Blood groups
... -This is system of agglutinogens normally present in the red cells of Rhesus monkey (hence the name Rh) -There are 6 varieties known as(dominant C , D and E) (antigens and recessive c , d and e ) antigens. -These antigens were also found in the human red cells. -Antigen D has the strongest antigenic ...
... -This is system of agglutinogens normally present in the red cells of Rhesus monkey (hence the name Rh) -There are 6 varieties known as(dominant C , D and E) (antigens and recessive c , d and e ) antigens. -These antigens were also found in the human red cells. -Antigen D has the strongest antigenic ...
Health Watch
... • Arteries - Arteries have muscular walls that pump oxygen-filled blood away from your heart to the tissues and organs, like the brain, kidneys and liver. Arteries get smaller as they get further from your heart. At their smallest point, arteries become capillaries. • Capillaries - Capillaries are t ...
... • Arteries - Arteries have muscular walls that pump oxygen-filled blood away from your heart to the tissues and organs, like the brain, kidneys and liver. Arteries get smaller as they get further from your heart. At their smallest point, arteries become capillaries. • Capillaries - Capillaries are t ...
Blood Types - MrsSconyersAnatomy
... Blood Types • Blood plasma contains proteins called antibodies • Antibodies will react with antigens if mixed – Type A blood – A antigens, anti-B antibodies – Type B blood – B antigens, anti-A antibodies – Type AB blood – A and B antigens, no antibodies – Type O blood – no antigens, anti-A and anti ...
... Blood Types • Blood plasma contains proteins called antibodies • Antibodies will react with antigens if mixed – Type A blood – A antigens, anti-B antibodies – Type B blood – B antigens, anti-A antibodies – Type AB blood – A and B antigens, no antibodies – Type O blood – no antigens, anti-A and anti ...
Phagocytosis
... 4. Identify white cells which have engulfed bacteria. 5. State two reasons why bacteria may not be observed on the blood smear. Principle A drop of whole blood is mixed with a drop of a bacterial culture. The specimen is incubated at room temperature to demonstrate vacuolization of bacteria by leuko ...
... 4. Identify white cells which have engulfed bacteria. 5. State two reasons why bacteria may not be observed on the blood smear. Principle A drop of whole blood is mixed with a drop of a bacterial culture. The specimen is incubated at room temperature to demonstrate vacuolization of bacteria by leuko ...
ANIMAL BLOOD PRODUcTs
... and DS/EN ISO 13485:2012. Blood products which form part of culture media or analyses for human diagnostics are CE-marked. Blood from horses, cattle, and sheep is collected and treated aseptically. From all lots of donor blood, a sample is tested by cultivating it for 48 hours in a medium suitable f ...
... and DS/EN ISO 13485:2012. Blood products which form part of culture media or analyses for human diagnostics are CE-marked. Blood from horses, cattle, and sheep is collected and treated aseptically. From all lots of donor blood, a sample is tested by cultivating it for 48 hours in a medium suitable f ...
Blood - luckyscience
... immune system Platelets – involved in clotting. Plasma – 55% of blood. Is a water solution. Red Blood Cells Carry oxygen throughout body Determine blood type ...
... immune system Platelets – involved in clotting. Plasma – 55% of blood. Is a water solution. Red Blood Cells Carry oxygen throughout body Determine blood type ...
Bloodborn Pathogens - Manteno School District
... Blood borne Pathogens Training - New Employee Purpose of Policy - To eliminate or minimize exposure to potentially infectious materials in the workplace. Blood borne Pathogens – microorganisms carried by blood and other body fluids that are infectious. Most common – HBV (Hepatitis B) and HIV *Your r ...
... Blood borne Pathogens Training - New Employee Purpose of Policy - To eliminate or minimize exposure to potentially infectious materials in the workplace. Blood borne Pathogens – microorganisms carried by blood and other body fluids that are infectious. Most common – HBV (Hepatitis B) and HIV *Your r ...
1) - mrnicholsscience
... 3. How do the subclavian artery and the common carotid artery differ on the left and right? What is so special about the left brachiocephalic artery? ...
... 3. How do the subclavian artery and the common carotid artery differ on the left and right? What is so special about the left brachiocephalic artery? ...
RhoGAM® Updates and Clarifications
... For I.M. use only Observe patient for 20 minutes after injection Allergic responses may occur (extremely rare) Inform patient to report early signs of hypersensitivity, hives, generalized urticaria, tightness of the chest, wheezing, hypotension and anaphylaxis Treatment depends on severity of reacti ...
