f = l - UCSD Department of Physics
... A healthy human eye can clearly see (focus) objects at distances from infinity to about 25 cm. How is that achieved? By changing the focal distance of the lens! We always have l’ 23 mm. ...
... A healthy human eye can clearly see (focus) objects at distances from infinity to about 25 cm. How is that achieved? By changing the focal distance of the lens! We always have l’ 23 mm. ...
reflection, refraction, lense and optical instruments
... Box with lenses (Use #3 and # 4 only – marked at bottom of shaft) Holders for lenses/screen ...
... Box with lenses (Use #3 and # 4 only – marked at bottom of shaft) Holders for lenses/screen ...
Converging Lens
... First, some definitions: a converging lens is defined as a lens with two convex surfaces. A diverging lens is a lens with two concave surfaces. An object is any article that is being viewed through an optical system; e.g., when one looks at a tree through a camera lens, telescope, or the naked eye ( ...
... First, some definitions: a converging lens is defined as a lens with two convex surfaces. A diverging lens is a lens with two concave surfaces. An object is any article that is being viewed through an optical system; e.g., when one looks at a tree through a camera lens, telescope, or the naked eye ( ...
PILE15_1.20040629140..
... What happens when parallel light rays pass through a concave lens? The rays diverge and appear to come from a single point. ...
... What happens when parallel light rays pass through a concave lens? The rays diverge and appear to come from a single point. ...
HP Unit 11-light & optics - student handout
... focal length is known as accommodation. • Your ciliary muscles flex and manipulate the curvature and shape of your lens which changes the focal length of the lens. ...
... focal length is known as accommodation. • Your ciliary muscles flex and manipulate the curvature and shape of your lens which changes the focal length of the lens. ...
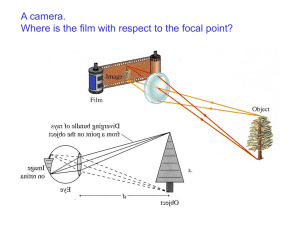
5.2 Optical Instruments Optical systems Camera Limitations of Lens
... The light is made to converge more by using a converging lens. ...
... The light is made to converge more by using a converging lens. ...
File
... In a compound microscope, a pair of convex lenses causes a small object to appear magnified when viewed through the eyepiece. The specimen is placed on a glass slide and then illuminated with a light source. Light travels through the objective lens, which is a convex lens at the bottom of the tube ...
... In a compound microscope, a pair of convex lenses causes a small object to appear magnified when viewed through the eyepiece. The specimen is placed on a glass slide and then illuminated with a light source. Light travels through the objective lens, which is a convex lens at the bottom of the tube ...
Chapter 25: Optical Instruments
... The simple refractor consists of a pair of lenses. The objective lens (closest to the object) has a large focal length fo while the eyepiece lens focal length fe is small. The objective produces a real, inverted, reduced image slightly less than one focal length fe from the eyepiece lens. The latter ...
... The simple refractor consists of a pair of lenses. The objective lens (closest to the object) has a large focal length fo while the eyepiece lens focal length fe is small. The objective produces a real, inverted, reduced image slightly less than one focal length fe from the eyepiece lens. The latter ...
Word
... The eye is a special _______ instrument. The front of the eye acts as a lens and bends light as it passes through it. This way an image of the object we are viewing is formed on the _______. Think about one letter of the print in front of you. Light enters your eye from each part of the letter. Your ...
... The eye is a special _______ instrument. The front of the eye acts as a lens and bends light as it passes through it. This way an image of the object we are viewing is formed on the _______. Think about one letter of the print in front of you. Light enters your eye from each part of the letter. Your ...
WI7: Lenses and Mirrors
... The eye is a special _______ instrument. The front of the eye acts as a lens and bends light as it passes through it. This way an image of the object we are viewing is formed on the _______. Think about one letter of the print in front of you. Light enters your eye from each part of the letter. Your ...
... The eye is a special _______ instrument. The front of the eye acts as a lens and bends light as it passes through it. This way an image of the object we are viewing is formed on the _______. Think about one letter of the print in front of you. Light enters your eye from each part of the letter. Your ...
Optical Lenses part 2
... F and F’: Both kinds of lenses have two principal focuses. The focal point where the light either comes to a focus or appears to diverge from a focus is given the symbol F, while that on the opposite side is represented by F’ Focal length (f): the distance from the axis of symmetry to the principal ...
... F and F’: Both kinds of lenses have two principal focuses. The focal point where the light either comes to a focus or appears to diverge from a focus is given the symbol F, while that on the opposite side is represented by F’ Focal length (f): the distance from the axis of symmetry to the principal ...
The Very Basics of Geometric Optics 5.1.2 Basic Geometric Optics
... measure of the size of the lens; see the picture below. Of course, lenses with small NA will not suffer much from spherical aberration but will also not transmit much light and thus produce "dark" pictures. The solution might be aspherical lenses but usually combinations of spherical lenses are used ...
