Isotope-Exchange Evidence that Glucose 6
... molecules, increases with the MgATP concentration but is independent of the glucose concentration. This behaviour requires that glucose must bind before MgATP when the reaction is proceeding in the normal physiological direction, i.e. phosphorylation of glucose. Although at low non-inhibitory glucos ...
... molecules, increases with the MgATP concentration but is independent of the glucose concentration. This behaviour requires that glucose must bind before MgATP when the reaction is proceeding in the normal physiological direction, i.e. phosphorylation of glucose. Although at low non-inhibitory glucos ...
Equilibrium Booklet - mrstorie
... d) increasing the volume of the container. e) adding a catalyst. 2. For the reaction: CH4(g) + H2O(g) + 49.3 kJ CO(g) + 3 H2(g) Predict the effect on the position of the equilibrium that results from a) increasing temperature. b) decreasing temperature. c) decreasing the pressure. d) decreasing t ...
... d) increasing the volume of the container. e) adding a catalyst. 2. For the reaction: CH4(g) + H2O(g) + 49.3 kJ CO(g) + 3 H2(g) Predict the effect on the position of the equilibrium that results from a) increasing temperature. b) decreasing temperature. c) decreasing the pressure. d) decreasing t ...
Mineralization of Drugs in Aqueous Medium by Advanced Oxidation
... Water is a limited resource that continuously recirculates through all the aquatic environments following a natural cycle. The increasing lack and contamination of this natural resource in many places of the world is alarming and demands urgent solutions. Recently, there is great interest in the env ...
... Water is a limited resource that continuously recirculates through all the aquatic environments following a natural cycle. The increasing lack and contamination of this natural resource in many places of the world is alarming and demands urgent solutions. Recently, there is great interest in the env ...
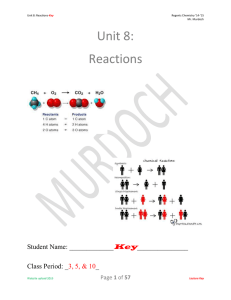
Unit 8: Reactions
... destroyed by physical or chemical change. This is the basis for writing chemical formulas and half-reactions, and for balancing redox reactions. 5. Law of Conservation of Energy: Energy may not be created or destroyed by physical or chemical change. This is the basis for calculating the heat of reac ...
... destroyed by physical or chemical change. This is the basis for writing chemical formulas and half-reactions, and for balancing redox reactions. 5. Law of Conservation of Energy: Energy may not be created or destroyed by physical or chemical change. This is the basis for calculating the heat of reac ...
21 More About Amines • Heterocyclic Compounds
... when we study how enzymes catalyze chemical reactriethylamine tions; in Chapter 25, when we investigate the ways in which coenzymes—compounds derived from vitamins—help enzymes catalyze chemical reactions; in Chapter 27, when we study nucleic acids (DNA and RNA); and in Chapter 30, when we take a lo ...
... when we study how enzymes catalyze chemical reactriethylamine tions; in Chapter 25, when we investigate the ways in which coenzymes—compounds derived from vitamins—help enzymes catalyze chemical reactions; in Chapter 27, when we study nucleic acids (DNA and RNA); and in Chapter 30, when we take a lo ...
Chapter 4 Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... Aqueous however, most notably in oxyanions. Reactions ...
... Aqueous however, most notably in oxyanions. Reactions ...
CHAPTER-7
... Explain common ion effect with an example. Ans. The suppression in degree of dissociation of a weak electrolyte by the addition of strong electrolyte having common ion is called common ion effect. Example: the ionization of acetic acid [weak electrolyte] is suppressed by addition of sodium acetate [ ...
... Explain common ion effect with an example. Ans. The suppression in degree of dissociation of a weak electrolyte by the addition of strong electrolyte having common ion is called common ion effect. Example: the ionization of acetic acid [weak electrolyte] is suppressed by addition of sodium acetate [ ...