... For I.M. use only Observe patient for 20 minutes after injection Allergic responses may occur (extremely rare) Inform patient to report early signs of hypersensitivity, hives, generalized urticaria, tightness of the chest, wheezing, hypotension and anaphylaxis Treatment depends on severity of reacti ...
Types of Dominance and Blood Types
... • The status is usually indicated by Rh positive (Rh+ does have the D antigen) or Rh negative (Rh− does not have the D antigen) suffix to the ABO blood type. • Rhesus Disease occurs when there is incompatibility between blood types of mother and fetus. • Untreated, the result can cause death of the ...
... • The status is usually indicated by Rh positive (Rh+ does have the D antigen) or Rh negative (Rh− does not have the D antigen) suffix to the ABO blood type. • Rhesus Disease occurs when there is incompatibility between blood types of mother and fetus. • Untreated, the result can cause death of the ...
Dihybrid Crosses
... type AB must have both the A and B alleles. The genotype must be AB. Someone with blood type O has neither the A nor the B allele. The genotype must be OO. ...
... type AB must have both the A and B alleles. The genotype must be AB. Someone with blood type O has neither the A nor the B allele. The genotype must be OO. ...
Therapeutic Apheresis Informed Consent
... All apheresis procedures have basic principles in common: Blood is withdrawn through a needle or catheter and mixed with an anticoagulant as it is drawn. The blood is pumped through the cell-separator and the desired components are collected in a sterile plastic container. Most of the blood in the c ...
... All apheresis procedures have basic principles in common: Blood is withdrawn through a needle or catheter and mixed with an anticoagulant as it is drawn. The blood is pumped through the cell-separator and the desired components are collected in a sterile plastic container. Most of the blood in the c ...
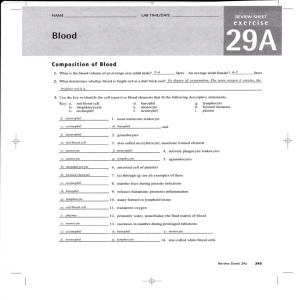
Composition of Blood
... Assuming the RBCs lnve a normal hemoglobin content, tlte higher the RBC volume, the higher the hemoglobin dctermination. ...
... Assuming the RBCs lnve a normal hemoglobin content, tlte higher the RBC volume, the higher the hemoglobin dctermination. ...
blood typing - mrsbrindley
... An B allele tells the red blood cell to put different “B” antigens on its surface ...
... An B allele tells the red blood cell to put different “B” antigens on its surface ...
Circulatory System
... -As your heart contracts to push blood into arteries 2. Diastolic Pressure - When BP is at its LOWEST point ...
... -As your heart contracts to push blood into arteries 2. Diastolic Pressure - When BP is at its LOWEST point ...
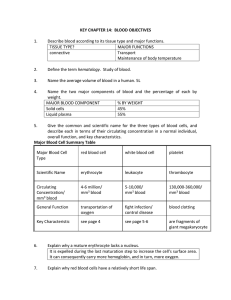
CHAPTER 16: LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY OBJECTIVES
... Discuss what is meant by Rh incompatibility and its consequences. Rh negative mother is pregnant with first Rh positive fetus. Mother makes anti-Rh antibodies which do not cross placenta, but she is now sensitized to the Rh factor. Second pregnancy allows for IgG; Rh antibodies to cross the placenta ...
... Discuss what is meant by Rh incompatibility and its consequences. Rh negative mother is pregnant with first Rh positive fetus. Mother makes anti-Rh antibodies which do not cross placenta, but she is now sensitized to the Rh factor. Second pregnancy allows for IgG; Rh antibodies to cross the placenta ...
The Genetics of Codominance
... Background: In humans the ABO blood types are inherited in a codominant fashion. There are four phenotypes: Type A, Type B, Type AB, and Type O. There are controlled by three alleles: the codominant alleles A and B and the recessive allele O. Blood types can be determined with a simple test that use ...
... Background: In humans the ABO blood types are inherited in a codominant fashion. There are four phenotypes: Type A, Type B, Type AB, and Type O. There are controlled by three alleles: the codominant alleles A and B and the recessive allele O. Blood types can be determined with a simple test that use ...
FO R IMMEDIAT E RELEASE Harness The Power in
... A small amount of blood will be obtained from your arm using a small needle and syringe. The blood will be put through a “soft” centrifugation spinning process that will separate and concentrate the platelets and other beneficial components including growth factors. The platelets and growth factors ...
... A small amount of blood will be obtained from your arm using a small needle and syringe. The blood will be put through a “soft” centrifugation spinning process that will separate and concentrate the platelets and other beneficial components including growth factors. The platelets and growth factors ...
