Thin Lenses
... Focal length for a lens in air is related to the curvature of its front and back surfaces (R1 and R2) and to the index of refraction, n, of the lens material. Sign convention of lens radii R1 and R2 The signs of the lens radii indicate whether the corresponding surfaces are convex (R > 0, bulging ou ...
... Focal length for a lens in air is related to the curvature of its front and back surfaces (R1 and R2) and to the index of refraction, n, of the lens material. Sign convention of lens radii R1 and R2 The signs of the lens radii indicate whether the corresponding surfaces are convex (R > 0, bulging ou ...
Physics 425L Optics Laboratory Chromatic Aberration
... + = the image distance will also be a function of wavelength, resulting in a so si f ...
... + = the image distance will also be a function of wavelength, resulting in a so si f ...
Problem Sheet
... it at a depth of 40 cm. At what depth will the fish appear to be? 5. *A thin symmetric biconvex lens with surfaces of radius of curvature R1 and R2 is made of glass with refractive index n2 and is used in a medium of refractive index n1 < n2 . Show that an object at a distance u from the lens will pr ...
... it at a depth of 40 cm. At what depth will the fish appear to be? 5. *A thin symmetric biconvex lens with surfaces of radius of curvature R1 and R2 is made of glass with refractive index n2 and is used in a medium of refractive index n1 < n2 . Show that an object at a distance u from the lens will pr ...
Aspheric Lenses
... elements to truly push the optical envelope." The truth is long lenses may use ULD and Fluorite glass, but wide angles and lenses of shorter than 200mm do not. Wide angles may use aspheric lens elements but not LD glass types. Long lenses do not use aspheric lenses. ...
... elements to truly push the optical envelope." The truth is long lenses may use ULD and Fluorite glass, but wide angles and lenses of shorter than 200mm do not. Wide angles may use aspheric lens elements but not LD glass types. Long lenses do not use aspheric lenses. ...
Ray Tracing
... Ray tracing is the graphical solution to problems with thin lenses aka geometric optics. Given a single, double, or any number of thin lenses, one can follow this simple procedure to achieve a satisfactory solution. Basically all of these problems are about locating the final image given an object a ...
... Ray tracing is the graphical solution to problems with thin lenses aka geometric optics. Given a single, double, or any number of thin lenses, one can follow this simple procedure to achieve a satisfactory solution. Basically all of these problems are about locating the final image given an object a ...
Problem Sheet
... it at a depth of 40 cm. At what depth will the fish appear to be? 5. *A thin symmetric biconvex lens with surfaces of radius of curvature R1 and R2 is made of glass with refractive index n2 and is used in a medium of refractive index n1 < n2 . Show that an object at a distance u from the lens will p ...
... it at a depth of 40 cm. At what depth will the fish appear to be? 5. *A thin symmetric biconvex lens with surfaces of radius of curvature R1 and R2 is made of glass with refractive index n2 and is used in a medium of refractive index n1 < n2 . Show that an object at a distance u from the lens will p ...
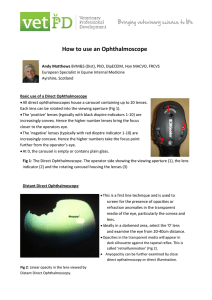
How to use an Ophthalmoscope
... viewing aperture bringing the focus closer to the operators’s eye. This is usually combined with slight alterations in the focal distance (the horse or operator moving their head back and forward, often inadvertently) until the anatomic feature is in focus. For me, with near normal refraction, the ...
... viewing aperture bringing the focus closer to the operators’s eye. This is usually combined with slight alterations in the focal distance (the horse or operator moving their head back and forward, often inadvertently) until the anatomic feature is in focus. For me, with near normal refraction, the ...
9-26 Geometrical Optics
... boundary that images light from one side of the boundary to another. This shape is a cartesian oval and is used for aspheric lenses Spherical lenses can well approximate the ideal shape of an aspherical lens for paraxial beams and are usually much cheaper to produce and are therefore more common tha ...
... boundary that images light from one side of the boundary to another. This shape is a cartesian oval and is used for aspheric lenses Spherical lenses can well approximate the ideal shape of an aspherical lens for paraxial beams and are usually much cheaper to produce and are therefore more common tha ...
