Human Blood Typing Lab
... genetically determined classes of human blood which are based on the presence or absence of certain erythrocyte surface antigens (glycoproteins) and are clinically identified by characteristic agglutination reactions; for blood transfusion purposes, the ABO and Rh blood group systems are the most im ...
... genetically determined classes of human blood which are based on the presence or absence of certain erythrocyte surface antigens (glycoproteins) and are clinically identified by characteristic agglutination reactions; for blood transfusion purposes, the ABO and Rh blood group systems are the most im ...
Click here for Screening Sign Up
... On February 6, 2017 Community ISD’s employees will have the opportunity to take part in a blood screening conducted by Health Matters. The blood screening includes the following: metabolic panel (checks vital organs), lipid panel (cholesterols), Hemoglobin A1c (diabetes), complete blood count, thyro ...
... On February 6, 2017 Community ISD’s employees will have the opportunity to take part in a blood screening conducted by Health Matters. The blood screening includes the following: metabolic panel (checks vital organs), lipid panel (cholesterols), Hemoglobin A1c (diabetes), complete blood count, thyro ...
Bell work Blood Types - Deltona-HSA
... Bell work Blood Types 1. Suppose a child is of blood type A and the mother is of type 0. What type or types may the father belong to? 2. Suppose a father and mother claim they have been given the wrong baby at the hospital. Both parents are blood type A. The baby they have been given is blood type O ...
... Bell work Blood Types 1. Suppose a child is of blood type A and the mother is of type 0. What type or types may the father belong to? 2. Suppose a father and mother claim they have been given the wrong baby at the hospital. Both parents are blood type A. The baby they have been given is blood type O ...
Blood Sample - Lead
... 3 mL of whole blood in a Vacutainer® 3-mL EDTA (lavender top) tube. 2. Refrigerate the whole blood immediately or place in a cooler with ice packs for delivery to the laboratory for processing. Blood tubes should never be placed directly on the ice source because this may cause hemolysis. 3. At the ...
... 3 mL of whole blood in a Vacutainer® 3-mL EDTA (lavender top) tube. 2. Refrigerate the whole blood immediately or place in a cooler with ice packs for delivery to the laboratory for processing. Blood tubes should never be placed directly on the ice source because this may cause hemolysis. 3. At the ...
Blood Web Activity
... 15. How many white blood cells are contained in a drop of blood? ________________________________________________________________________ 16. A significantly high white blood cell count can be an indicator that a patient has what disease? _____________________________________________________________ ...
... 15. How many white blood cells are contained in a drop of blood? ________________________________________________________________________ 16. A significantly high white blood cell count can be an indicator that a patient has what disease? _____________________________________________________________ ...
Hematopoiesis and Hemostasis
... proximal epiphyses of long bones. • Each type of blood cell is produced in response to changing needs of the body. • On average, an ounce of new blood is produced each day with about 100 billion new blood cells/formed elements. ...
... proximal epiphyses of long bones. • Each type of blood cell is produced in response to changing needs of the body. • On average, an ounce of new blood is produced each day with about 100 billion new blood cells/formed elements. ...
Become A Blood Donor
... We are the American Red Cross. Governed by volunteers and supported by giving individuals and communities, the American Red Cross is the single largest supplier of blood products to hospitals throughout the United States. While local hospital needs are always met first, the Red Cross also helps ensu ...
... We are the American Red Cross. Governed by volunteers and supported by giving individuals and communities, the American Red Cross is the single largest supplier of blood products to hospitals throughout the United States. While local hospital needs are always met first, the Red Cross also helps ensu ...
What`s Wrong With this Blood?
... Blood contains 140,000 to 400,000 platelets/mm3 and they live for 10 days ...
... Blood contains 140,000 to 400,000 platelets/mm3 and they live for 10 days ...
Permission for Minor to Donate Form
... Your child may be asked to participate in an apheresis donation, where the desired blood components—platelets, red blood cells, and/or or plasma—are collected, and the remaining blood components are returned. Additional risks of reactions due to reduced calcium levels and possibly allergic effects a ...
