Weather Review Sheet High pressure (no clouds, good weather) vs
... ➢ Convection is the rising of warm air and sinking of more dense, cooler air (helps form clouds and storms from heating of the Earth's surface) ➢ Advection is the movement of air masses horizontally (north, south, east, west) ➢ Jet stream (fast stream of winds in the atmosphere) separates colder air ...
... ➢ Convection is the rising of warm air and sinking of more dense, cooler air (helps form clouds and storms from heating of the Earth's surface) ➢ Advection is the movement of air masses horizontally (north, south, east, west) ➢ Jet stream (fast stream of winds in the atmosphere) separates colder air ...
weathe~2 - Rosierulescience
... The properties of this are determined by the part of the Earth’s surface over which it forms ...
... The properties of this are determined by the part of the Earth’s surface over which it forms ...
pressure_and_wind_notes
... Convection in the atmosphere is a major cause of weather. Convection is the major mechanism of energy transfers in the oceans, atmosphere, and Earth’s interior. Extreme weather: o Rapidly falling air pressure indicates a storm is approaching. o Tornado – a narrow, violent funnel-shaped column of spi ...
... Convection in the atmosphere is a major cause of weather. Convection is the major mechanism of energy transfers in the oceans, atmosphere, and Earth’s interior. Extreme weather: o Rapidly falling air pressure indicates a storm is approaching. o Tornado – a narrow, violent funnel-shaped column of spi ...
WASL Review Homework #3
... Use complete sentences unless you use an approved outline form. b. Write, print, or type each question followed by the answer. c. Skip one line between a question and the answer and skip two lines between an answer and the next question. d. You may look at a variety of sources for answers but do not ...
... Use complete sentences unless you use an approved outline form. b. Write, print, or type each question followed by the answer. c. Skip one line between a question and the answer and skip two lines between an answer and the next question. d. You may look at a variety of sources for answers but do not ...
Atmosphere And Climate
... • Anabatic winds- a warm wind which blows up a steep slope or mountain side, driven by heating of the slope through insolation, • Katabatic winds- down-slope winds, frequently produced at night by the opposite effect, the air near to the ground losing heat to it faster than air at a similar altitude ...
... • Anabatic winds- a warm wind which blows up a steep slope or mountain side, driven by heating of the slope through insolation, • Katabatic winds- down-slope winds, frequently produced at night by the opposite effect, the air near to the ground losing heat to it faster than air at a similar altitude ...
1) What is the theory of plate tectonics? a. The lithosphere (top layer
... solidifies (the slower it cools, the larger the crystal is). c. Metamorphic Rock – formed under great heat and pressure which change the texture and composition of the rock. d. Earth’s rocks don’t sta ...
... solidifies (the slower it cools, the larger the crystal is). c. Metamorphic Rock – formed under great heat and pressure which change the texture and composition of the rock. d. Earth’s rocks don’t sta ...
Honors Earth Science EOC Exam Review
... 47. If Earth’s average temperature increases (global warming), what will be the impact on severe weather events such as hurricanes? Benchmark SC.912.E.7.7: Identify, analyze, and relate the internal (Earth system) and external (astronomical) conditions that contribute to global climate change. 48. W ...
... 47. If Earth’s average temperature increases (global warming), what will be the impact on severe weather events such as hurricanes? Benchmark SC.912.E.7.7: Identify, analyze, and relate the internal (Earth system) and external (astronomical) conditions that contribute to global climate change. 48. W ...
Earth Science - Canajoharie Central Schools
... of minerals, rocks, mountains, earthquakes, volcanoes, etc… and the role that Plate Tectonics plays in all of these processes. It is an objective of this course to provide students with a clear understanding of the dynamic nature of the Earth and its natural constructive and destructive processes so ...
... of minerals, rocks, mountains, earthquakes, volcanoes, etc… and the role that Plate Tectonics plays in all of these processes. It is an objective of this course to provide students with a clear understanding of the dynamic nature of the Earth and its natural constructive and destructive processes so ...
File
... A. On a sunny day, the air over a piece of land will be cooler than the air over a bordering lake. B. On a sunny day, the air over a lake will be cooler than the air over the bordering land. C. On a cloudy day, the air over a southern section of the ocean will be warmer than the air over a northern ...
