WALK THE WALK - Hoxworth Blood Center
... some donors may experience some light-headedness, which is why we provide refreshments for donors. In rare instances, some donors may experience more pronounced post donation symptoms that require additional follow up and care with blood drive donation staff. If you experience any changes after the ...
... some donors may experience some light-headedness, which is why we provide refreshments for donors. In rare instances, some donors may experience more pronounced post donation symptoms that require additional follow up and care with blood drive donation staff. If you experience any changes after the ...
Blood Facts:
... Type O negative is the universal donor and can give blood to any other blood type. ONLY 8% of the U.S. population has blood type O negative. AB positive is the universal recipient and can receive blood from any other blood type. 2 ½ % of the U.S. population has blood type AB positive. How long until ...
... Type O negative is the universal donor and can give blood to any other blood type. ONLY 8% of the U.S. population has blood type O negative. AB positive is the universal recipient and can receive blood from any other blood type. 2 ½ % of the U.S. population has blood type AB positive. How long until ...
WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW ABOUT PLATELET DONATION
... in the last 12 months, as long as they are healthy and not on any medication that affects their platelets. Male donors are predominately recruited as a risk reduction strategy forTransfusion-Related Acute Lung Injury (TRALI), a rare but sometimes fatal transfusion complication. It can cause breathin ...
... in the last 12 months, as long as they are healthy and not on any medication that affects their platelets. Male donors are predominately recruited as a risk reduction strategy forTransfusion-Related Acute Lung Injury (TRALI), a rare but sometimes fatal transfusion complication. It can cause breathin ...
Guidance Standard17
... What arrangements do you have for documenting all adverse incidents, near misses, complaints, serious adverse reactions and serious adverse events to the MHRA (via SABRE)? What arrangements do you have for reporting to external bodies, e.g. Report to the Serious Hazards of Transfusion (SHOT), Welsh ...
... What arrangements do you have for documenting all adverse incidents, near misses, complaints, serious adverse reactions and serious adverse events to the MHRA (via SABRE)? What arrangements do you have for reporting to external bodies, e.g. Report to the Serious Hazards of Transfusion (SHOT), Welsh ...
Action - Allnurses.com
... most side effects are due to excessive vasoconstriction of blood vessels which results in: - hypertension - hypertensive crisis - heart palpitations - hemorrhage (usually cerebral) - cardiac arrhythmias irritation of nasal sinuses (when used as decongestant due to excessive dryness from the vasocons ...
... most side effects are due to excessive vasoconstriction of blood vessels which results in: - hypertension - hypertensive crisis - heart palpitations - hemorrhage (usually cerebral) - cardiac arrhythmias irritation of nasal sinuses (when used as decongestant due to excessive dryness from the vasocons ...
Slide 1
... Nomogram of supine MOPP versus IOP as a function of SBP and DBP values. Note that at IOP of 35 mm Hg, deemed safe throughout most PPV procedures, patient with lower blood pressure ranges show frankly critical MOPP values. At 40 mm Hg IOP all exemplified blood pressure rages should be considered bord ...
... Nomogram of supine MOPP versus IOP as a function of SBP and DBP values. Note that at IOP of 35 mm Hg, deemed safe throughout most PPV procedures, patient with lower blood pressure ranges show frankly critical MOPP values. At 40 mm Hg IOP all exemplified blood pressure rages should be considered bord ...
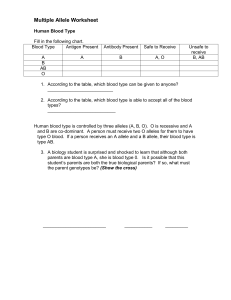
Multiple Allele Worksheet
... finally calmed down enough to talk coherently, you learn that one of his orderlies came on duty the previous night after spending a few hours with his friends at a local bar, and as a joke proceeded to exchange wrist bands on the four babies in the nursery, all of whom are the same age, resemble wri ...
... finally calmed down enough to talk coherently, you learn that one of his orderlies came on duty the previous night after spending a few hours with his friends at a local bar, and as a joke proceeded to exchange wrist bands on the four babies in the nursery, all of whom are the same age, resemble wri ...
red blood cell platelet white blood cell
... fragments, and plasma. • Whole blood is made up of different materials. – Plasma • 90% H2O- allows for materials to dissolve • Concentrations- diffusion into or out of blood plasma • Amino acids, glucose, salts, waste, vitamins, hormones ...
