
Growth(NoTP)
... 1. Redundant DNA-repair mechanisms needed by both normal and neoplastic cells to repair DNA lesions incurred normally during cell division. 2. Repair of damaged DNA is even more important if chemotherapy with DNA-directed anticancer agents or radiation therapy is being carried out. 3. One type of DN ...
... 1. Redundant DNA-repair mechanisms needed by both normal and neoplastic cells to repair DNA lesions incurred normally during cell division. 2. Repair of damaged DNA is even more important if chemotherapy with DNA-directed anticancer agents or radiation therapy is being carried out. 3. One type of DN ...
KEY WORDS/
... saturated (membrane more solid b/c pack closer together) or unsaturated (membrane more fluid b/c don’t pack tightly) F: cholesterol: prevents membrane from solidifying G: sugars: helps as an ID tag for the cell H: skip I: skip J: cytoskeleton fibers: cell structure Fluid: all the stuff moves around ...
... saturated (membrane more solid b/c pack closer together) or unsaturated (membrane more fluid b/c don’t pack tightly) F: cholesterol: prevents membrane from solidifying G: sugars: helps as an ID tag for the cell H: skip I: skip J: cytoskeleton fibers: cell structure Fluid: all the stuff moves around ...
Chapter 3 Vocabulary
... A membrane that surrounds the cell and acts as a barrier between the inside of the cell and the cell’s environment. ...
... A membrane that surrounds the cell and acts as a barrier between the inside of the cell and the cell’s environment. ...
Transport Chapter 5 - local.brookings.k12.sd.us
... What if the HIGH and LOW places are on different sides of a cell membrane? Molecules will still go from HIGH to LOW if the cell membrane will let them through! ...
... What if the HIGH and LOW places are on different sides of a cell membrane? Molecules will still go from HIGH to LOW if the cell membrane will let them through! ...
Cells are the basic unit of life.
... Helps the cell keep its shape and protects the cell. Cell organelles are found in the ...
... Helps the cell keep its shape and protects the cell. Cell organelles are found in the ...
The Building Blocks of Life
... 4 – Function - How does your picture connect to the function of the cell part? Example: the cell wall is like the walls of the factory because it supports and protects the factory. 5 - Type - Plant or Animal cell; Prokaryote or Eukaryote; Example: found in all prokaryotes, fungi and, plant cells; NO ...
... 4 – Function - How does your picture connect to the function of the cell part? Example: the cell wall is like the walls of the factory because it supports and protects the factory. 5 - Type - Plant or Animal cell; Prokaryote or Eukaryote; Example: found in all prokaryotes, fungi and, plant cells; NO ...
bacteria
... • The mitochondria found in eukaryotic cells contain their own loop of DNA as well as 70S ribosomes. Given this information suggest how mitochondria may have originated ...
... • The mitochondria found in eukaryotic cells contain their own loop of DNA as well as 70S ribosomes. Given this information suggest how mitochondria may have originated ...
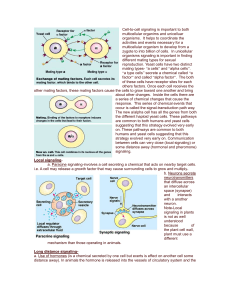
Cell-to-cell signaling is important to both multicellular organims and
... reproduction. Yeast cells have two distinct mating types- “a cells” and “alpha cells”. “a type cells” secrete a chemical called “a factor” and called “alpha factor”. The both of these cells have receptor sites for each others factors. Once each cell receives the other mating factors, these mating fa ...
... reproduction. Yeast cells have two distinct mating types- “a cells” and “alpha cells”. “a type cells” secrete a chemical called “a factor” and called “alpha factor”. The both of these cells have receptor sites for each others factors. Once each cell receives the other mating factors, these mating fa ...
Supplementary Methods (docx 21K)
... Co-Culture of TAM with HCC cells Co-culture of TAM with HCC cells was achieved with Falcon cell culture insert (0.8μm, Corning, New York, USA). HCC cells were cultured in receiving chamber and pre-treated TAM was seeded into culture insert and allowed co-incubation for ...
... Co-Culture of TAM with HCC cells Co-culture of TAM with HCC cells was achieved with Falcon cell culture insert (0.8μm, Corning, New York, USA). HCC cells were cultured in receiving chamber and pre-treated TAM was seeded into culture insert and allowed co-incubation for ...
Cell to Organism - Moore Public Schools
... 2. Interphase is the period of growth and development for a cell. 3. During interphase, most cells go through three stages—rapid growth and replication of the organelles;; replication of DNA, the genetic information in a cell;; and ...
