Lecture 5-Variation
... Mutant gene Xh When XHXH - Normal When XHXh carrier When XhXh or Xh (males) hemophiliac - die • Lethal, • Will not make a big impact in the process of evolution. ...
... Mutant gene Xh When XHXH - Normal When XHXh carrier When XhXh or Xh (males) hemophiliac - die • Lethal, • Will not make a big impact in the process of evolution. ...
Slide 1
... of DNA from a complex mixture of DNA molecules. Major disadvantage: it is time-consuming (several days to produce recombinants) and, in parts, difficult procedure. The next major technical breakthrough (1983) after gene cloning was PCR. It achieves the amplifying of a short fragment of a DNA molecul ...
... of DNA from a complex mixture of DNA molecules. Major disadvantage: it is time-consuming (several days to produce recombinants) and, in parts, difficult procedure. The next major technical breakthrough (1983) after gene cloning was PCR. It achieves the amplifying of a short fragment of a DNA molecul ...
Cells and Inheritance - Gaiser Middle School
... - The number of chromosomes are reduced to half to form sex cells – sperm and egg. Chromosome pairs separate and are distributed to 2 different cells. The new cells have half as many chromosomes as body cells. ...
... - The number of chromosomes are reduced to half to form sex cells – sperm and egg. Chromosome pairs separate and are distributed to 2 different cells. The new cells have half as many chromosomes as body cells. ...
with an intron
... Transcription involves an enzyme (RNA polymerase) making an RNA copy of part of one DNA strand. There are four main classes of RNA: i. Messenger RNAs (mRNA), which specify the amino acid sequence of a protein by using codons of the genetic code. ...
... Transcription involves an enzyme (RNA polymerase) making an RNA copy of part of one DNA strand. There are four main classes of RNA: i. Messenger RNAs (mRNA), which specify the amino acid sequence of a protein by using codons of the genetic code. ...
Sem2 Final Practice Test
... 6. To remove DNA from an organism’s genome, which process is used? a. Gene therapy b. Restriction digest c. Ligation d. DNA fingerprinting e. Transformation ...
... 6. To remove DNA from an organism’s genome, which process is used? a. Gene therapy b. Restriction digest c. Ligation d. DNA fingerprinting e. Transformation ...
Control of gene expression - Missouri State University
... • Eukaryotes don’t have operons • functionally related genes are not necessarily grouped spatially • coordinated expression is achieved by multiple similar control regions associated with functionally related genes ...
... • Eukaryotes don’t have operons • functionally related genes are not necessarily grouped spatially • coordinated expression is achieved by multiple similar control regions associated with functionally related genes ...
genetic engineering - St Vincent College
... been changed to make them more muscular, unexpectedly became very timid compared to other non-genetically engineered mice! However, some scientists think they will become more certain about how a gene will act if it is engineered into a person or an animal. Will future humans have animal genes added ...
... been changed to make them more muscular, unexpectedly became very timid compared to other non-genetically engineered mice! However, some scientists think they will become more certain about how a gene will act if it is engineered into a person or an animal. Will future humans have animal genes added ...
Nutrigenomics – taking Nutritional Medicine to the next
... Unravelling our DNA sequence One of this century’s most remarkable achievements must surely be the mapping of the entire human genome. The human genome is the term used to describe the long cabled strands of human DNA which are assembled into groups of genes and located on 23 pairs of chromosomes de ...
... Unravelling our DNA sequence One of this century’s most remarkable achievements must surely be the mapping of the entire human genome. The human genome is the term used to describe the long cabled strands of human DNA which are assembled into groups of genes and located on 23 pairs of chromosomes de ...
4.1 Intro to Bioengineering
... Many people believe that, in the future, we will be able to alter the genes in sperm and egg cells to create “designer babies” – parents will be able to pick and choose their children’s traits. What ...
... Many people believe that, in the future, we will be able to alter the genes in sperm and egg cells to create “designer babies” – parents will be able to pick and choose their children’s traits. What ...
Cell Evolution in Fast Motion - Max-Planck
... host cell and then mercilessly enslaved: it lost its independence, became the mitochondrion and served its host cell thereafter as a powerhouse for the generation of energy. This cell type with two genomes – in the nucleus and in the mitochondria – is still found in all animals and fungi today. ...