... measure of the size of the lens; see the picture below. Of course, lenses with small NA will not suffer much from spherical aberration but will also not transmit much light and thus produce "dark" pictures. The solution might be aspherical lenses but usually combinations of spherical lenses are used ...
6.2 Refraction
... • the f-number of a lens is given by the focal length divided by the diameter, f/# = f/D • the f-number is used as a metric for the _____________ that can be gathered from a point source - the lower the value the higher the collection efficiency • referring to the figure it can be seen that the frac ...
... • the f-number of a lens is given by the focal length divided by the diameter, f/# = f/D • the f-number is used as a metric for the _____________ that can be gathered from a point source - the lower the value the higher the collection efficiency • referring to the figure it can be seen that the frac ...
Factors controlling heat exchange between the human body and its
... The pathway of important rays through diverging lens when object is located in front of the diverging lens A ray parallel to the optical axis will pass through the lens as if it came from the focal point on the incidence side A ray moving towards the focal point on the refraction side will run p ...
... The pathway of important rays through diverging lens when object is located in front of the diverging lens A ray parallel to the optical axis will pass through the lens as if it came from the focal point on the incidence side A ray moving towards the focal point on the refraction side will run p ...
Test Review 3
... For the converging lens data shown below, calculate the focal length. Be sure to include proper units. (Attach separate calculations, but show the answer here.) Include proper units for all numerical results! List results on the page below, but attach separate calculations. (Warning: Be careful of o ...
... For the converging lens data shown below, calculate the focal length. Be sure to include proper units. (Attach separate calculations, but show the answer here.) Include proper units for all numerical results! List results on the page below, but attach separate calculations. (Warning: Be careful of o ...
Emerging Trends in Contact Lens Technology Jason Jedlicka, OD
... Translating Bifocal designs Soft translating designs – are they possible? Designs currently being tested Other concepts Daily Multifocals Emerging Trends in GP Lens Technology Irregular Cornea Scleral lenses – will they last – will they displace corneal lenses eventually? Where is the trend in terms ...
... Translating Bifocal designs Soft translating designs – are they possible? Designs currently being tested Other concepts Daily Multifocals Emerging Trends in GP Lens Technology Irregular Cornea Scleral lenses – will they last – will they displace corneal lenses eventually? Where is the trend in terms ...
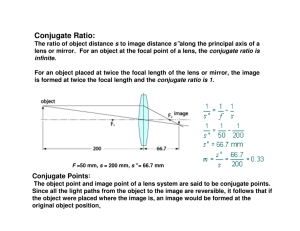
Conjugate Ratio:
... Design of any optical system starts with this approximation. The assumption that sin θ = θ is reasonably valid for θ close to zero (i.e., high f-number lenses). With more highly curved surfaces (and particularly marginal rays), paraxial theory yields increasingly large deviations from real performan ...
... Design of any optical system starts with this approximation. The assumption that sin θ = θ is reasonably valid for θ close to zero (i.e., high f-number lenses). With more highly curved surfaces (and particularly marginal rays), paraxial theory yields increasingly large deviations from real performan ...
Thin Lenses
... image of a given object when geometric characteristics of the optical device are known. ...
... image of a given object when geometric characteristics of the optical device are known. ...
Entry Task
... separate the wavelengths of sunlight to produce a spectrum. – Unlike a prism, only one color reaches your eye from each drop. • Red appears at the top of a rainbow because it is coming from higher drops • Violet comes from lower drops ...
... separate the wavelengths of sunlight to produce a spectrum. – Unlike a prism, only one color reaches your eye from each drop. • Red appears at the top of a rainbow because it is coming from higher drops • Violet comes from lower drops ...
Thin Lenses - Saddleback College
... 1. Construct four large (accurate, scaled down) ray diagrams for a CONVERGING LENS for p>2f, f
... 1. Construct four large (accurate, scaled down) ray diagrams for a CONVERGING LENS for p>2f, f
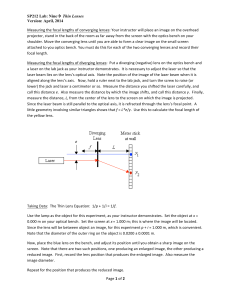
SP212 Lab: Nine→ Thin Lenses Version: April, 2014 Page 1 of 2
... a laser on the lab jack as your instructor demonstrates. It is necessary to adjust the laser so that the laser beam lies on the lens’s optical axis. Note the position of the image of the ...
... a laser on the lab jack as your instructor demonstrates. It is necessary to adjust the laser so that the laser beam lies on the lens’s optical axis. Note the position of the image of the ...
Lens (optics)
A lens is a transmissive optical device that affects the focus of a light beam through refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (elements), usually along a common axis. Lenses are made from transparent materials such as glass, ground and polished to a desired shape. A lens can focus light to form an image, unlike a prism, which refracts light without focusing. Devices that similarly refract radiation other than visible light are also called lenses, such as microwave lenses or acoustic lenses.