CLS 2215 Principles of Immunohematology
... • Untested autologous units must be labeled “Donor Untested” • If the blood tested negative within the last 30 days it must be labeled “Donor Tested Within the last 30 Days”. ...
... • Untested autologous units must be labeled “Donor Untested” • If the blood tested negative within the last 30 days it must be labeled “Donor Tested Within the last 30 Days”. ...
Blood is a complex, living tissue that contains many cell types and
... Distinct molecules called agglutinogens (a type of antigen) are attached to the surface of red blood cells. There are two different types of agglutinogens, type “A” and type “B”. Each type has different properties. The ABO blood type classification system uses the presence or absence of these molecu ...
... Distinct molecules called agglutinogens (a type of antigen) are attached to the surface of red blood cells. There are two different types of agglutinogens, type “A” and type “B”. Each type has different properties. The ABO blood type classification system uses the presence or absence of these molecu ...
blood types
... • Blood type A has the A antigen • Blood type B has the B antigen • Blood type AB has both A and B antigens • Blood type O doesn’t have either antigen ...
... • Blood type A has the A antigen • Blood type B has the B antigen • Blood type AB has both A and B antigens • Blood type O doesn’t have either antigen ...
Introduction to Blood Typing
... the presence of specific antigens found on the surface of red blood cells. 1940: Landsteiner and Weiner reported the discovery of Rh factor by studying the blood of the Rhesus monkey. ...
... the presence of specific antigens found on the surface of red blood cells. 1940: Landsteiner and Weiner reported the discovery of Rh factor by studying the blood of the Rhesus monkey. ...
File
... 11. Which blood type is the universal donor? 12. If an injured area becomes red, swollen, warm to the touch and blood work indicates increased white blood cells, what process is probably occurring? 13. AB+ blood types can donate blood to which blood type? 14. What happens to veins when they are not ...
... 11. Which blood type is the universal donor? 12. If an injured area becomes red, swollen, warm to the touch and blood work indicates increased white blood cells, what process is probably occurring? 13. AB+ blood types can donate blood to which blood type? 14. What happens to veins when they are not ...
DriveLine Summer 2012_ PSBC_newlogo.pub
... policies frequently change? Here are some common misconceptions: Iron Deficiency: Hemoglobin is an iron-rich protein inside red blood cells. Donors can be deferred because they have a low hemoglobin count. This does not necessarily mean the donor is anemic - hemoglobin levels can fluctuate over time ...
... policies frequently change? Here are some common misconceptions: Iron Deficiency: Hemoglobin is an iron-rich protein inside red blood cells. Donors can be deferred because they have a low hemoglobin count. This does not necessarily mean the donor is anemic - hemoglobin levels can fluctuate over time ...
Slide 1
... Thrombocytopenia = not enough platelets to clot. Liver can’t produce clotting factors due to lack of ...
... Thrombocytopenia = not enough platelets to clot. Liver can’t produce clotting factors due to lack of ...
Blood donation
A blood donation occurs when a person voluntarily has blood drawn and used for transfusions and/or made into biopharmaceutical medications by a process called fractionation (separation of whole-blood components). Donation may be of whole blood (WB), or of specific components directly (the latter called apheresis). Blood banks often participate in the collection process as well as the procedures that follow it.Today, in the developed world, most blood donors are unpaid volunteers who donate blood for a community supply. In poorer countries, established supplies are limited and donors usually give blood when family or friends need a transfusion (directed donation). Many donors donate as an act of charity, but in countries that allow paid donation some donors are paid, and in some cases there are incentives other than money such as paid time off from work. Donors can also have blood drawn for their own future use (autologous donation). Donating is relatively safe, but some donors have bruising where the needle is inserted or may feel faint.Potential donors are evaluated for anything that might make their blood unsafe to use. The screening includes testing for diseases that can be transmitted by a blood transfusion, including HIV and viral hepatitis. The donor must also answer questions about medical history and take a short physical examination to make sure the donation is not hazardous to his or her health. How often a donor can give varies from days to months based on what he or she donates and the laws of the country where the donation takes place. For example, in the United States, donors must wait eight weeks (56 days) between whole blood donations but only seven days between platelet pheresis donations.The amount of blood drawn and the methods vary. The collection can be done manually or with automated equipment that only takes specific portions of the blood. Most of the components of blood used for transfusions have a short shelf life, and maintaining a constant supply is a persistent problem. This has led to some increased interest in autotransfusion, whereby a patient's blood is salvaged during surgery for continuous reinfusion — or alternatively, is ""self-donated"" prior to when it will be needed. (Generally, the notion of ""donation"" does not refer to giving to one's self, though in this context it has become somewhat acceptably idiomatic.)