Optics Review
... be 3 cm tall? How tall is the object? (tough question!) 14. A 19-cm tall object is placed 21 cm from a converging lens that has a focal length of 14 cm. How far from the lens will the image be formed? How tall is the image? Describe the characteristics of the image. (tough question!) 15. Determine t ...
... be 3 cm tall? How tall is the object? (tough question!) 14. A 19-cm tall object is placed 21 cm from a converging lens that has a focal length of 14 cm. How far from the lens will the image be formed? How tall is the image? Describe the characteristics of the image. (tough question!) 15. Determine t ...
13.1_Lens_Forming_Images_-_PPT[1]
... once from air to glass, and once from glass to air. • Ray diagrams are simplified by drawing a line through the center of the lens and showing refraction occurring at this line. ...
... once from air to glass, and once from glass to air. • Ray diagrams are simplified by drawing a line through the center of the lens and showing refraction occurring at this line. ...
Physics 212 HW17 - University of St. Thomas
... L03. The (“normal”) adult human eye uses a converging lens to focus images onto the retina which is typically 2.45 cm behind the lens. The eye’s lens is special in that it can change its focal length in order to focus images from very far and very close onto the retina, which stays 2.45 cm away. Th ...
... L03. The (“normal”) adult human eye uses a converging lens to focus images onto the retina which is typically 2.45 cm behind the lens. The eye’s lens is special in that it can change its focal length in order to focus images from very far and very close onto the retina, which stays 2.45 cm away. Th ...
diffraction and interference
... Maximum angular magnification f = 2.5 cm Mmax = 1+N/f Mrelax = N/f ...
... Maximum angular magnification f = 2.5 cm Mmax = 1+N/f Mrelax = N/f ...
Physics 161 Lecture 26 Mirrors and Lenses December 6, 2016
... You will be able to explain images formed by atmospheric refraction, such as mirages. You will be able to apply the lens-maker’s equation to thin lenses. You will be able to master the sign conventions for: concave and convex mirrors; refracting surfaces; and thin lenses. Sep. 1, 20152 ...
... You will be able to explain images formed by atmospheric refraction, such as mirages. You will be able to apply the lens-maker’s equation to thin lenses. You will be able to master the sign conventions for: concave and convex mirrors; refracting surfaces; and thin lenses. Sep. 1, 20152 ...
Focal Point and Focal Length Ray Diagram for lenses
... Object (O) is in front of F1 : real, inverted, enlarged or reduced ...
... Object (O) is in front of F1 : real, inverted, enlarged or reduced ...
Parts of the Microscope and Their Function
... Complete the chart below with the proper name of the microscope part: Name of part: ...
... Complete the chart below with the proper name of the microscope part: Name of part: ...
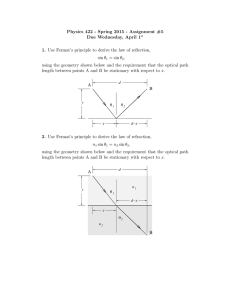
Physics 422 - Spring 2015 - Assignment #5
... 3. (a) Calculate the distance to the object focal point, fo , and the image focal point fi for a single spherical concave refracting surface with radius of curvature R = −10 cm, made of a material with index of refraction n2 = 1.5, and with air (n1 = 1) on the object side. (b) Calculate fo and fi f ...
... 3. (a) Calculate the distance to the object focal point, fo , and the image focal point fi for a single spherical concave refracting surface with radius of curvature R = −10 cm, made of a material with index of refraction n2 = 1.5, and with air (n1 = 1) on the object side. (b) Calculate fo and fi f ...
slides - Smith Lab
... light behind the lens; whereas, a concave lens, also known as a minus power lens, focuses light in front of the lens. The power of a lens is measured in Diopters (D) and reflects the focusing distance in meters of the lens- a + 10 D lens focuses an image at 10 cm= 1m/10D ...
... light behind the lens; whereas, a concave lens, also known as a minus power lens, focuses light in front of the lens. The power of a lens is measured in Diopters (D) and reflects the focusing distance in meters of the lens- a + 10 D lens focuses an image at 10 cm= 1m/10D ...