... 2. Interphase is the period of growth and development for a cell. 3. During interphase, most cells go through three stages—rapid growth and replication of the organelles;; replication of DNA, the genetic information in a cell;; and ...
THE CELL/THE CITY - Westerville City Schools
... – An average egg weighs about three pounds (1.4 kg) – Roughly equivalent to about two dozen chicken eggs. – It would take approximately 40 minutes to hard-boil an ostrich egg. ...
... – An average egg weighs about three pounds (1.4 kg) – Roughly equivalent to about two dozen chicken eggs. – It would take approximately 40 minutes to hard-boil an ostrich egg. ...
Life of a Protein #1 This outline describes the job of a specialized
... Determine 1) the cells location in the human body and 2) its job description from these clues. Epithelial cells release proteins, which communicate to our cell through the PLASMA MEMBRANE. The NUCLEUS gets the signal. Genes in the NUCLEUS that code for specialized proteins are activated. Messanger R ...
... Determine 1) the cells location in the human body and 2) its job description from these clues. Epithelial cells release proteins, which communicate to our cell through the PLASMA MEMBRANE. The NUCLEUS gets the signal. Genes in the NUCLEUS that code for specialized proteins are activated. Messanger R ...
1. D Bacteria are unicellular organisms. They are made up of only
... of cells, responding to the world around them, adapting to the environment, use of energy, and growth. ...
... of cells, responding to the world around them, adapting to the environment, use of energy, and growth. ...
In a plant cell - Cloudfront.net
... energy. This energy is used by cells to do work. This work may be building new molecules which have a particular function in the body, or it may be to produce movement (muscle cells, for example). ...
... energy. This energy is used by cells to do work. This work may be building new molecules which have a particular function in the body, or it may be to produce movement (muscle cells, for example). ...
Partitioning 2 - CS Course Webpages
... ni - number of cells on neti si - size (area) of celli smax - largest cell = max(si) S - total size of cells = sum(si) pi - number of pins on celli pmax - most pins on a cell = max(pi) P - total number of pins = sum(pi) C - total number of cells N - total number of nets r - fraction of cell area in ...
... ni - number of cells on neti si - size (area) of celli smax - largest cell = max(si) S - total size of cells = sum(si) pi - number of pins on celli pmax - most pins on a cell = max(pi) P - total number of pins = sum(pi) C - total number of cells N - total number of nets r - fraction of cell area in ...
The Anatomy of a Cell
... Even though your body cells have different jobs to do, certain aspects of their internal anatomies (structures) are similar. While doing this project, you will learn the internal anatomy of a generalized cell. Animal cells and plants have many similarities and many differences. Look at the two diffe ...
... Even though your body cells have different jobs to do, certain aspects of their internal anatomies (structures) are similar. While doing this project, you will learn the internal anatomy of a generalized cell. Animal cells and plants have many similarities and many differences. Look at the two diffe ...
Cell division (mitosis) lab
... Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells (Adapted PDF from marietta.edu) A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules, or chromosomes. For example, each human cell possesses 46 chromosomes, wh ...
... Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells (Adapted PDF from marietta.edu) A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules, or chromosomes. For example, each human cell possesses 46 chromosomes, wh ...
Name: Date: Period: Cell Organelles Worksheet[1].doc Organelle
... Provides temporary storage of food, enzymes and waste products Firm, protective structure that gives the cell its shape in plants, fungi, most bacteria and some protests Produces a usable form of energy for the cell Packages proteins for transport out of the cell Everything inside the cell including ...
... Provides temporary storage of food, enzymes and waste products Firm, protective structure that gives the cell its shape in plants, fungi, most bacteria and some protests Produces a usable form of energy for the cell Packages proteins for transport out of the cell Everything inside the cell including ...
Chp_7
... Desmosomes & Adhesion Belts intermediate filaments penetrate & are shared through the membranes of both cells. (collagen, keratin) Intracellular space still present ...
... Desmosomes & Adhesion Belts intermediate filaments penetrate & are shared through the membranes of both cells. (collagen, keratin) Intracellular space still present ...
Extracellular matrix

In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM) is a collection of extracellular molecules secreted by cells that provides structural and biochemical support to the surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM.The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest.The plant ECM includes cell wall components, like cellulose, in addition to more complex signaling molecules. Some single-celled organisms adopt multicelluar biofilms in which the cells are embedded in an ECM composed primarily of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS).




















![Name: Date: Period: Cell Organelles Worksheet[1].doc Organelle](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014152553_1-fd24a25ff154c0312a2390f004444c80-300x300.png)