... fragments, and plasma. • Whole blood is made up of different materials. – Plasma • 90% H2O- allows for materials to dissolve • Concentrations- diffusion into or out of blood plasma • Amino acids, glucose, salts, waste, vitamins, hormones ...
blood type diets - Rode Kruis
... BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES • An association between particular blood types and vulnerability towards certain diseases has been researched. • This association between blood types and disease has been translated into a range of blood type diets. • Blood type diets are designed specifically for each ...
... BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES • An association between particular blood types and vulnerability towards certain diseases has been researched. • This association between blood types and disease has been translated into a range of blood type diets. • Blood type diets are designed specifically for each ...
Blood Typing Guided Notes
... The key to transfusions: ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ ...
... The key to transfusions: ________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________ ...
Blood Types
... i: does not produce antigens (recessive) Type AB shows codominance, both the A and B antigens are present on the cell Type O blood is homozygous recessive ...
... i: does not produce antigens (recessive) Type AB shows codominance, both the A and B antigens are present on the cell Type O blood is homozygous recessive ...
5198 Assist in the collection and storage of blood and
... Blood volumes and safe sample volumes Element 2 Long term care of donor (dietary, work) Element 3 Immunological and non-immunological causes of transfusion reactions Rate and volume of administration. ...
... Blood volumes and safe sample volumes Element 2 Long term care of donor (dietary, work) Element 3 Immunological and non-immunological causes of transfusion reactions Rate and volume of administration. ...
blood - Chatt
... The liquid portion of the blood. Made up mostly of water, but also contains nutrients, electrolytes, hormones and cellular wastes. Plasma carries gases as well (oxygen, carbon dioxide and nitrogen). The plasma also contains three proteins which are made by the liver. Albumin is a large prote ...
... The liquid portion of the blood. Made up mostly of water, but also contains nutrients, electrolytes, hormones and cellular wastes. Plasma carries gases as well (oxygen, carbon dioxide and nitrogen). The plasma also contains three proteins which are made by the liver. Albumin is a large prote ...
Regional Plan for Regulatory System For Blood, Blood
... Regional Plan for Regulatory System For Blood, Blood Components and Blood Products Objective/Target: By 2012 all member states will have in place a functioning Regulatory system for Blood, Blood Components and Blood products as an integral section of the integrated Regulatory system that covers medi ...
... Regional Plan for Regulatory System For Blood, Blood Components and Blood Products Objective/Target: By 2012 all member states will have in place a functioning Regulatory system for Blood, Blood Components and Blood products as an integral section of the integrated Regulatory system that covers medi ...
Regional Plan for Regulatory System For Blood, Blood Components
... Regional Plan for Regulatory System For Blood, Blood Components and Blood Products Objective/Target: By 2012 all member states will have in place a functioning Regulatory system for Blood, Blood Components and Blood products as an integral section of the integrated Regulatory system that covers medi ...
... Regional Plan for Regulatory System For Blood, Blood Components and Blood Products Objective/Target: By 2012 all member states will have in place a functioning Regulatory system for Blood, Blood Components and Blood products as an integral section of the integrated Regulatory system that covers medi ...
Circulatory System and Blood
... to supply oxygen to the body tissues C. Reflects as red because of the iron atoms used in hemoglobin used to bond with the oxygen molecules D. Mixes with the other body fluids and bathes the cells directly ...
... to supply oxygen to the body tissues C. Reflects as red because of the iron atoms used in hemoglobin used to bond with the oxygen molecules D. Mixes with the other body fluids and bathes the cells directly ...
Circulation Diagram
... Name: _________________________________________ Date: ________________________ Sec: _______ Circulation Diagram Imagine that you are a red blood cell. What would be the path you might follow through Gary’s body as you traveled from his right thumb, through his heart, lungs, and back to his right thu ...
... Name: _________________________________________ Date: ________________________ Sec: _______ Circulation Diagram Imagine that you are a red blood cell. What would be the path you might follow through Gary’s body as you traveled from his right thumb, through his heart, lungs, and back to his right thu ...
Phlebotomy Definitions Teacher Guide
... the site prior to blood collection Disinfectants: chemicals regulated by the EPA that are used to kill or remove microorganisms on surfaces and laboratory instruments; not used on human skin! Tourniquet: elastic strap that fits around patient’s arm to stop the flow of blood for a small amount of tim ...
... the site prior to blood collection Disinfectants: chemicals regulated by the EPA that are used to kill or remove microorganisms on surfaces and laboratory instruments; not used on human skin! Tourniquet: elastic strap that fits around patient’s arm to stop the flow of blood for a small amount of tim ...
I. Blood Collection - Austin Community College
... high risk activities which may make the donor ineligible Donor must be informed and give consent that blood will be used for others unless they are in a special donor category First time donors must provide proof of identification such as SS#, DL#, DOB, address and any other unique information. Repe ...