Lecture 37: MON 20 APR
... point and the mirror. It will produce a virtual image behind the mirror. When the object is at the focal point the image is produced at infinity. If the object is beyond the focal point, a real image forms at a distance i from the mirror. ...
... point and the mirror. It will produce a virtual image behind the mirror. When the object is at the focal point the image is produced at infinity. If the object is beyond the focal point, a real image forms at a distance i from the mirror. ...
Refraction of Light
... light behind the lens; whereas, a concave lens, also known as a minus power lens, focuses light in front of the lens. The power of a lens is measured in Diopters (D) and reflects the focusing distance in meters of the lens- a + 10 D lens focuses an image at 10 cm= 1m/10D ...
... light behind the lens; whereas, a concave lens, also known as a minus power lens, focuses light in front of the lens. The power of a lens is measured in Diopters (D) and reflects the focusing distance in meters of the lens- a + 10 D lens focuses an image at 10 cm= 1m/10D ...
Section 1 Supplement
... An object is anything that is being viewed, e.g., when one looks at a tree through a lens, with a mirror or any other optical device the tree is referred to an optical object. Object Distance, s, is the distance from an object to an optical element. An image is the likeness of an object produced at ...
... An object is anything that is being viewed, e.g., when one looks at a tree through a lens, with a mirror or any other optical device the tree is referred to an optical object. Object Distance, s, is the distance from an object to an optical element. An image is the likeness of an object produced at ...
PHYSICS 504 OPTICS REVIEW: Important things to remember: 1
... diameter pipeline that lies between them. By means of a fully labelled ray diagram and appropriate calculations, explain how it is possible for Marlin and Nemo to see each other from their present positions. Justify your answer. Air ...
... diameter pipeline that lies between them. By means of a fully labelled ray diagram and appropriate calculations, explain how it is possible for Marlin and Nemo to see each other from their present positions. Justify your answer. Air ...
PHYSICS 504 OPTICS REVIEW: Important things to remember
... diameter pipeline that lies between them. By means of a fully labelled ray diagram and appropriate calculations, explain how it is possible for Marlin and Nemo to see each other from their present positions. Justify your answer. Air ...
... diameter pipeline that lies between them. By means of a fully labelled ray diagram and appropriate calculations, explain how it is possible for Marlin and Nemo to see each other from their present positions. Justify your answer. Air ...
Mirrors and Images
... 1. A light ray passing through the center of the lens is not deflected at all (A). 2. A light ray parallel to the axis passes through the far focal point (B). 3. A light ray passing through the near focal point emerges parallel to the axis (C). ...
... 1. A light ray passing through the center of the lens is not deflected at all (A). 2. A light ray parallel to the axis passes through the far focal point (B). 3. A light ray passing through the near focal point emerges parallel to the axis (C). ...
CP Physics - Ms. Lisa Cole-
... 2. The area of the eye on which light is focused is called the ____________________ 3. As a ray of light passes from air into the lens, the speed of light ____________. 4. A diverging lens ____________________________ 5. A magnifying glass is usually a ____________________________. 6. If a person’s ...
... 2. The area of the eye on which light is focused is called the ____________________ 3. As a ray of light passes from air into the lens, the speed of light ____________. 4. A diverging lens ____________________________ 5. A magnifying glass is usually a ____________________________. 6. If a person’s ...
Aberration File
... The objective lens brings each image to a slightly different focus. The eyepiece lens has to be 1 focal length from the principal focus of the objective lens. Choosing this distance for green light leaves the blue and red out of focus. ...
... The objective lens brings each image to a slightly different focus. The eyepiece lens has to be 1 focal length from the principal focus of the objective lens. Choosing this distance for green light leaves the blue and red out of focus. ...
Lens (optics)
A lens is a transmissive optical device that affects the focus of a light beam through refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (elements), usually along a common axis. Lenses are made from transparent materials such as glass, ground and polished to a desired shape. A lens can focus light to form an image, unlike a prism, which refracts light without focusing. Devices that similarly refract radiation other than visible light are also called lenses, such as microwave lenses or acoustic lenses.







![13.1_Lens_Forming_Images_-_PPT[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008538239_1-d1798f6d27c8a2d8c0931d41a70fff89-300x300.png)