... Your child may be asked to participate in an apheresis donation, where the desired blood components—platelets, red blood cells, and/or or plasma—are collected, and the remaining blood components are returned. Additional risks of reactions due to reduced calcium levels and possibly allergic effects a ...
INTERNSHIP OPPORTUNITIES WITH BLOODCONNECT About
... mails/telephonic conversations. The internship provides a unique opportunity of working at ground level to understand the situation of Blood donation and then to tackle it. Internship opportunities: Ground level research internship (required in all cities): You will have to find answers to the follo ...
... mails/telephonic conversations. The internship provides a unique opportunity of working at ground level to understand the situation of Blood donation and then to tackle it. Internship opportunities: Ground level research internship (required in all cities): You will have to find answers to the follo ...
Massive Transfusion Guidelines 02
... major head injury, uncontrolled hemorrhage NOTE: It is Blood Bank policy to irradiate all blood products for children 12 months of age. Irradiation takes about 7 additional minutes per unit of blood product. The clinical team could instruct the Blood Bank to forego irradiation in urgent cases. ...
... major head injury, uncontrolled hemorrhage NOTE: It is Blood Bank policy to irradiate all blood products for children 12 months of age. Irradiation takes about 7 additional minutes per unit of blood product. The clinical team could instruct the Blood Bank to forego irradiation in urgent cases. ...
Blood Typing Virtual Lab
... 5. Record your observations from the procedure into the table below and in the notebook. Enter “yes: if the blood sample clumped together when mixed with serum, and enter “no” if the blood sample did not clump together. After you’ve entered all of your observations, determine the type of each sampl ...
... 5. Record your observations from the procedure into the table below and in the notebook. Enter “yes: if the blood sample clumped together when mixed with serum, and enter “no” if the blood sample did not clump together. After you’ve entered all of your observations, determine the type of each sampl ...
Chapter 30 - Virtual Lab Blood Typing
... Go to “classzone.com”. Click on High School; California; Go. Then choose the McDougal Littell book with the hatching alligator on it. Under “Labs” choose Virtual labs, and pick Blood Typing. Read the Problem. 1. What must the doctors do before the transfusion? Follow the steps and answer the questio ...
... Go to “classzone.com”. Click on High School; California; Go. Then choose the McDougal Littell book with the hatching alligator on it. Under “Labs” choose Virtual labs, and pick Blood Typing. Read the Problem. 1. What must the doctors do before the transfusion? Follow the steps and answer the questio ...
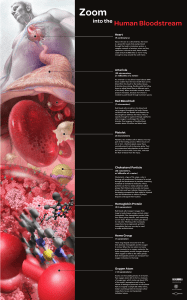
Zoom into the Human Bloodstream Annotated
... hundreds of cholesterol molecules. These particles can form a sticky substance called plaque that thickens artery walls and causes blood clots and heart attacks. Researchers are developing nanoparticles that might be injected into the bloodstream to collect at plaque deposits and signal their locati ...
... hundreds of cholesterol molecules. These particles can form a sticky substance called plaque that thickens artery walls and causes blood clots and heart attacks. Researchers are developing nanoparticles that might be injected into the bloodstream to collect at plaque deposits and signal their locati ...
Lecture 1 - gserianne.com
... Antigens and Antibodies • The major function of the immune system is to distinguish ‘self’ from ‘non-self’ • Antigens are glycoproteins that can potentially trigger an immune response (agglutinogens) ...
... Antigens and Antibodies • The major function of the immune system is to distinguish ‘self’ from ‘non-self’ • Antigens are glycoproteins that can potentially trigger an immune response (agglutinogens) ...
ASSESSMENT OF BACTERIAL CONTAMINANTS IN WHOLE
... The prevalence of bacterial contaminants in whole blood and packed red cells at Kenyatta National Hospital is high at 11.4%. Majority of the bacteria isolated were Gram negative bacilli which may have come from the donor or contaminated laboratory environment. The organisms showed high resistance to ...
... The prevalence of bacterial contaminants in whole blood and packed red cells at Kenyatta National Hospital is high at 11.4%. Majority of the bacteria isolated were Gram negative bacilli which may have come from the donor or contaminated laboratory environment. The organisms showed high resistance to ...
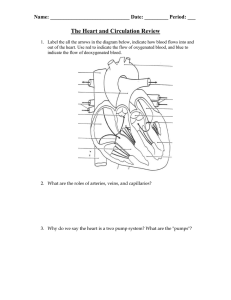
Systemic and Pulmonary Circulation Worksheet
... 1. Label the all the arrows in the diagram below, indicate how blood flows into and out of the heart. Use red to indicate the flow of oxygenated blood, and blue to indicate the flow of deoxygenated blood. ...
... 1. Label the all the arrows in the diagram below, indicate how blood flows into and out of the heart. Use red to indicate the flow of oxygenated blood, and blue to indicate the flow of deoxygenated blood. ...
Ch 12 Blood Cells
... sample, should be 45%. The remaining fluid is plasma (55%). To determine the percentages, blood is placed in a centrifuge ...
... sample, should be 45%. The remaining fluid is plasma (55%). To determine the percentages, blood is placed in a centrifuge ...
BLOOD DISORDERS
... And because they grow uncontrollably, they take over the bone marrow and interfere with the body's production of other important types of cells in the bloodstream, like red blood cells (which carry oxygen) and platelets (which help blood to clot). ...
... And because they grow uncontrollably, they take over the bone marrow and interfere with the body's production of other important types of cells in the bloodstream, like red blood cells (which carry oxygen) and platelets (which help blood to clot). ...
red blood cells - Crestwood Local Schools
... And because they grow uncontrollably, they take over the bone marrow and interfere with the body's production of other important types of cells in the bloodstream, like red blood cells (which carry oxygen) and platelets (which help blood to clot). ...
... And because they grow uncontrollably, they take over the bone marrow and interfere with the body's production of other important types of cells in the bloodstream, like red blood cells (which carry oxygen) and platelets (which help blood to clot). ...
Blood donation
A blood donation occurs when a person voluntarily has blood drawn and used for transfusions and/or made into biopharmaceutical medications by a process called fractionation (separation of whole-blood components). Donation may be of whole blood (WB), or of specific components directly (the latter called apheresis). Blood banks often participate in the collection process as well as the procedures that follow it.Today, in the developed world, most blood donors are unpaid volunteers who donate blood for a community supply. In poorer countries, established supplies are limited and donors usually give blood when family or friends need a transfusion (directed donation). Many donors donate as an act of charity, but in countries that allow paid donation some donors are paid, and in some cases there are incentives other than money such as paid time off from work. Donors can also have blood drawn for their own future use (autologous donation). Donating is relatively safe, but some donors have bruising where the needle is inserted or may feel faint.Potential donors are evaluated for anything that might make their blood unsafe to use. The screening includes testing for diseases that can be transmitted by a blood transfusion, including HIV and viral hepatitis. The donor must also answer questions about medical history and take a short physical examination to make sure the donation is not hazardous to his or her health. How often a donor can give varies from days to months based on what he or she donates and the laws of the country where the donation takes place. For example, in the United States, donors must wait eight weeks (56 days) between whole blood donations but only seven days between platelet pheresis donations.The amount of blood drawn and the methods vary. The collection can be done manually or with automated equipment that only takes specific portions of the blood. Most of the components of blood used for transfusions have a short shelf life, and maintaining a constant supply is a persistent problem. This has led to some increased interest in autotransfusion, whereby a patient's blood is salvaged during surgery for continuous reinfusion — or alternatively, is ""self-donated"" prior to when it will be needed. (Generally, the notion of ""donation"" does not refer to giving to one's self, though in this context it has become somewhat acceptably idiomatic.)