... high risk activities which may make the donor ineligible Donor must be informed and give consent that blood will be used for others unless they are in a special donor category First time donors must provide proof of identification such as SS#, DL#, DOB, address and any other unique information. Repe ...
The Skeletal System
... the skeleton along. Your skeletal system is made up of cartilage and calcified bone that work together. They help the process of movement happen in a smoother manner. The calcified bones of your skeleton also work with the circulatory system. Marrow inside of your bones helps produce the cells insid ...
... the skeleton along. Your skeletal system is made up of cartilage and calcified bone that work together. They help the process of movement happen in a smoother manner. The calcified bones of your skeleton also work with the circulatory system. Marrow inside of your bones helps produce the cells insid ...
Blood Web Quest
... 22. What type of patients might use the plasma? ___________________________________________ Phase 5: The Transfusion 23. Which blood type can receive blood from all groups? ___________________________ 24. What are the two most common blood types in the U.S.? ____________________________ Test Your Bl ...
... 22. What type of patients might use the plasma? ___________________________________________ Phase 5: The Transfusion 23. Which blood type can receive blood from all groups? ___________________________ 24. What are the two most common blood types in the U.S.? ____________________________ Test Your Bl ...
Unit 1 Part 2 Blood Collection
... Transfusion Service Testing The only repeat testing required is: ABO on red cell products D typing (IS) on D negative red cell products Plasma products (FFP, CRYO, PLTS) do not require any testing. Donor samples must be stored at 1-6C for at least 7 days after ...
... Transfusion Service Testing The only repeat testing required is: ABO on red cell products D typing (IS) on D negative red cell products Plasma products (FFP, CRYO, PLTS) do not require any testing. Donor samples must be stored at 1-6C for at least 7 days after ...
blood type edit
... – Barry has Type AB Blood. Although he can receive blood from any other type, he can only donate to other people with Type AB. – John has Type O Blood. Although he can donate blood to any other type, he can only receive blood from other people with Type O. Otherwise, his anti-A and anti-B antibodi ...
... – Barry has Type AB Blood. Although he can receive blood from any other type, he can only donate to other people with Type AB. – John has Type O Blood. Although he can donate blood to any other type, he can only receive blood from other people with Type O. Otherwise, his anti-A and anti-B antibodi ...
Blood Typing Online Activity
... Read and answer the following questions. Then click on the link at the bottom of page to play the blood typing game. Blood Groups, Blood Typing and Transfusions Discovery of Blood groups 1. When were blood groups first discovered? 2. Who first described blood groups? 3. If you mix 2 bloods together ...
... Read and answer the following questions. Then click on the link at the bottom of page to play the blood typing game. Blood Groups, Blood Typing and Transfusions Discovery of Blood groups 1. When were blood groups first discovered? 2. Who first described blood groups? 3. If you mix 2 bloods together ...
Blood donation
A blood donation occurs when a person voluntarily has blood drawn and used for transfusions and/or made into biopharmaceutical medications by a process called fractionation (separation of whole-blood components). Donation may be of whole blood (WB), or of specific components directly (the latter called apheresis). Blood banks often participate in the collection process as well as the procedures that follow it.Today, in the developed world, most blood donors are unpaid volunteers who donate blood for a community supply. In poorer countries, established supplies are limited and donors usually give blood when family or friends need a transfusion (directed donation). Many donors donate as an act of charity, but in countries that allow paid donation some donors are paid, and in some cases there are incentives other than money such as paid time off from work. Donors can also have blood drawn for their own future use (autologous donation). Donating is relatively safe, but some donors have bruising where the needle is inserted or may feel faint.Potential donors are evaluated for anything that might make their blood unsafe to use. The screening includes testing for diseases that can be transmitted by a blood transfusion, including HIV and viral hepatitis. The donor must also answer questions about medical history and take a short physical examination to make sure the donation is not hazardous to his or her health. How often a donor can give varies from days to months based on what he or she donates and the laws of the country where the donation takes place. For example, in the United States, donors must wait eight weeks (56 days) between whole blood donations but only seven days between platelet pheresis donations.The amount of blood drawn and the methods vary. The collection can be done manually or with automated equipment that only takes specific portions of the blood. Most of the components of blood used for transfusions have a short shelf life, and maintaining a constant supply is a persistent problem. This has led to some increased interest in autotransfusion, whereby a patient's blood is salvaged during surgery for continuous reinfusion — or alternatively, is ""self-donated"" prior to when it will be needed. (Generally, the notion of ""donation"" does not refer to giving to one's self, though in this context it has become somewhat acceptably idiomatic.)