CfE Higher Chemistry Unit 1: Chemical Changes and Structure
... Members of the SCHOLAR Forum may reproduce this publication in whole or in part for educational purposes within their establishment providing that no profit accrues at any stage, Any other use of the materials is governed by the general copyright statement that follows. All rights reserved. No part ...
... Members of the SCHOLAR Forum may reproduce this publication in whole or in part for educational purposes within their establishment providing that no profit accrues at any stage, Any other use of the materials is governed by the general copyright statement that follows. All rights reserved. No part ...
Question Bank - Edudel.nic.in
... Show that the relative lowering of vapour pressure of a solvent is a colligative property. Benzene and toluene form a nearly ideal solution. At a certain temperature, calculate the vapour pressure of solution containing equal moles of the two substances. [Given : P°Benzene = 150 mm of Hg, P°Toluene ...
... Show that the relative lowering of vapour pressure of a solvent is a colligative property. Benzene and toluene form a nearly ideal solution. At a certain temperature, calculate the vapour pressure of solution containing equal moles of the two substances. [Given : P°Benzene = 150 mm of Hg, P°Toluene ...
Chapter 1 – Reaction Kinetics Answer Key
... water will occur as water is formed in a reaction that occurs in aqueous solution. This is, of course, nonsense! As the entire reaction occurs in the solvent water, there will simply be a ...
... water will occur as water is formed in a reaction that occurs in aqueous solution. This is, of course, nonsense! As the entire reaction occurs in the solvent water, there will simply be a ...
Ch 10 - Enrico Fermi High School
... In an experiment involving the determination of the equilibrium constant for a reaction, 10.0 mL of 2.00 x 10-3 M Fe+3 (aq) was mixed with 20.0 mL of 4.00 x 10-3 M SCN-(aq). The number of moles of FeSCN2+(aq) that was formed after the reaction of Fe+3 (aq) and SCN-(aq) came to equilibrium was 3.50 x ...
... In an experiment involving the determination of the equilibrium constant for a reaction, 10.0 mL of 2.00 x 10-3 M Fe+3 (aq) was mixed with 20.0 mL of 4.00 x 10-3 M SCN-(aq). The number of moles of FeSCN2+(aq) that was formed after the reaction of Fe+3 (aq) and SCN-(aq) came to equilibrium was 3.50 x ...
Chapter 6 Chemical Reactions
... Molecules move faster at higher temperatures. (Their internal motions (vibrations and rotations) also gain more energy, so vibrations and rotations are more active.) Molecules have to come together to react, so they should come together faster if they are moving faster and reactions should speed up ...
... Molecules move faster at higher temperatures. (Their internal motions (vibrations and rotations) also gain more energy, so vibrations and rotations are more active.) Molecules have to come together to react, so they should come together faster if they are moving faster and reactions should speed up ...
Supramolecular catalysis

Supramolecular catalysis is not a well-defined field but it generally refers to an application of supramolecular chemistry, especially molecular recognition and guest binding, toward catalysis. This field was originally inspired by enzymatic system which, unlike classical organic chemistry reactions, utilizes non-covalent interactions such as hydrogen bonding, cation-pi interaction, and hydrophobic forces to dramatically accelerate rate of reaction and/or allow highly selective reactions to occur. Because enzymes are structurally complex and difficult to modify, supramolecular catalysts offer a simpler model for studying factors involved in catalytic efficiency of the enzyme. Another goal that motivates this field is the development of efficient and practical catalysts that may or may not have an enzyme equivalent in nature.A closely related field of study is asymmetric catalysis which requires molecular recognition to differentiate two chiral starting material or chiral transition states and thus it could be categorized as an area of supramolecular catalysis, but supramolecular catalysis however does not necessarily have to involve asymmetric reaction. As there is another Wikipedia article already written about small molecule asymmetric catalysts, this article focuses primarily on large catalytic host molecules. Non-discrete and structurally poorly defined system such as micelle and dendrimers are not included.