... host cell and then mercilessly enslaved: it lost its independence, became the mitochondrion and served its host cell thereafter as a powerhouse for the generation of energy. This cell type with two genomes – in the nucleus and in the mitochondria – is still found in all animals and fungi today. ...
Bacteria cells reproduce differently from other single celled
... phase of the Human Genome Project. What have they accomplished through this project? a. They used a single cell from one organism to create an identical organism. b. They created a single pedigree for every genetic disorder. c. They created DNA synthetically in a laboratory. d. They identified the s ...
... phase of the Human Genome Project. What have they accomplished through this project? a. They used a single cell from one organism to create an identical organism. b. They created a single pedigree for every genetic disorder. c. They created DNA synthetically in a laboratory. d. They identified the s ...
Förslag på process för tentamen
... B. Cut inside a DNA molecule C. Ligate DNA fragments D. Cut a DNA molecule at its ends E. None of above Question 5 What is a polylinker? (2p) A. A double stranded oligonucleotide which can make blunt ends into sticky ends B. A double stranded oligonucleotide which can make sticky ends into blunt C. ...
... B. Cut inside a DNA molecule C. Ligate DNA fragments D. Cut a DNA molecule at its ends E. None of above Question 5 What is a polylinker? (2p) A. A double stranded oligonucleotide which can make blunt ends into sticky ends B. A double stranded oligonucleotide which can make sticky ends into blunt C. ...
Handout- What are the different ways in which a genetic condition
... What are the different ways in which a genetic condition can be inherited? Some genetic conditions are caused by mutations in a single gene. These conditions are usually inherited in one of several patterns, depending on the gene involved: Patterns of inheritance Inheritance Description Examples pat ...
... What are the different ways in which a genetic condition can be inherited? Some genetic conditions are caused by mutations in a single gene. These conditions are usually inherited in one of several patterns, depending on the gene involved: Patterns of inheritance Inheritance Description Examples pat ...
sex
... TRANSLOCATION: breaks off a segment from one chromosome and attaches it to another gain-of-function mutation: increases the activity of the gene or makes it active in inappropriate circumstances; these mutations are usually dominant. dominant-negative mutation: dominant-acting mutation that blocks g ...
... TRANSLOCATION: breaks off a segment from one chromosome and attaches it to another gain-of-function mutation: increases the activity of the gene or makes it active in inappropriate circumstances; these mutations are usually dominant. dominant-negative mutation: dominant-acting mutation that blocks g ...
Guidelines and Assignments
... 1. (MT1) A. How is the 5-mC distributed within the human genome? B. Do all human genes have CpG island at their promoters? C. How bisulfite treatment may affect the CpG methylation status? D. What methods can be used to detect the methylation status of DNA? Please describe at least four different me ...
... 1. (MT1) A. How is the 5-mC distributed within the human genome? B. Do all human genes have CpG island at their promoters? C. How bisulfite treatment may affect the CpG methylation status? D. What methods can be used to detect the methylation status of DNA? Please describe at least four different me ...
Mechanisms of Evolution (on
... • Genetic drift refers to the change in a type of genes in a population due to a random occurrence. In other words, a random circumstance causes a certain genetic trait to become more common or rarer over time. Occurrences of Genetic Drift: • Genetic drift can be seen in these examples: • An explodi ...
... • Genetic drift refers to the change in a type of genes in a population due to a random occurrence. In other words, a random circumstance causes a certain genetic trait to become more common or rarer over time. Occurrences of Genetic Drift: • Genetic drift can be seen in these examples: • An explodi ...
RNA-Seq - iPlant Pods
... iPlant Collaborative DNA Learning Center, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory; Bio5 Institute, University of Arizona ...
... iPlant Collaborative DNA Learning Center, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory; Bio5 Institute, University of Arizona ...
11. Genetic engineering case study 1 - Human Insulin
... (c) It is useful for bacteria to take up plasmids because the plasmids may contain useful genes (1 mark) that increase their chance of survival (1 mark) ...
... (c) It is useful for bacteria to take up plasmids because the plasmids may contain useful genes (1 mark) that increase their chance of survival (1 mark) ...
