INTEGRATION FROM PROTEINS TO ORGANS: THE PHYSIOME
... (MALDI) MALDI-MS - simple peptide mixtures whereas ESI-MS - for complex samples. ...
... (MALDI) MALDI-MS - simple peptide mixtures whereas ESI-MS - for complex samples. ...
CALL FOR PROPOSALS 2008
... axeny, specific information on genome size (bibliographic references or techniques for estimation of size), G+C content, information on ploidy, polymorphism level (details and methods of estimation), repeat structure with details about how these are known, etc. ...
... axeny, specific information on genome size (bibliographic references or techniques for estimation of size), G+C content, information on ploidy, polymorphism level (details and methods of estimation), repeat structure with details about how these are known, etc. ...
Albinism Advanced - xy-zoo
... which are yellow/red pigments, or eumelanins, which are brown/black pigments. In the eumelanin pathway, dopaquinone first is converted to a brown pigment. The enzyme TYRP-1 converts brown pigment into black, and will be designated as the “B” gene. Mice that don’t have a functional TYRP-1 gene will b ...
... which are yellow/red pigments, or eumelanins, which are brown/black pigments. In the eumelanin pathway, dopaquinone first is converted to a brown pigment. The enzyme TYRP-1 converts brown pigment into black, and will be designated as the “B” gene. Mice that don’t have a functional TYRP-1 gene will b ...
Brooker Chapter 9
... • Homologous Chromosomes: The pair of chromosomes in a diploid individual that have the same overall genetic content. – One member of each homologous pair of chromosomes is inherited from each parent. ...
... • Homologous Chromosomes: The pair of chromosomes in a diploid individual that have the same overall genetic content. – One member of each homologous pair of chromosomes is inherited from each parent. ...
X-linked Inheritance - Great Ormond Street Hospital
... of genes and have two copies of nearly every gene. Normally we inherit one copy from each parent and pass one copy onto each child. We all have several genes that have a misprint in them, but usually these are paired with a normal gene and so we are not aware of them. Sometimes these altered genes a ...
... of genes and have two copies of nearly every gene. Normally we inherit one copy from each parent and pass one copy onto each child. We all have several genes that have a misprint in them, but usually these are paired with a normal gene and so we are not aware of them. Sometimes these altered genes a ...
Study Questions for the Second Exam in Bio 0200
... (in other words, how does electron transport make ATP synthesis possible?) Explain the Pasteur effect (it's in your lab manual in the pathways game section) What is a photosystem? Where are photosystems located? What are photosystem I and II? How do their functions differ? In what ways is the Calvin ...
... (in other words, how does electron transport make ATP synthesis possible?) Explain the Pasteur effect (it's in your lab manual in the pathways game section) What is a photosystem? Where are photosystems located? What are photosystem I and II? How do their functions differ? In what ways is the Calvin ...
File - Alexis Kezirian
... site with a loxP site, upstream of the Lnp gene. The other transgenic line used the same (inverted) Hoxd9lacZ transgene, inserted into the rel5 site with a loxP site, downstream of the ltga6 ex1-24 gene. b) Figure C compares the expression of the LacZ gene product in maternallyand paternally-inherit ...
... site with a loxP site, upstream of the Lnp gene. The other transgenic line used the same (inverted) Hoxd9lacZ transgene, inserted into the rel5 site with a loxP site, downstream of the ltga6 ex1-24 gene. b) Figure C compares the expression of the LacZ gene product in maternallyand paternally-inherit ...
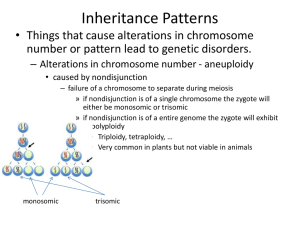
Inheritance Patterns - Santa Susana High School
... • Genomic imprinting – effect of the depends on the sex of the person inherited from – occurs during the formation of gametes – certain genes are turned off in the sperm & the ova • insulin-like growth factor (used in prenatal growth) – only the paternal version is expressed ...