... A. On a sunny day, the air over a piece of land will be cooler than the air over a bordering lake. B. On a sunny day, the air over a lake will be cooler than the air over the bordering land. C. On a cloudy day, the air over a southern section of the ocean will be warmer than the air over a northern ...
File
... Arrange the following in order from smallest to largest: Universe, solar system, Astronomical unit, Earth, Galaxy, Light year ...
... Arrange the following in order from smallest to largest: Universe, solar system, Astronomical unit, Earth, Galaxy, Light year ...
Scientist - Email lists service
... numerical weather predictions to its Member States. ECMWF carries out scientific and technical research directed to the improvement of its forecasts, collects and processes large amounts of observations, and manages a long-term archive of meteorological data. Satellite and in situ observations provi ...
... numerical weather predictions to its Member States. ECMWF carries out scientific and technical research directed to the improvement of its forecasts, collects and processes large amounts of observations, and manages a long-term archive of meteorological data. Satellite and in situ observations provi ...
Unit 3 Weather and climate_wiki
... just like aerostatic balloons). It is considered that the normal point of pressure is 1013 mbar. If a place has higher pressure there is an anticyclone, with cold air descending and stable weather. If the pressure is lower than 1013 mbar there is a cyclone, with hot air rising and unstable weather. ...
... just like aerostatic balloons). It is considered that the normal point of pressure is 1013 mbar. If a place has higher pressure there is an anticyclone, with cold air descending and stable weather. If the pressure is lower than 1013 mbar there is a cyclone, with hot air rising and unstable weather. ...
Clouds
... – Occurs in midlatitudes to poles – All three states of water present – Supercooled water crystallizes upon contact with freezing nuclei – Ice crystals form around freezing nuclei and grow through deposition at the expense of water droplets – Precipitation leaves cloud as ice crystal ...
... – Occurs in midlatitudes to poles – All three states of water present – Supercooled water crystallizes upon contact with freezing nuclei – Ice crystals form around freezing nuclei and grow through deposition at the expense of water droplets – Precipitation leaves cloud as ice crystal ...
Wind, Water, Weather and Seasons Test Review
... Please use your notes on “Reading a Weather Map” your “Weather Instruments” left page activity, or pages 470-‐479 in your Texas Fusion Science textbook to complete the ...
... Please use your notes on “Reading a Weather Map” your “Weather Instruments” left page activity, or pages 470-‐479 in your Texas Fusion Science textbook to complete the ...
STRUCTURE OF THE ATMOSPHERE
... • Some parts of the Earth receive more insolation than others and the Earth tries to move this heat around via winds and ocean currents. ...
... • Some parts of the Earth receive more insolation than others and the Earth tries to move this heat around via winds and ocean currents. ...
Ch 6 - EARTH NOTES
... a. 4 interconnected oceans (Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Arctic), Pacific is largest b. Patterns of Circulation in the Ocean i. __________________ = mass movements of surface ocean water 1. caused by ____________. ii. _____________ = circular currents 1. Earth rotates toward the __________, influencin ...
... a. 4 interconnected oceans (Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Arctic), Pacific is largest b. Patterns of Circulation in the Ocean i. __________________ = mass movements of surface ocean water 1. caused by ____________. ii. _____________ = circular currents 1. Earth rotates toward the __________, influencin ...
Canada`s Geography Quiz 1 Study Sheet Key Terms Region – an
... Region – an area of land that has unique features, such as climate, landforms, and natural resources Scale – a tool we use to compare the distance on a map to the actual distance on earth’s surface Physical features – include landforms, such as mountains, hills, and plains. It also includes bodies o ...
... Region – an area of land that has unique features, such as climate, landforms, and natural resources Scale – a tool we use to compare the distance on a map to the actual distance on earth’s surface Physical features – include landforms, such as mountains, hills, and plains. It also includes bodies o ...
JUNIOR CERTIFICATE GEOGRAPHY
... Weather Stations use many instruments to record the weather and then make forecasts based on their recordings Air Temperature is measured using a thermometer Sunshine is measured by using a Campbell-Stokes recorder Air Pressure is measured by a ...
... Weather Stations use many instruments to record the weather and then make forecasts based on their recordings Air Temperature is measured using a thermometer Sunshine is measured by using a Campbell-Stokes recorder Air Pressure is measured by a ...
4th Grade Weathering, Weather and Atmosphere Study Guide
... Wearing away of rock and soil by wind, water, waves and glaciers; slow change Tropical system of rain and winds which circles around a center of low pressure and has sustained winds of at least 74mph; quick change Front The boundary between two unlike air masses Cold front The leading edge of a cold ...
... Wearing away of rock and soil by wind, water, waves and glaciers; slow change Tropical system of rain and winds which circles around a center of low pressure and has sustained winds of at least 74mph; quick change Front The boundary between two unlike air masses Cold front The leading edge of a cold ...
1 Climate
... erupting volcano → gas combines with water vapor in stratosphere → a layer of haze forms that blocks the sunlight from reaching earth → temperature on earth decreases ...
... erupting volcano → gas combines with water vapor in stratosphere → a layer of haze forms that blocks the sunlight from reaching earth → temperature on earth decreases ...
Name: June Proficiency Exam Study Guide 7th Grade Science
... 16. What is a front? Boundary where two different air masses meet 17. The Coriolis Effect explains why winds curve to the right in the Northern Hemisphere, and to the left in the Southern Hemisphere. 18. Global winds are caused by Unequal heating of Earth’s atmosphere 19. What are the Doldrums? Calm ...
... 16. What is a front? Boundary where two different air masses meet 17. The Coriolis Effect explains why winds curve to the right in the Northern Hemisphere, and to the left in the Southern Hemisphere. 18. Global winds are caused by Unequal heating of Earth’s atmosphere 19. What are the Doldrums? Calm ...
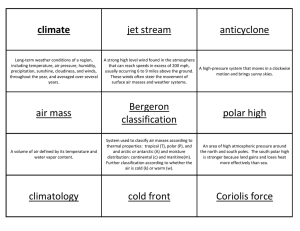
Climate Cards Activity
... climate Long-term weather conditions of a region, including temperature, air pressure, humidity, precipitation, sunshine, cloudiness, and winds, throughout the year, and averaged over several years. ...
... climate Long-term weather conditions of a region, including temperature, air pressure, humidity, precipitation, sunshine, cloudiness, and winds, throughout the year, and averaged over several years. ...
Slide 1 - CUNY.edu
... 2. Tell whether weather near the equator is generally (wet, dry) and the weather in the subtropics is generally (wet, dry) and then Explain. 3. How does air have to move to produce clouds and precipitation? Explain. 4. Fill in the data for the circled weather station and find the front on the Surfac ...
... 2. Tell whether weather near the equator is generally (wet, dry) and the weather in the subtropics is generally (wet, dry) and then Explain. 3. How does air have to move to produce clouds and precipitation? Explain. 4. Fill in the data for the circled weather station and find the front on the Surfac ...
Meteorology

Meteorology is the interdisciplinary scientific study of the atmosphere. Studies in the field stretch back millennia, though significant progress in meteorology did not occur until the 18th century. The 19th century saw modest progress in the field after observing networks formed across several countries. It wasn't until after the development of the computer in the latter half of the 20th century that significant breakthroughs in weather forecasting were achieved.Meteorological phenomena are observable weather events that illuminate, and are explained by the science of meteorology. Those events are bound by the variables of Earth's atmosphere: temperature, air pressure, water vapor, and the gradients and interactions of each variable, and how they change over time. Different spatial scales are studied to determine how systems on local, regional, and global levels impact weather and climatology.Meteorology, climatology, atmospheric physics, and atmospheric chemistry are sub-disciplines of the atmospheric sciences. Meteorology and hydrology compose the interdisciplinary field of hydrometeorology. Interactions between Earth's atmosphere and the oceans are part of coupled ocean-atmosphere studies. Meteorology has application in many diverse fields such as the military, energy production, transport, agriculture and construction.The word ""meteorology"" is from Greek μετέωρος metéōros ""lofty; high (in the sky)"" (from μετα- meta- ""above"" and ἀείρω aeiro ""I lift up"") and -λογία -logia ""-(o)logy"", i.e. ""the study of things in the air"".