Annelise Mah - New Genomics Technology: Copy Number Variation Analysis Methods
... are regions of the genome that are copied, deleted, or varied in number in some way. Normally these regions are defined as a kilobase (Kb, 10^3) to several megabases (Mb, 10^6) in size. These CNVRs make up around 12% of the human genome, cause disease, affect gene expression, and alter the organism’ ...
... are regions of the genome that are copied, deleted, or varied in number in some way. Normally these regions are defined as a kilobase (Kb, 10^3) to several megabases (Mb, 10^6) in size. These CNVRs make up around 12% of the human genome, cause disease, affect gene expression, and alter the organism’ ...
introduction modeling gene expression profiles kl
... components are utilized in the KL divergence approximation based on their mixture weights. ...
... components are utilized in the KL divergence approximation based on their mixture weights. ...
Study = Practice with your BRAIN!
... egg & sperm cells (sex cells) which are haploids. Since it makes haploid cells each new generation starts off with the same number of chromosomes as the parent. ...
... egg & sperm cells (sex cells) which are haploids. Since it makes haploid cells each new generation starts off with the same number of chromosomes as the parent. ...
Greatest Discoveries with Bill Nye: Genetics
... 12. What did Morgan and his students show that is important to modern genetics? Genes control Biochemical Events 13. What organism did Beadle and Tatum use for their experiments? 14. What did Beadle and Tatum do to this organisms to produce genetic changes? 15. What changes did this process cause to ...
... 12. What did Morgan and his students show that is important to modern genetics? Genes control Biochemical Events 13. What organism did Beadle and Tatum use for their experiments? 14. What did Beadle and Tatum do to this organisms to produce genetic changes? 15. What changes did this process cause to ...
The rhesus macaque is the third primate genome to be completed
... a list of diseases where the same genetic mutation that makes people ill seems normal for the macaques. "That is really quite a stunner," said Dr. Francis Collins, genetics chief at the National Institutes of Health, which funded the research. "It gives you a glimmer of how subtle changes in DNA cau ...
... a list of diseases where the same genetic mutation that makes people ill seems normal for the macaques. "That is really quite a stunner," said Dr. Francis Collins, genetics chief at the National Institutes of Health, which funded the research. "It gives you a glimmer of how subtle changes in DNA cau ...
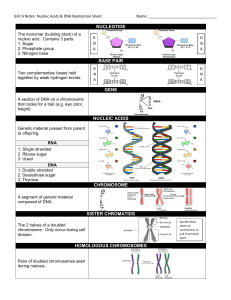
NUCLEOTIDE BASE PAIR GENE NUCLEIC ACIDS CHROMOSOME
... CHROMOSOME A segment of genetic material composed of DNA. ...
... CHROMOSOME A segment of genetic material composed of DNA. ...
Biology 303 EXAM II 3/14/00 NAME
... The fact that there is a problem maintaining the very ends of eukaryotic chromosomes during replication has to do with A. the fact that eukaryotic chromosomes are linear. B. the inability of DNA polymerases to initiate synthesis without a primer. C. the restriction that DNA synthesis must occur in a ...
... The fact that there is a problem maintaining the very ends of eukaryotic chromosomes during replication has to do with A. the fact that eukaryotic chromosomes are linear. B. the inability of DNA polymerases to initiate synthesis without a primer. C. the restriction that DNA synthesis must occur in a ...
Site-specific recombinase technology

Nearly every human gene has a counterpart in the mouse (regardless of the fact that a minor set of orthologues had to follow species specific selection routes). This made the mouse the major model for elucidating the ways in which our genetic material encodes information. In the late 1980s gene targeting in murine embryonic stem (ES-)cells enabled the transmission of mutations into the mouse germ line and emerged as a novel option to study the genetic basis of regulatory networks as they exist in the genome. Still, classical gene targeting proved to be limited in several ways as gene functions became irreversibly destroyed by the marker gene that had to be introduced for selecting recombinant ES cells. These early steps led to animals in which the mutation was present in all cells of the body from the beginning leading to complex phenotypes and/or early lethality. There was a clear need for methods to restrict these mutations to specific points in development and specific cell types. This dream became reality when groups in the USA were able to introduce bacteriophage and yeast-derived site-specific recombination (SSR-) systems into mammalian cells as well as into the mouse