... • Genomic imprinting – effect of the depends on the sex of the person inherited from – occurs during the formation of gametes – certain genes are turned off in the sperm & the ova • insulin-like growth factor (used in prenatal growth) – only the paternal version is expressed ...
Science 9 - Biological Diversity and Chemistry Review
... b) a section of DNA c) flowering plants d) splitting of a single cell into 2 new organisms e) a multi-celled organism during early development f) a reproductive cell containing half the number of chromosomes g) characteristics that can be passed on from parent to offspring h) an area of cell divisio ...
... b) a section of DNA c) flowering plants d) splitting of a single cell into 2 new organisms e) a multi-celled organism during early development f) a reproductive cell containing half the number of chromosomes g) characteristics that can be passed on from parent to offspring h) an area of cell divisio ...
Mechanisms of Evolution
... representative sample of all genes present in original population – Environment is different • different selection pressures • Therefore, evolve in new direction ...
... representative sample of all genes present in original population – Environment is different • different selection pressures • Therefore, evolve in new direction ...
Joining the Dots: Network Analysis of Gene Perturbation Screens
... • What information do we get out of gene perturbations? – Phenotypes and their ‘richness’ • How do we use this information to infer the internal architecture of a cell? – Guilt-by-association – Nested Effects Models ...
... • What information do we get out of gene perturbations? – Phenotypes and their ‘richness’ • How do we use this information to infer the internal architecture of a cell? – Guilt-by-association – Nested Effects Models ...
Human Nature
... thesis • Grants a correspondence, isomorphism, in consequences of moral behavior. • Rejects thesis that the causes of human moral behavior are products of natural selection. ...
... thesis • Grants a correspondence, isomorphism, in consequences of moral behavior. • Rejects thesis that the causes of human moral behavior are products of natural selection. ...
Genetics - Wantagh School
... • Replication= the process in which DNA molecules form exact duplicates. The Steps of Replication: 1. The DNA ladder separates, along the bases 2. Free nitrogen bases that are floating in the cytoplasm begin to pair up with the bases on each half of the DNA. 3. Two new DNA molecules form ...
... • Replication= the process in which DNA molecules form exact duplicates. The Steps of Replication: 1. The DNA ladder separates, along the bases 2. Free nitrogen bases that are floating in the cytoplasm begin to pair up with the bases on each half of the DNA. 3. Two new DNA molecules form ...
Slide 1
... Alleles are genes at the same position (locus) on homologous chromosomes (i.e. chromosomes that carry the same genes and that pair up early in meiosis I). Homologous chromosomes in an individual may carry the same or different alleles at a given locus. A plant is homozygous for a given gene if it h ...
... Alleles are genes at the same position (locus) on homologous chromosomes (i.e. chromosomes that carry the same genes and that pair up early in meiosis I). Homologous chromosomes in an individual may carry the same or different alleles at a given locus. A plant is homozygous for a given gene if it h ...
Chapter 14 Transposons, Plasmids, and Bacteriophage
... occurs, in case after c+ gene has been transferred but before d gene has entered recipient cell. ...
... occurs, in case after c+ gene has been transferred but before d gene has entered recipient cell. ...
013368718X_CH04_047
... Define mutations and describe the different types of mutations. Describe the effects mutations can have on genes. ...
... Define mutations and describe the different types of mutations. Describe the effects mutations can have on genes. ...
Geneticsworksheet
... 13. What provides the “blueprint” for making a protein? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 14. Which organelle is responsible for actually making proteins? _____________________ ...
... 13. What provides the “blueprint” for making a protein? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 14. Which organelle is responsible for actually making proteins? _____________________ ...
Pharmacogenetics Glossary
... function by itself. It is made of a nucleus surrounded by cytoplasm, organelles (similar to organs in a body) and proteins. Each cell contains the entire genome. chromosome - a long coiled strand in the nucleus, made up of DNA and protein. There are 46 human chromosomes, each containing DNA for hund ...
... function by itself. It is made of a nucleus surrounded by cytoplasm, organelles (similar to organs in a body) and proteins. Each cell contains the entire genome. chromosome - a long coiled strand in the nucleus, made up of DNA and protein. There are 46 human chromosomes, each containing DNA for hund ...
Cystic Fibrosis - Bellarmine University
... (CFTR = CF Transmembrane Conductance Regulator) About 1000 known mutations, but 70% of the cases involve a ...
... (CFTR = CF Transmembrane Conductance Regulator) About 1000 known mutations, but 70% of the cases involve a ...
What is another name for a polypeptide?
... DNA polymerase makes a mistake, adding the wrong nucleotide during DNA replication. Other mutations are caused by mutagens (MYEW tuh junz), which are chemicals or radiation that can damage DNA. Chemical mutagens are being studied for possible use in treating HIV—the virus that ...
... DNA polymerase makes a mistake, adding the wrong nucleotide during DNA replication. Other mutations are caused by mutagens (MYEW tuh junz), which are chemicals or radiation that can damage DNA. Chemical mutagens are being studied for possible use in treating HIV—the virus that ...
DNA and proteins
... organism (about 25000 genes in the human genome). • Each gene occupies a specific locus (position) on a chromosome and each chromosome consists of one molecule of DNA. • The DNA is wrapped around basic histone proteins (Chromatin) • In between genes is non coding DNA ...
... organism (about 25000 genes in the human genome). • Each gene occupies a specific locus (position) on a chromosome and each chromosome consists of one molecule of DNA. • The DNA is wrapped around basic histone proteins (Chromatin) • In between genes is non coding DNA ...
Bacterial_Resistance
... CDC Case Study • Variant Salmonella Genomic Island 1 Antibiotic Resistance Gene Cluster in Salmonella enterica Serovar Albany – Benoît Doublet et.al. Emerg Infect Dis 2003 May Available from: URL: http://www.cdc.gov/ncidod/EID/vol9no5/02-0609.htm ...
... CDC Case Study • Variant Salmonella Genomic Island 1 Antibiotic Resistance Gene Cluster in Salmonella enterica Serovar Albany – Benoît Doublet et.al. Emerg Infect Dis 2003 May Available from: URL: http://www.cdc.gov/ncidod/EID/vol9no5/02-0609.htm ...
Timeline of Genetic Engineering
... Gene Therapy 1. Process of changing a gene to treat a medical disease or disorder. 2. Absent or faulty gene is replaced by a normal, working gene. 3. This process allows the body to make the protein or enzyme it needs, which eliminates the cause of the disorder. ...
... Gene Therapy 1. Process of changing a gene to treat a medical disease or disorder. 2. Absent or faulty gene is replaced by a normal, working gene. 3. This process allows the body to make the protein or enzyme it needs, which eliminates the cause of the disorder. ...
Site-specific recombinase technology

Nearly every human gene has a counterpart in the mouse (regardless of the fact that a minor set of orthologues had to follow species specific selection routes). This made the mouse the major model for elucidating the ways in which our genetic material encodes information. In the late 1980s gene targeting in murine embryonic stem (ES-)cells enabled the transmission of mutations into the mouse germ line and emerged as a novel option to study the genetic basis of regulatory networks as they exist in the genome. Still, classical gene targeting proved to be limited in several ways as gene functions became irreversibly destroyed by the marker gene that had to be introduced for selecting recombinant ES cells. These early steps led to animals in which the mutation was present in all cells of the body from the beginning leading to complex phenotypes and/or early lethality. There was a clear need for methods to restrict these mutations to specific points in development and specific cell types. This dream became reality when groups in the USA were able to introduce bacteriophage and yeast-derived site-specific recombination (SSR-) systems into mammalian cells as well as into the mouse