover that onions are made up of cells. Students will observe onion cells under a microscope. Students will discover that their skin is made up of cells. Students will observe cheek cells under a microscope. Key Questions: What are cells? How are cells similar to the bri ...
... Objectives: Students will discover that onions are made up of cells. Students will observe onion cells under a microscope. Students will discover that their skin is made up of cells. Students will observe cheek cells under a microscope. Key Questions: What are cells? How are cells similar to the bri ...
CellReviewANS
... ...a double membrane with pores that allow materials to ...ribosomes are found on move in and out of the cell the rough ER ...newly made proteins move from the ribosomes to the ER where they may be ...
... ...a double membrane with pores that allow materials to ...ribosomes are found on move in and out of the cell the rough ER ...newly made proteins move from the ribosomes to the ER where they may be ...
Cell - Cobb Learning
... •Thick and inflexible •Function: Provides support for plant cell •Never found in animal cells ...
... •Thick and inflexible •Function: Provides support for plant cell •Never found in animal cells ...
Cellular Transport Unit - Winona Senior High School
... then inside the cell is hypertonic and vice versa ** Water tends to diffuse from hypotonic to hypertonic ...
... then inside the cell is hypertonic and vice versa ** Water tends to diffuse from hypotonic to hypertonic ...
Exam 1 Fa08 Key
... 13. List two differences between microtubules and intermediate filaments. (1 pt) [hollow rods vs. cables, microtubules larger, microtubules assembled/disassembled but intermediate filaments permanent; tubulin vs. keratin; resist compression vs. resist tension] 14. Name one component of the extracell ...
... 13. List two differences between microtubules and intermediate filaments. (1 pt) [hollow rods vs. cables, microtubules larger, microtubules assembled/disassembled but intermediate filaments permanent; tubulin vs. keratin; resist compression vs. resist tension] 14. Name one component of the extracell ...
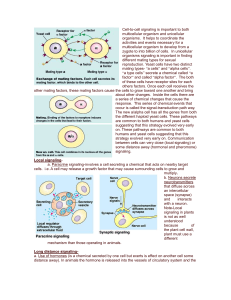
Long distance signaling
... These biochemical pathways include developmental pathways, sensory perception in vision and smell. NoteBacteria that often cause disease by secreting toxins. These toxins may interfere with G-protein functions. 60% of all medicines exert their effect by influencing G-protein pathways. b. Tyrosine-Ki ...
... These biochemical pathways include developmental pathways, sensory perception in vision and smell. NoteBacteria that often cause disease by secreting toxins. These toxins may interfere with G-protein functions. 60% of all medicines exert their effect by influencing G-protein pathways. b. Tyrosine-Ki ...
Tissues - Reocities
... A. Epithelial tissue- covers and protects body surface, cavities. Moves things through it. B. Connective tissue- support body & its parts, connects. Made up of mostly non-living matrix. C. Muscle tissue- produces movement. Made up of contractile units D. Nervous tissue- specializes in communication. ...
... A. Epithelial tissue- covers and protects body surface, cavities. Moves things through it. B. Connective tissue- support body & its parts, connects. Made up of mostly non-living matrix. C. Muscle tissue- produces movement. Made up of contractile units D. Nervous tissue- specializes in communication. ...
CELLS: Structures and Functions
... produced by the cell so they can be exported from the cell. • It is part of the “cytomembrane system” & forms vesicles that eventually fuse with the ...
... produced by the cell so they can be exported from the cell. • It is part of the “cytomembrane system” & forms vesicles that eventually fuse with the ...
Notes - LHSdiffbio
... plants have a cell wall - Animal cells do NOT have a cell wall. - rigid, layered structure on the outside of cells that protects and supports cell - found on cells of plants, fungi, and bacteria - plant cell walls made of cellulose ...
... plants have a cell wall - Animal cells do NOT have a cell wall. - rigid, layered structure on the outside of cells that protects and supports cell - found on cells of plants, fungi, and bacteria - plant cell walls made of cellulose ...
Cell Structure and Function
... 2. M and C DNA is similar to prokaryotic DNA 3. M and C multiply independent from nucleus/mitosis 4. M, C, and N have double membranes ...
... 2. M and C DNA is similar to prokaryotic DNA 3. M and C multiply independent from nucleus/mitosis 4. M, C, and N have double membranes ...
MITOTIC CELL DIVISION
... • longest phase of life cycle • G1 – phase of rapid growth and increase in protein and cell RNA • S – synthesis phase when DNA duplicates • G2 - phase of organelle development and growth in preparation for cell division ...
... • longest phase of life cycle • G1 – phase of rapid growth and increase in protein and cell RNA • S – synthesis phase when DNA duplicates • G2 - phase of organelle development and growth in preparation for cell division ...
chapter 3 powerpoint
... Stem and Progenitor Cells Stem cell • can divide to form two new stem cells • can divide to form a stem cell and a progenitor cell • totipotent – can give rise to any cell type • pluripotent – can give rise to a restricted number of cell ...
... Stem and Progenitor Cells Stem cell • can divide to form two new stem cells • can divide to form a stem cell and a progenitor cell • totipotent – can give rise to any cell type • pluripotent – can give rise to a restricted number of cell ...
Cell Membrane Movement
... Because the cell is filled with salts, sugars, proteins, and other molecules, it will almost always be _________ to fresh _______. • If so, the osmotic pressure should produce a net _________ of water into the cell. As a result, the volume of the cell will _________ until the cell becomes swollen or ...
... Because the cell is filled with salts, sugars, proteins, and other molecules, it will almost always be _________ to fresh _______. • If so, the osmotic pressure should produce a net _________ of water into the cell. As a result, the volume of the cell will _________ until the cell becomes swollen or ...
Mitosis Lab
... Hypothesis: Write a hypothesis on which phase of the cell cycle the onion cell spends most of its time on. HYPOTHESIS: ______________________________________________________________ Procedure: Part I 1. The onion root tip slides have already been positioned to show cells dividing and are on high pow ...
... Hypothesis: Write a hypothesis on which phase of the cell cycle the onion cell spends most of its time on. HYPOTHESIS: ______________________________________________________________ Procedure: Part I 1. The onion root tip slides have already been positioned to show cells dividing and are on high pow ...
5.5 Lecture slides
... • Organs are groups of tissues that perform a specific or related function. • Organ systems are groups of organs that carry out similar functions. ...
... • Organs are groups of tissues that perform a specific or related function. • Organ systems are groups of organs that carry out similar functions. ...
Cell Organelles and their Functions
... Inside the nucleus is another organelle called the nucleolus. It is responsible for making ribosomes. It is similar to all the neuron pathways inside a turtle’s brain. ...
... Inside the nucleus is another organelle called the nucleolus. It is responsible for making ribosomes. It is similar to all the neuron pathways inside a turtle’s brain. ...
Extracellular matrix

In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM) is a collection of extracellular molecules secreted by cells that provides structural and biochemical support to the surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM.The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest.The plant ECM includes cell wall components, like cellulose, in addition to more complex signaling molecules. Some single-celled organisms adopt multicelluar biofilms in which the cells are embedded in an ECM composed primarily of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS).