GMO and Biotechnology - Western Washington University
... 12. (16 pts) In bacterial matings , prophage can be transferred from Hfr to F-. The prophage is auto ma tic all y induced when it enters F- cell s when ther e is no ph age repressor, and the cell is then lysed . Seve ral new Hfr strains of E. coli were independ ently isolated. All were wild type , ...
... 12. (16 pts) In bacterial matings , prophage can be transferred from Hfr to F-. The prophage is auto ma tic all y induced when it enters F- cell s when ther e is no ph age repressor, and the cell is then lysed . Seve ral new Hfr strains of E. coli were independ ently isolated. All were wild type , ...
Conjugation
... The F- cell does not become F+ or Hfr because the F factor does not transfer The F factor can be inserted at different positions in different bacterial chromosomes, the genes move over in the same order but from different starting points in different strains. The F factor can be present in the rever ...
... The F- cell does not become F+ or Hfr because the F factor does not transfer The F factor can be inserted at different positions in different bacterial chromosomes, the genes move over in the same order but from different starting points in different strains. The F factor can be present in the rever ...
Topic 12 DNA Technology
... • Most genetic diseases do not have a cure, but gene therapy could provide new treatment options • Gene therapy corrects defective genes with genes from another human – Swaps for the bad copy, reverses mutation, or turns off the gene ...
... • Most genetic diseases do not have a cure, but gene therapy could provide new treatment options • Gene therapy corrects defective genes with genes from another human – Swaps for the bad copy, reverses mutation, or turns off the gene ...
Genetics - Doc Ireland
... • Selection – a procedure where strains with a selective advantage of interest are favored in the environment and therefore become more numerous (contrast natural and artificial selection). • Mutation – Changes are made to selected DNA (either directed or random) to change the properties of the sequ ...
... • Selection – a procedure where strains with a selective advantage of interest are favored in the environment and therefore become more numerous (contrast natural and artificial selection). • Mutation – Changes are made to selected DNA (either directed or random) to change the properties of the sequ ...
Human Mitochondrial DNA
... The process of transferring foreign DNA fragments into a recipient (host) cell for growth and replication Scientists begin this process by fusing two different sets of DNA together creating a molecule of recombinant DNA or rDNA. This particular molecule is the product of the gene of interest (the de ...
... The process of transferring foreign DNA fragments into a recipient (host) cell for growth and replication Scientists begin this process by fusing two different sets of DNA together creating a molecule of recombinant DNA or rDNA. This particular molecule is the product of the gene of interest (the de ...
Reciprocal Translocation
... In Robertsonian translocation, long arms of two acrocentric chromosomes are combined to form one large chromosome and one small chromosome. If the short metacentric chromosome does not contain essential genetic information, it could be lost without any consequence to viability. ...
... In Robertsonian translocation, long arms of two acrocentric chromosomes are combined to form one large chromosome and one small chromosome. If the short metacentric chromosome does not contain essential genetic information, it could be lost without any consequence to viability. ...
NMPDRposter - Edwards @ SDSU
... Clicking on the option Show Compare Regions provides a visual comparison of your gene (in red) with its five closest homologs. This tool may be reset to display a wider or narrower view of the region matched to more or fewer other genomes. Sets of homologous genes share the same label and color. Tab ...
... Clicking on the option Show Compare Regions provides a visual comparison of your gene (in red) with its five closest homologs. This tool may be reset to display a wider or narrower view of the region matched to more or fewer other genomes. Sets of homologous genes share the same label and color. Tab ...
Answers ch20
... Embryonic induction occurs when cell fate during development is regulated by interactions between cells or tissues. For example, if animal pole blastomeres and vegetal pole blastomeres are separated in an early blastula, the animal pole blastomeres develop features of ectoderm and vegetal pole blast ...
... Embryonic induction occurs when cell fate during development is regulated by interactions between cells or tissues. For example, if animal pole blastomeres and vegetal pole blastomeres are separated in an early blastula, the animal pole blastomeres develop features of ectoderm and vegetal pole blast ...
2368AOS1-genefunctiongenesinaction2
... The final phenotype is more complex than just the proteins produced by genes. At any given moment in any cell only a few of the many genes are ‘switched on’ A ‘switched on’ gene is one that is being transcribed into mRNA at the time. A ‘switched off’ gene is one that is not. Pattern of gen ...
... The final phenotype is more complex than just the proteins produced by genes. At any given moment in any cell only a few of the many genes are ‘switched on’ A ‘switched on’ gene is one that is being transcribed into mRNA at the time. A ‘switched off’ gene is one that is not. Pattern of gen ...
anth-260-midterm-review-sheet
... 2. External validity 3. Variables IV, DV, confoundsSample questions: • According to Boyd and Silk, stabilizing selection tends to prevent traits of organisms changing over time. a. True b. False ...
... 2. External validity 3. Variables IV, DV, confoundsSample questions: • According to Boyd and Silk, stabilizing selection tends to prevent traits of organisms changing over time. a. True b. False ...
3. Genetic Drift
... Some really important phenotypic changes, like DDT resistance in insects are sometimes caused by single mutations1. A single mutation can also have strong negative effects for the organism. Mutations that cause the death of an organism are called lethal — and it doesn't get more negative than that. ...
... Some really important phenotypic changes, like DDT resistance in insects are sometimes caused by single mutations1. A single mutation can also have strong negative effects for the organism. Mutations that cause the death of an organism are called lethal — and it doesn't get more negative than that. ...
Eukaryotic Gene Regulation
... b. Determination of a cell occurs due to molecular changes. Once a cell differentiates, it expresses genes based on what kind of cell it is/what kind of tissue it makes up. Thus, they only express genes for _____________________________. i. These proteins are found only in a specific cell type. ii. ...
... b. Determination of a cell occurs due to molecular changes. Once a cell differentiates, it expresses genes based on what kind of cell it is/what kind of tissue it makes up. Thus, they only express genes for _____________________________. i. These proteins are found only in a specific cell type. ii. ...
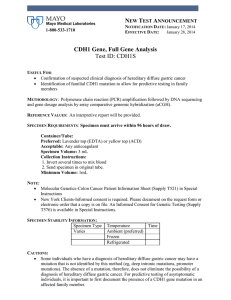
CDH1 Gene, Full Gene Analysis Test ID: CDH1S
... In some cases, DNA alterations of undetermined significance may be identified. We strongly recommend that asymptomatic patients undergoing predictive testing receive genetic counseling both prior to testing and after results are available. Predictive testing of an asymptomatic child is not recommend ...
... In some cases, DNA alterations of undetermined significance may be identified. We strongly recommend that asymptomatic patients undergoing predictive testing receive genetic counseling both prior to testing and after results are available. Predictive testing of an asymptomatic child is not recommend ...
Lecture ** - Telomeres
... a) Telomere structure: Repetitive DNA sequences at ends of chromosomes • telomeric heterochromatin (gene silencing assay) • human telomere repeat: GGGTTA (many copies: ~ 10,000 bp) • binding sites for telomere-specific proteins b) Telomerase replication mechanism (vertebrates, most other eukaryotic ...
... a) Telomere structure: Repetitive DNA sequences at ends of chromosomes • telomeric heterochromatin (gene silencing assay) • human telomere repeat: GGGTTA (many copies: ~ 10,000 bp) • binding sites for telomere-specific proteins b) Telomerase replication mechanism (vertebrates, most other eukaryotic ...
Anatomy and Physiology BIO 137
... Autosomal dominant means you only need to get the abnormal gene from one parent in order for you to inherit the disease. Autosomal recessive disorder means two copies of an abnormal gene must be present in order for the disease or trait to develop. ...
... Autosomal dominant means you only need to get the abnormal gene from one parent in order for you to inherit the disease. Autosomal recessive disorder means two copies of an abnormal gene must be present in order for the disease or trait to develop. ...
The process of meiosis - Deans Community High School
... Meiosis enables new combinations of existing alleles of genes to pass to the gamete as a result of crossing over at chiasmata resulting in new combinations of alleles for genes on the same chromosome. This can give 4 genetically different chromatids each of which ends up in a different gamete. Also, ...
... Meiosis enables new combinations of existing alleles of genes to pass to the gamete as a result of crossing over at chiasmata resulting in new combinations of alleles for genes on the same chromosome. This can give 4 genetically different chromatids each of which ends up in a different gamete. Also, ...
Human Biology Unit III: INHERITANCE AND HUMAN GENETIC
... Unit III: INHERITANCE AND HUMAN GENETIC VARIATION Mellon/MCHS ...
... Unit III: INHERITANCE AND HUMAN GENETIC VARIATION Mellon/MCHS ...
Issues and Ethics
... deals with the life sciences • Religion: a system of beliefs and practices that an individual chooses to follow ...
... deals with the life sciences • Religion: a system of beliefs and practices that an individual chooses to follow ...
Workshop IX Fungal Genomics Chair: Peter Philippsen 206
... the case the gene is smaller than 700 bp, we took the entire gene. Then, we included 150 bp of sequence downstream of the gene or as much as there is in the intergenic region when it is shorter than 150 bp. These comprise the target sequences which provide a minimum of 850 bp for each gene. We condu ...
... the case the gene is smaller than 700 bp, we took the entire gene. Then, we included 150 bp of sequence downstream of the gene or as much as there is in the intergenic region when it is shorter than 150 bp. These comprise the target sequences which provide a minimum of 850 bp for each gene. We condu ...
Document
... adenovirus can cause liver and lung damage. (The virus can trigger widespread bloodclotting and inflame surrounding tissue.) ...
... adenovirus can cause liver and lung damage. (The virus can trigger widespread bloodclotting and inflame surrounding tissue.) ...
Cancer Gene Detection
... The p53 tumor suppressor protein The p53 gene like the Rb gene, is a tumor suppressor gene, i.e., its activity stops the formation of tumors. If a person inherits only one functional copy of the p53 gene from their parents, they are predisposed to cancer and usually develop several independent tumor ...
... The p53 tumor suppressor protein The p53 gene like the Rb gene, is a tumor suppressor gene, i.e., its activity stops the formation of tumors. If a person inherits only one functional copy of the p53 gene from their parents, they are predisposed to cancer and usually develop several independent tumor ...
Site-specific recombinase technology

Nearly every human gene has a counterpart in the mouse (regardless of the fact that a minor set of orthologues had to follow species specific selection routes). This made the mouse the major model for elucidating the ways in which our genetic material encodes information. In the late 1980s gene targeting in murine embryonic stem (ES-)cells enabled the transmission of mutations into the mouse germ line and emerged as a novel option to study the genetic basis of regulatory networks as they exist in the genome. Still, classical gene targeting proved to be limited in several ways as gene functions became irreversibly destroyed by the marker gene that had to be introduced for selecting recombinant ES cells. These early steps led to animals in which the mutation was present in all cells of the body from the beginning leading to complex phenotypes and/or early lethality. There was a clear need for methods to restrict these mutations to specific points in development and specific cell types. This dream became reality when groups in the USA were able to introduce bacteriophage and yeast-derived site-specific recombination (SSR-) systems into mammalian cells as well as into the mouse