Chapter 4 Section 1 Worksheet
... 6. The partial breakdown of glucose in the absence of oxygen is a type of cellular respiration better known as _______________________. 7. ________________ is also used to produce alcohol products. Yeast is added to some form of sugar and as the yeast break down the glucose they give off carbon diox ...
... 6. The partial breakdown of glucose in the absence of oxygen is a type of cellular respiration better known as _______________________. 7. ________________ is also used to produce alcohol products. Yeast is added to some form of sugar and as the yeast break down the glucose they give off carbon diox ...
chapter 23 roots, stems and leaves
... -outer covering of a plant consists of dermal tissue which consists of layers of epidermal cells. -dermal tissue is often covered a thick waxy layer that protects against water loss and injury - this waxy covering is called the cuticle. -some epidermal cells have tiny projections called trichomes wh ...
... -outer covering of a plant consists of dermal tissue which consists of layers of epidermal cells. -dermal tissue is often covered a thick waxy layer that protects against water loss and injury - this waxy covering is called the cuticle. -some epidermal cells have tiny projections called trichomes wh ...
Mitosis Lab Activity
... Part B: Number of Cells in Interphase vs. M Phase How can dividing cells (in M phase) be identified when compared to non-dividing cells (in interphase)? ...
... Part B: Number of Cells in Interphase vs. M Phase How can dividing cells (in M phase) be identified when compared to non-dividing cells (in interphase)? ...
Epithelial Tissue
... • Form continuous sheets bound by cell junctions (p. 57) • Free surface or apical surface is exposed to body’s exterior or cavity of an organ • Basement membrane are underlining layers • Avascular – no blood vessels; rely on diffusion of gases & nutrients from underlying connective tissues • regener ...
... • Form continuous sheets bound by cell junctions (p. 57) • Free surface or apical surface is exposed to body’s exterior or cavity of an organ • Basement membrane are underlining layers • Avascular – no blood vessels; rely on diffusion of gases & nutrients from underlying connective tissues • regener ...
The Cell - myndrs.com
... May looks similar to smooth ER, but it is a set of about 7 or 8 flattened saccules between ER and the cell membrane “Packages, processes and labels” the products from the ER Makes concentrated packages of proteins Puts carbohydrate chains (labels) on the packages of proteins so that specific c ...
... May looks similar to smooth ER, but it is a set of about 7 or 8 flattened saccules between ER and the cell membrane “Packages, processes and labels” the products from the ER Makes concentrated packages of proteins Puts carbohydrate chains (labels) on the packages of proteins so that specific c ...
Name - OnCourse
... 2. In the circles provided sketch what you see. 3. Please use color pencils where appropriate. 4. Please label all cell parts that are visible to you. ...
... 2. In the circles provided sketch what you see. 3. Please use color pencils where appropriate. 4. Please label all cell parts that are visible to you. ...
APOplast
... • Directly proportional to the molarity (M) • An increase in solutes has a negative effect on water potential • Ψs is always a negative number • As the solute concentration increases, the solute potential becomes more negative – Unless it is pure water, in which case the solute potential is zero ...
... • Directly proportional to the molarity (M) • An increase in solutes has a negative effect on water potential • Ψs is always a negative number • As the solute concentration increases, the solute potential becomes more negative – Unless it is pure water, in which case the solute potential is zero ...
Part 1: Biology Basics
... Small, hydrophobic molecules such as O2 and CO2 are compatible with the hydrophobic tails of the phospholipid bilayer, so they can scoot across membranes Hydrophilic molecules such as ions can’t get through by themselves, so they need help to cross. Larger molecules (think food and hormones) also ...
... Small, hydrophobic molecules such as O2 and CO2 are compatible with the hydrophobic tails of the phospholipid bilayer, so they can scoot across membranes Hydrophilic molecules such as ions can’t get through by themselves, so they need help to cross. Larger molecules (think food and hormones) also ...
Part 1: Biology Basics
... Small, hydrophobic molecules such as O2 and CO2 are compatible with the hydrophobic tails of the phospholipid bilayer, so they can scoot across membranes Hydrophilic molecules such as ions can’t get through by themselves, so they need help to cross. Larger molecules (think food and hormones) also ...
... Small, hydrophobic molecules such as O2 and CO2 are compatible with the hydrophobic tails of the phospholipid bilayer, so they can scoot across membranes Hydrophilic molecules such as ions can’t get through by themselves, so they need help to cross. Larger molecules (think food and hormones) also ...
1.4 Energy Organelles, Plants and Animals
... What is the function of the cell membrane? If a cell’s nucleus is destroyed, the cell immediately dies. Using the function of the nucleus, explain why. Write in complete sentences! Don’t talk during the Catalyst! ...
... What is the function of the cell membrane? If a cell’s nucleus is destroyed, the cell immediately dies. Using the function of the nucleus, explain why. Write in complete sentences! Don’t talk during the Catalyst! ...
3-1 Cells are the Basic unit of life
... •Vacuoles are fluid-filled sacs that hold materials such as water, salts, pigments, etc. •Lysosomes contain enzymes to digest lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins into particles that can be used by the cell. •Centrioles are formed from microtubules in animal cells. They are important in cell division ...
... •Vacuoles are fluid-filled sacs that hold materials such as water, salts, pigments, etc. •Lysosomes contain enzymes to digest lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins into particles that can be used by the cell. •Centrioles are formed from microtubules in animal cells. They are important in cell division ...
Ch. 2-2: The Organelles of the Cell ER, Golgi Complex, Lysosomes
... 1. Organelles are very _________ in size and can only be observed with a __________. 2. They each have a specific ___________and are found throughout the ____________. 3. ___________ takes part in nearly every cell _______________. 4. What makes these proteins? ________________ 5. RIbosomes do not h ...
... 1. Organelles are very _________ in size and can only be observed with a __________. 2. They each have a specific ___________and are found throughout the ____________. 3. ___________ takes part in nearly every cell _______________. 4. What makes these proteins? ________________ 5. RIbosomes do not h ...
chapter 4 study guide
... (contain: plaque, cadherins) desmosomes (attach adjacent cells to each other in “spot welds”) (contain: plaque, cadherins, intermediate filaments) hemidesmosomes (anchor cells to basement membrane) (contain: plaque, integrins, intermediate filaments) gap junctions (allow ions and small molecules to ...
... (contain: plaque, cadherins) desmosomes (attach adjacent cells to each other in “spot welds”) (contain: plaque, cadherins, intermediate filaments) hemidesmosomes (anchor cells to basement membrane) (contain: plaque, integrins, intermediate filaments) gap junctions (allow ions and small molecules to ...
Chapter 6: A. 4 types of tissues I. Epithelial Tissue Types of
... Epithelial tissue Connective tissue Nervous tissue Muscular tissue ...
... Epithelial tissue Connective tissue Nervous tissue Muscular tissue ...
Physical Oceanography
... • All living things are composed of 1 or more cells (uni- vs. multi) • Basic units of structure and function in an organism • Come only from existing cells ...
... • All living things are composed of 1 or more cells (uni- vs. multi) • Basic units of structure and function in an organism • Come only from existing cells ...
developed
... turning other genes on and off. The DNA-binding piece of a Hox protein is called the homeodomain, and it's encoded by the homeobox. The homeodomains in different Hox proteins are similar but not identical— they bind to different DNA sequences. So different Hox proteins regulate different sets of gen ...
... turning other genes on and off. The DNA-binding piece of a Hox protein is called the homeodomain, and it's encoded by the homeobox. The homeodomains in different Hox proteins are similar but not identical— they bind to different DNA sequences. So different Hox proteins regulate different sets of gen ...
Animal Plant
... I. B. Cell Theory The cell is the basic living unit of structure and function. – All organisms are composed of one or more cells. ...
... I. B. Cell Theory The cell is the basic living unit of structure and function. – All organisms are composed of one or more cells. ...
Scavenger Hunt
... cell. It accepts vesicles from the ER containing proteins, modifies the proteins then repackages them into new vesicles for transport. 7. This organelle has its own double layer membrane surrounding it as the most important information within a cell is stored here. 8. The role of this organelle ...
... cell. It accepts vesicles from the ER containing proteins, modifies the proteins then repackages them into new vesicles for transport. 7. This organelle has its own double layer membrane surrounding it as the most important information within a cell is stored here. 8. The role of this organelle ...
Cellular respiration
... respiration occurs. The electron transport chain. • In this 2nd step, the most number of ATP is produced. About 36 molecules of ATP is made. More or less can be made depending on the type of cell. A fat cell will make less ATP than a muscle cell. • In addition to making ATP water is also produced. • ...
... respiration occurs. The electron transport chain. • In this 2nd step, the most number of ATP is produced. About 36 molecules of ATP is made. More or less can be made depending on the type of cell. A fat cell will make less ATP than a muscle cell. • In addition to making ATP water is also produced. • ...
Name
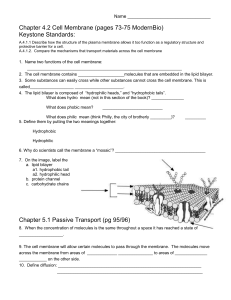
... A.4.1.1 Describe how the structure of the plasma membrane allows it too function as a regulatory structure and protective barrier for a cell. A.4.1.2. Compare the mechanisms that transport materials across the cell membrane ...
... A.4.1.1 Describe how the structure of the plasma membrane allows it too function as a regulatory structure and protective barrier for a cell. A.4.1.2. Compare the mechanisms that transport materials across the cell membrane ...
INTRODUCTION TO MICROBIOLOGY
... larger (80S) ribosomes • Whereas prokaryotic cells contain no organelles and smaller (70S) ribosomes • Most prokaryotes have a rigid external cell wall that contains peptidoglycan a polymer of aminoacids and sugars as its unique structural component. • Eukaryotes do not contain peptidoglycan . They ...
... larger (80S) ribosomes • Whereas prokaryotic cells contain no organelles and smaller (70S) ribosomes • Most prokaryotes have a rigid external cell wall that contains peptidoglycan a polymer of aminoacids and sugars as its unique structural component. • Eukaryotes do not contain peptidoglycan . They ...
The Cell
... • a network of tunnels and passageways • 2 types – • rough ER has ribosomes • smooth ER does not have ribosomes ...
... • a network of tunnels and passageways • 2 types – • rough ER has ribosomes • smooth ER does not have ribosomes ...
cell unit targets - www .alexandria .k12 .mn .us
... Cell Biology is an exploding field with many job opportunities. Cell Biologists battle cancer, create Clones of animals and plants, maintain frozen embryos of endangered species, teach bacteria to make medicines for human use, and many other exciting things. If you are interested in cells or any top ...
... Cell Biology is an exploding field with many job opportunities. Cell Biologists battle cancer, create Clones of animals and plants, maintain frozen embryos of endangered species, teach bacteria to make medicines for human use, and many other exciting things. If you are interested in cells or any top ...
Extracellular matrix

In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM) is a collection of extracellular molecules secreted by cells that provides structural and biochemical support to the surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM.The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest.The plant ECM includes cell wall components, like cellulose, in addition to more complex signaling molecules. Some single-celled organisms adopt multicelluar biofilms in which the cells are embedded in an ECM composed primarily of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS).